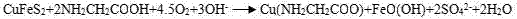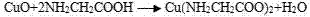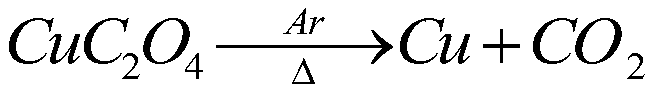Patents
Literature
67 results about "Glycine solution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
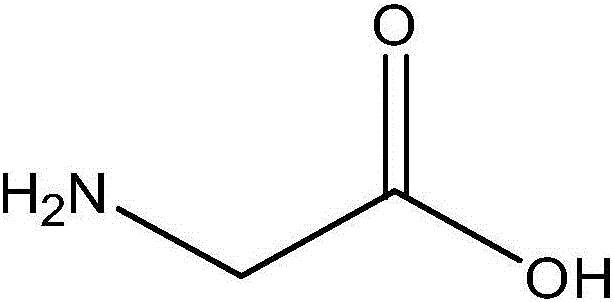
Glycine is an amino acid and a nonelectrolyte. A solution of Glycine in water is therefore nonconductive and suitable for urologic irrigation during electrosurgical procedures.
Method for using a static electric field to induce crystallization and to control crystal form
InactiveUS20050256300A1From normal temperature solutionsPeptide/protein