Method for rapidly passivating soil cadmium based on amino acid complexing redistribution principle
A soil and complexation technology, applied in the restoration of polluted soil, etc., can solve the problems of soil compaction and acidification, high cost of Cd-contaminated farmland soil, and achieve the effects of fast passivation, friendly environmental response, and stable response.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
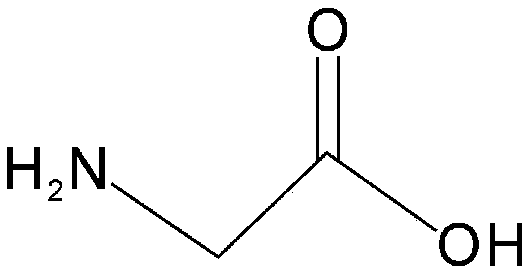
[0036] Glycine (structure such as figure 1 As shown, purchased from Aladdin Reagent Company) after being prepared as a glycine solution, it was added to the soil contaminated by Cd. See Table 1 for the physical and chemical properties of soil.
[0037] Table 1 Basic physical and chemical properties of tested soil
[0038]
[0039] To investigate the rapid (3h) addition of amino acids to inactivate Cd in typical contaminated farmland soil.
[0040] There are two treatments of CK (control) and TA (glycine), each with 12 replicates. Weigh 30 g of fresh soil for testing (the soil for testing is sampled from a cultivated layer with a thickness of 20 cm), and put it into a 100 mL polytetrafluoroethylene beaker. Match glycine concentration to 750mg N kg -1 Add the soil and adjust with deionized water to 60% of the maximum water holding capacity of the soil field; the control treatment is to add the same amount of deionized water. Placed in a 25°C constant temperature biological incubator...
Embodiment 2
[0045] This example further investigates the degree of passivation of Cd pollution in typical farmland soil by glycine addition.
[0046] Select 3 replicates of the two treatment groups of CK (control) and TA (glycine) involved in Example 1, and perform sampling at 6 and 12 hours after the start of the experiment to determine the effective state Cd content. The other operating steps are the same as in Example 1. .
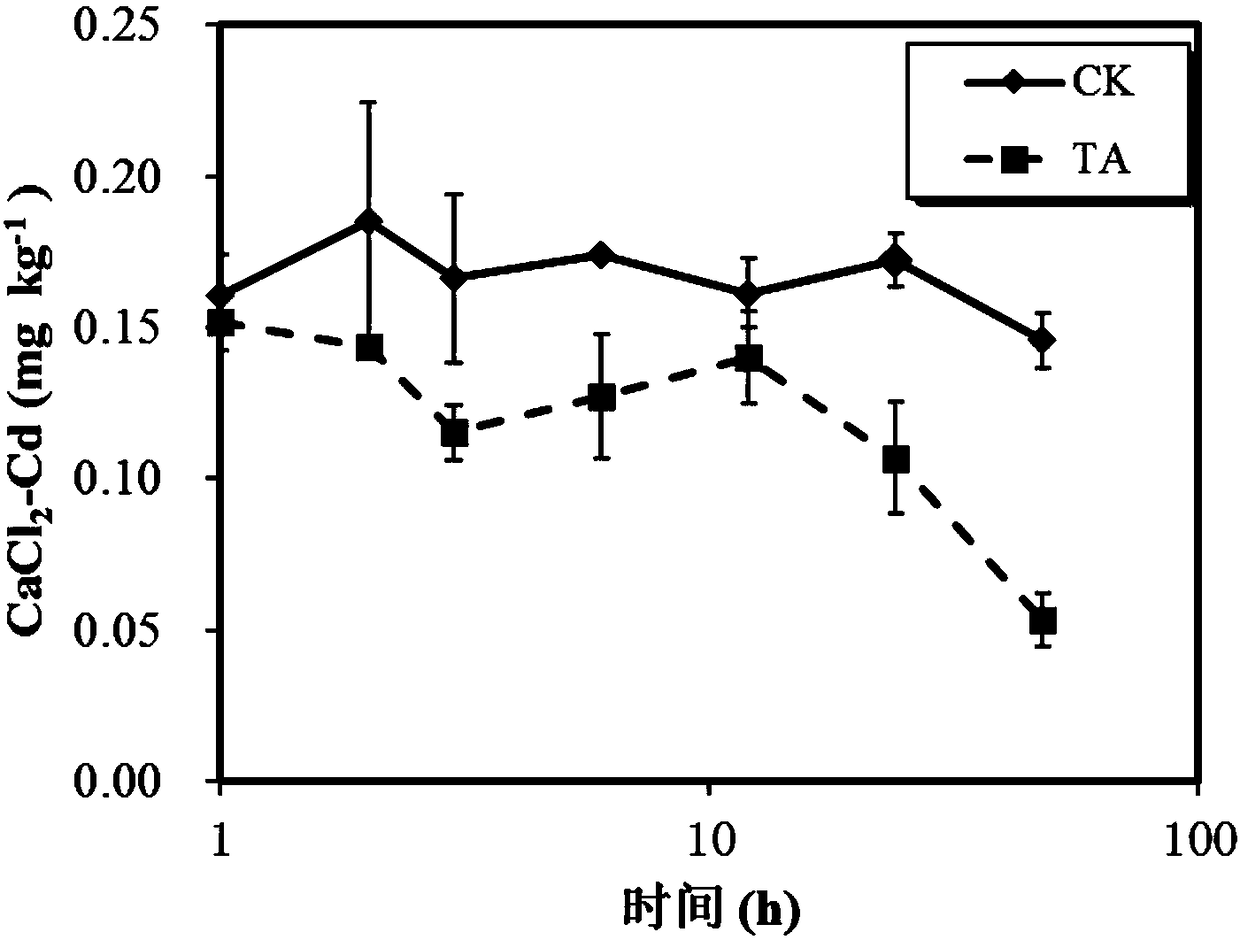
[0047] The results are shown in Table 3 and figure 2 As shown, CaCl 6 and 12 hours after adding glycine 2 -Cd decreased by 16% and 27% respectively.
[0048] Table 3 Passivation effect of glycine on contaminated soil after treatment
[0049] Time(h)
Embodiment 3
[0051] This example further investigates the degree of passivation of Cd pollution in typical farmland soil by the addition of glycine involved in Example 2.
[0052] Three replicates of the two treatment groups of CK (control) and TA (glycine) involved in Example 1 were selected, and samples were taken 24 and 48 hours after the start of the experiment to determine the effective Cd content.
[0053] The results are shown in Table 4. CaCl 24 and 48 hours after the addition of glycine 2 -Cd decreased by 30% and 65% respectively.
[0054] Table 4 Passivation effect of glycine on contaminated soil after treatment
[0055] Time(h)
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com