A method for realizing ultra-fine packaging leads based on photolithography and electroplating
An ultra-fine technology for encapsulating leads, applied in circuits, electrical components, electrical solid devices, etc., which can solve the problems of insufficient lead structure strength, complicated capillary design, limited strength of copper materials, etc., to achieve a good flattening effect and overcome structural strength. Insufficient, high coating thickness uniformity effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] This embodiment provides a method for realizing ultra-fine packaging leads based on photolithography and electroplating, which uses photolithography and electroplating instead of wire bonding to realize the connection between electrodes.
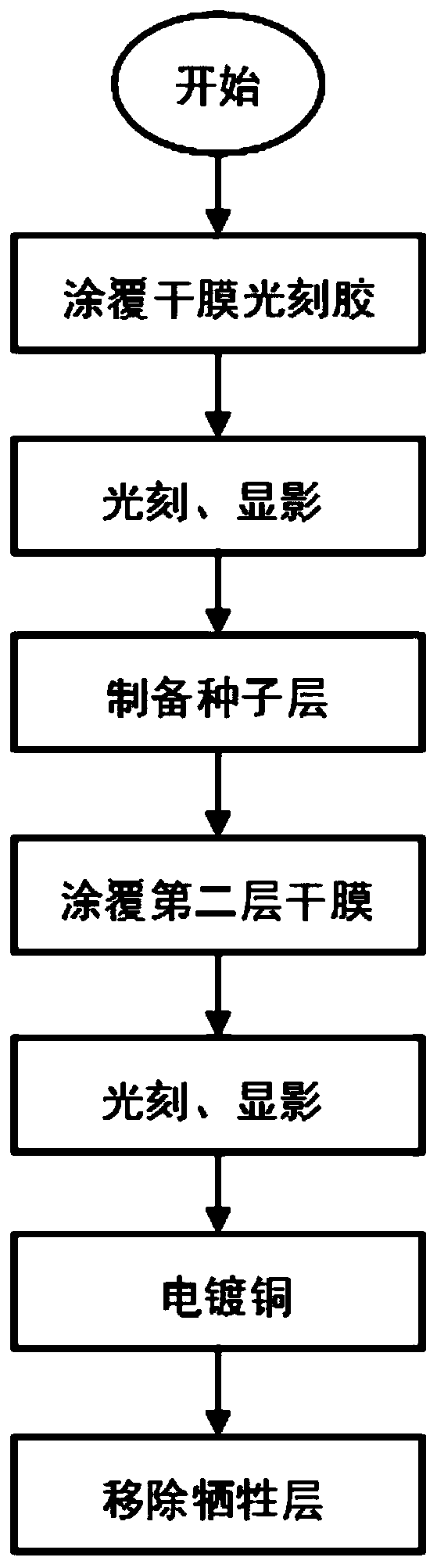
[0047] Described method specifically comprises the steps:
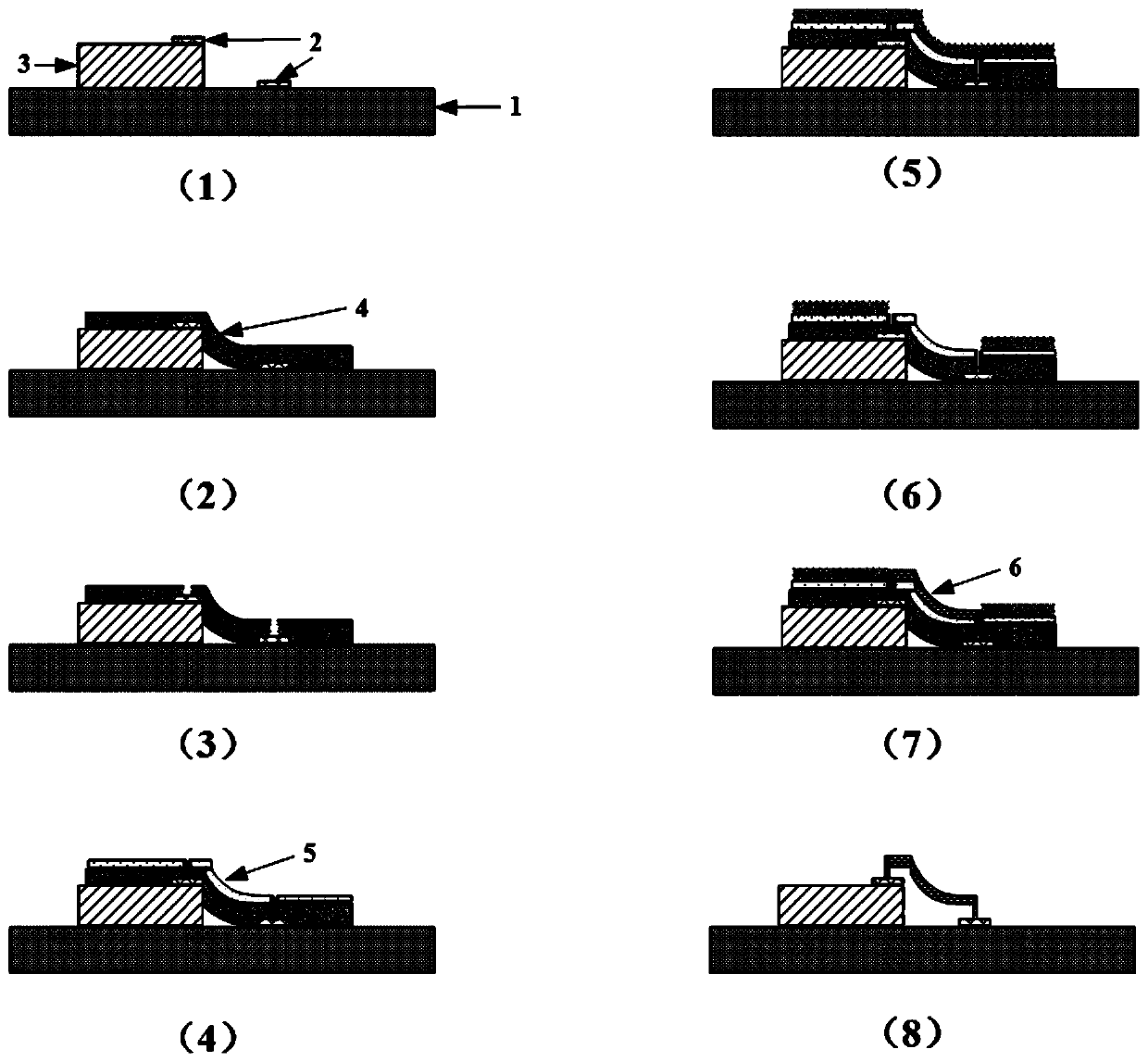
[0048] 1) Coating a layer of 20 μm thick dry film photoresist on the surface of the glass substrate fixed with a 20 μm thick chip and a metal pad;
[0049] In this step, the substrate can be made of glass, and the dry film photoresist can be coated with hot rolling technology; of course, in other embodiments, the thickness of the chip and the thickness of the dry film can be adjusted according to the actual situation.
[0050] 2) Expose and develop the substrate processed in step 1), develop a group of via holes with a size of 20 μm on the metal pads of the chip and the substrate respectively, and use the two via holes facing the chip and the substrate The holes are a group,...
Embodiment 2
[0061] This embodiment provides a method for realizing ultra-fine packaging leads based on photolithography and electroplating, which uses photolithography and electroplating instead of wire bonding to realize the connection between electrodes.
[0062] Described method specifically comprises the steps:
[0063] 1) Coating a layer of 60 μm thick dry film photoresist on the surface of the silicon wafer substrate fixed with a 100 μm thick chip and a metal pad;
[0064] In this step, the substrate can be a silicon wafer, and the dry film photoresist can be coated with a vacuum lamination technique; of course, in other embodiments, the thickness of the chip and the thickness of the dry film can be adjusted according to actual conditions.
[0065] 2) Expose and develop the substrate processed in step 1), and develop via holes with a size of 50 μm on the metal pads of the chip and the substrate respectively, taking the two via holes facing each other on the chip and the substrate as...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com