ingredientsTesting tubesDc voltage
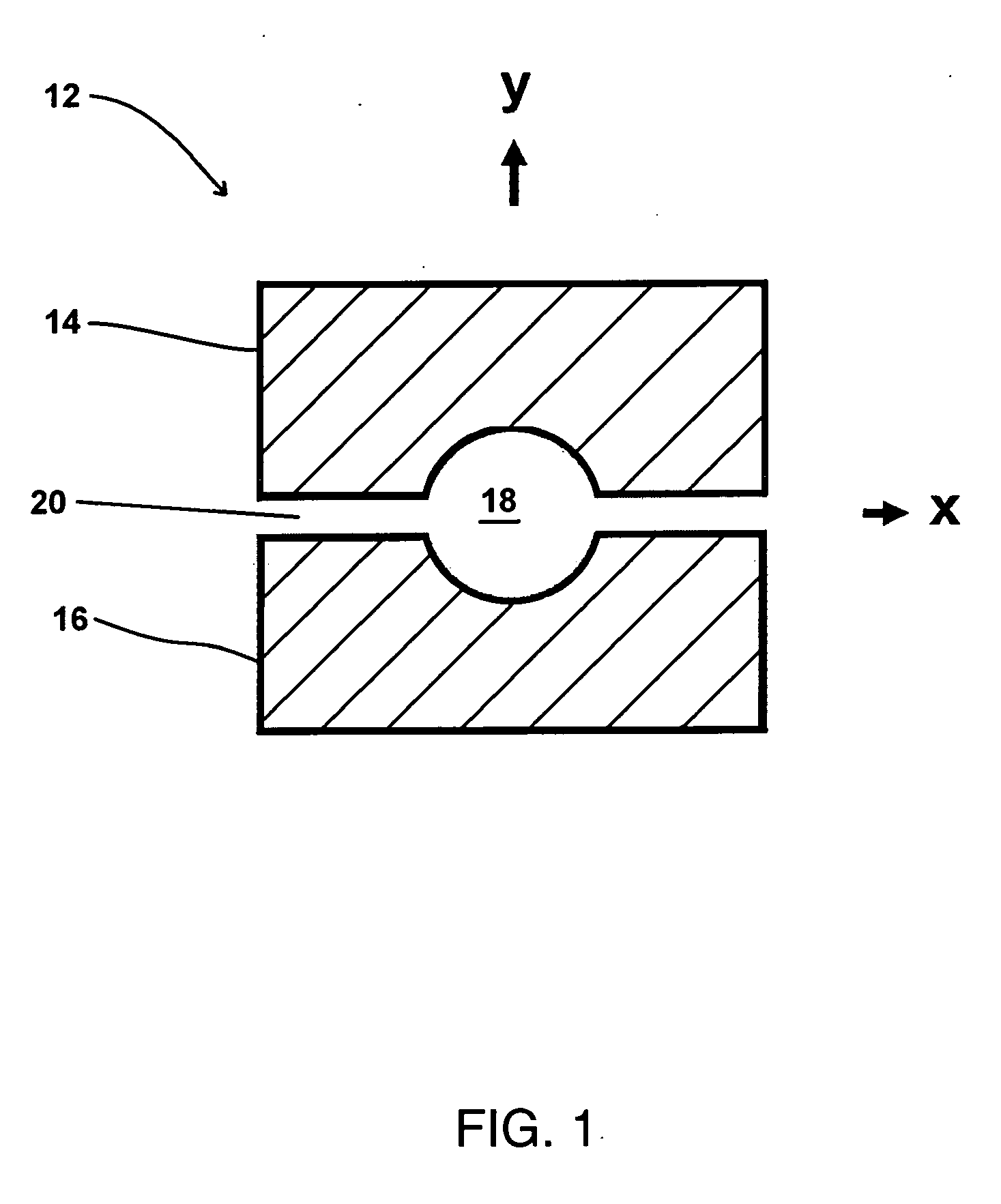
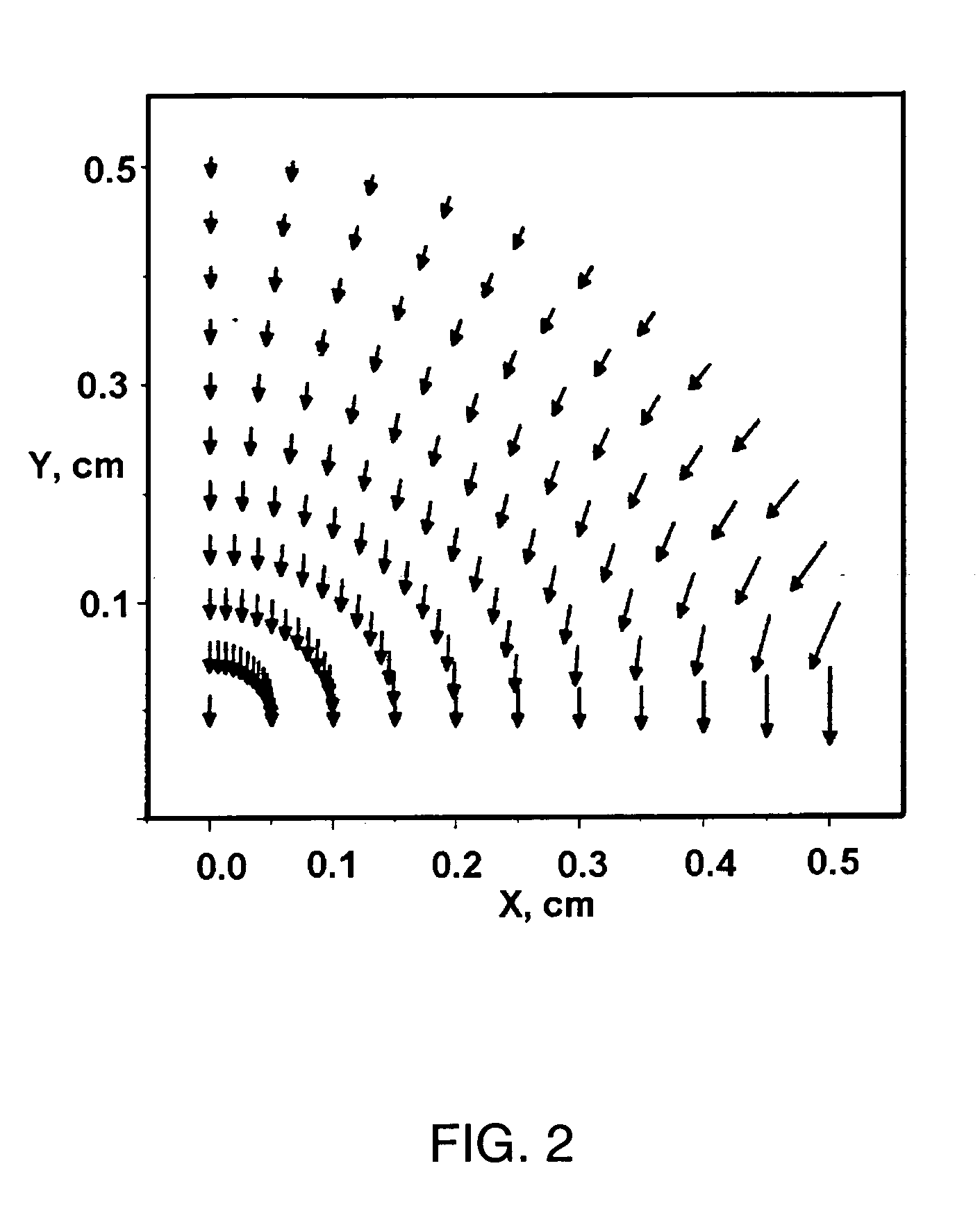
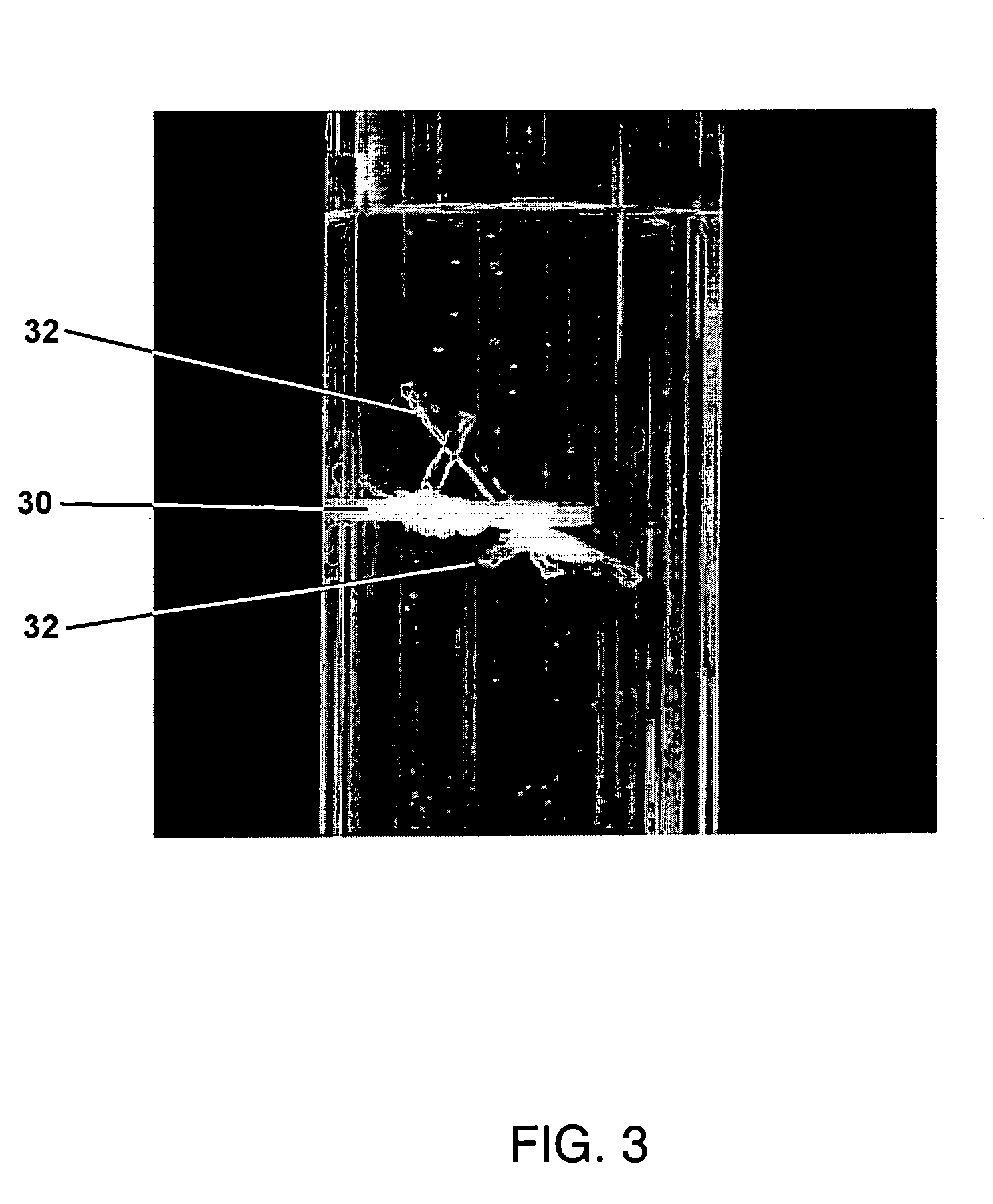
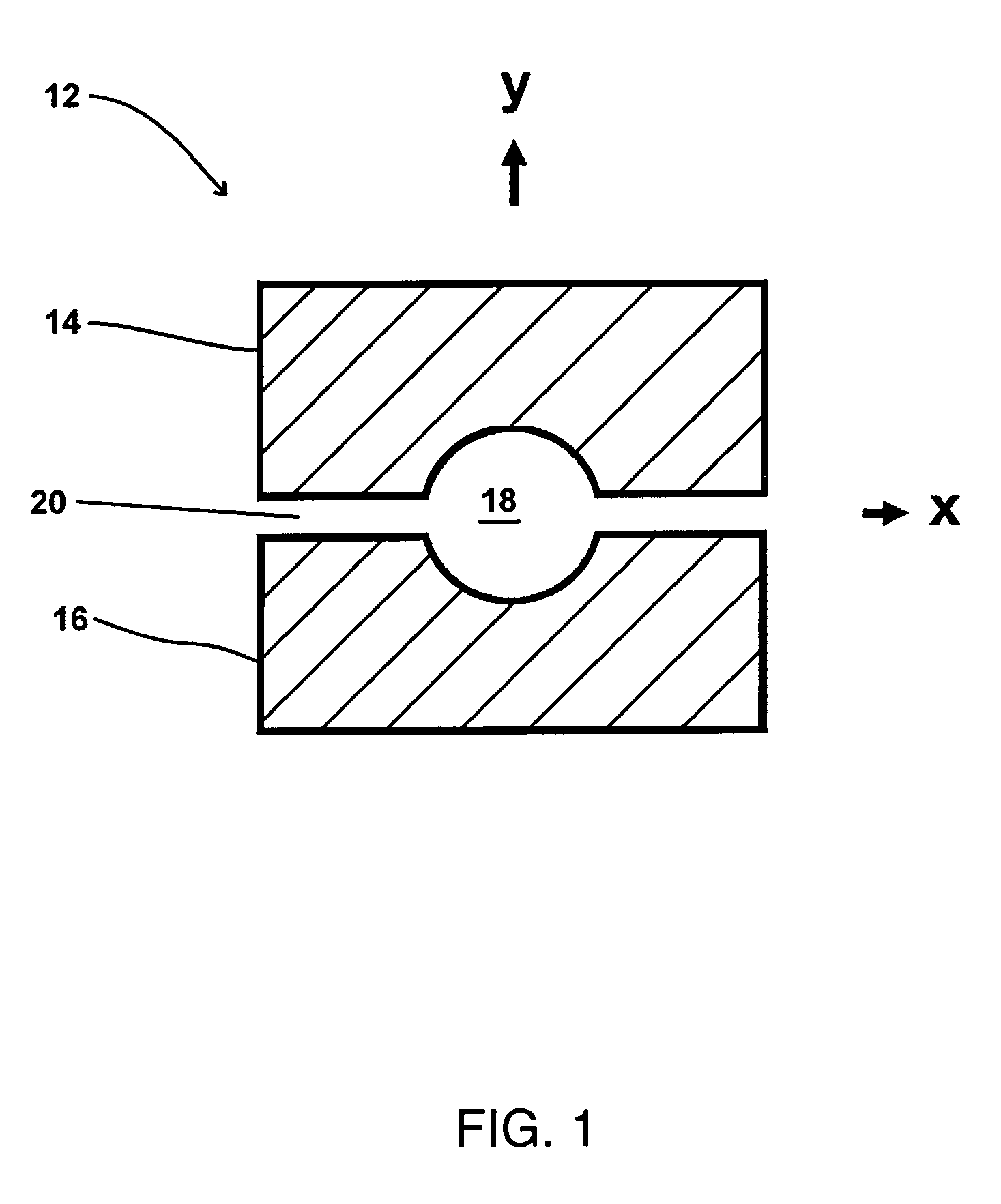
