Method for improving silkworm parthenogenesis early generation hatching rate
A technology of parthenogenesis and hatching rate, which is applied in the field of insect genetic breeding, can solve the problems of reducing the hatching rate of silkworm eggs, protein denaturation and inactivation, etc., and achieve the effects of increasing hatching rate, reducing negative effects, and improving breeding efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
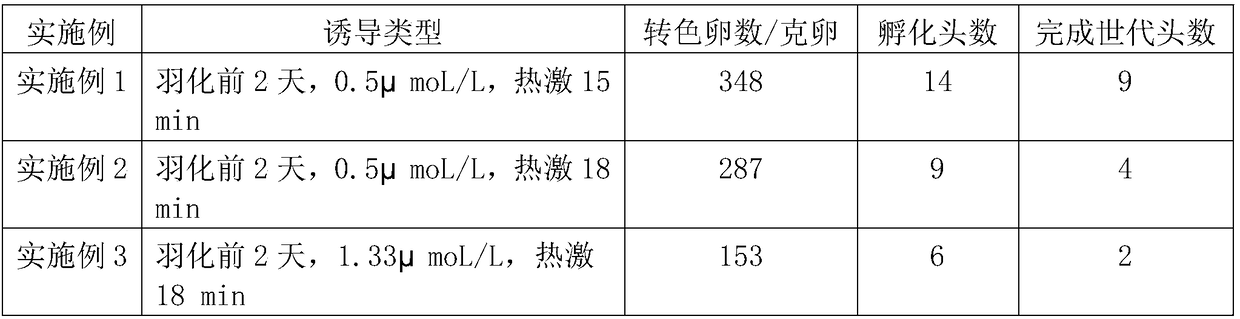
Embodiment 1
[0025] A method for improving parthenogenesis of silkworm, the method is carried out according to the following steps:
[0026] 1) Treatment of mature female pupae: After cocooning in the upper cocoons, after 10 days of routine protection, the cocoons were peeled to take pupae and identify male and female; healthy female pupae were poured into freshly prepared 0.25% bleach solution, soaked for 2 minutes, and removed from room temperature After drying, routinely protect until 1-2 days before eclosion;
[0027] 2) Inhibitor preparation and pupal injection: Dissolve the proteasome inhibitor MG132 powder in DMSO, prepare the inhibitor stock solution, and dilute it to an appropriate concentration with 1×PBS before use; inject 20 microliters per pupa into the abdomen of the female pupa , so that the final concentration of the inhibitor is 0.5-2 μmoL / L, and routinely protect to eclosion;
[0028] 3) Collection and cleaning of unfertilized eggs: pick the abdomen of virgin moths after...
Embodiment 2
[0032] In the step (1) of this example: the female pupae is routinely protected until 2 days before eclosion; in the step (2): the final concentration of the inhibitor MG132 after injection is 0.5 μmoL / L; in the step (4): heat shock induction for 18 minutes; Step process is the same as embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0034] In the step (1) of this example: the female pupae is routinely protected until 2 days before eclosion; in the step (2): the final concentration of the inhibitor MG132 after injection is 1.33 μmoL / L; in the step (4): heat shock induction for 18 minutes; Step process is the same as embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com