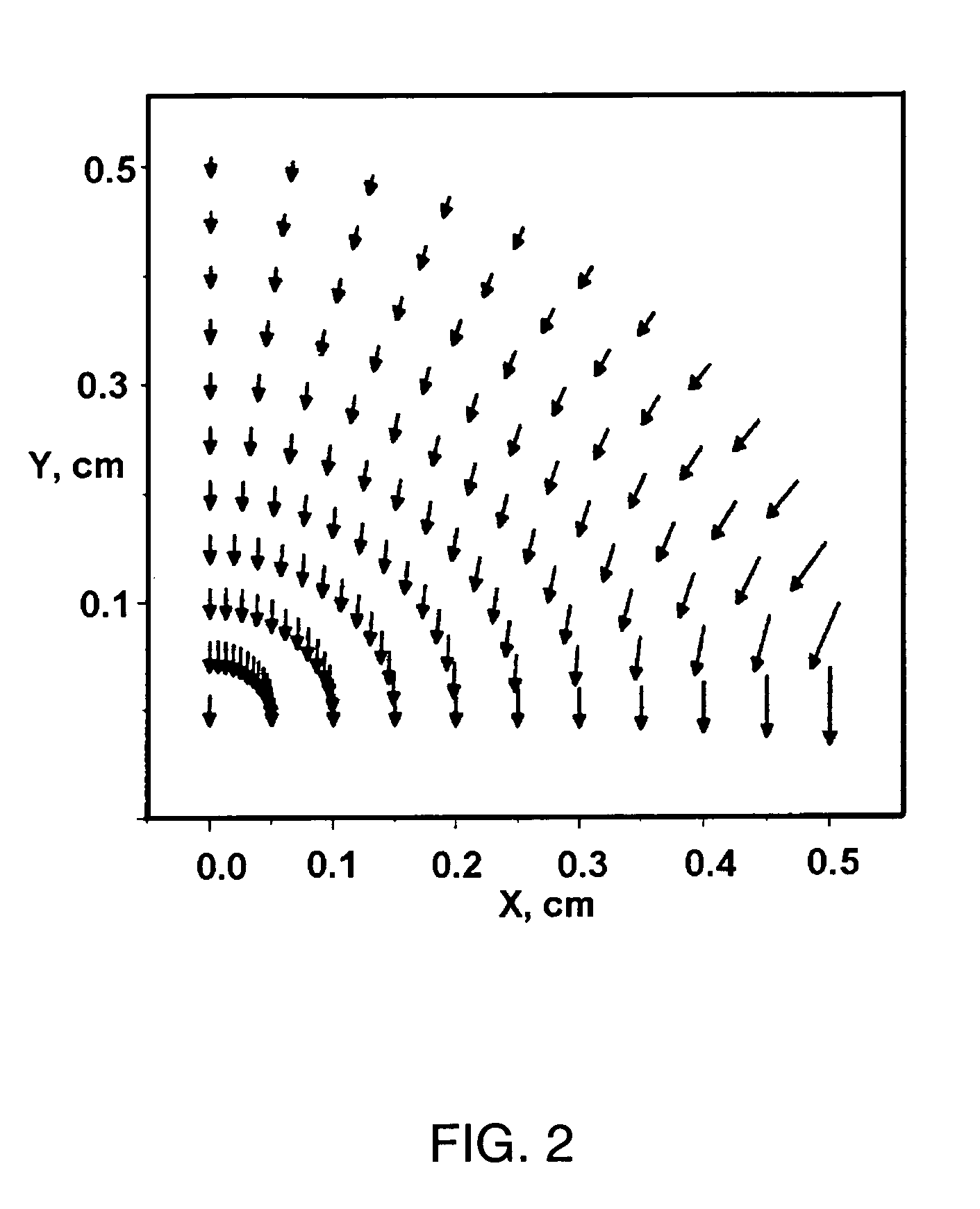
Applying a strong static DC electric field to supersaturated aqueous glycine solutions resulted in the nucleation of the γ polymorph attributed to the electric-field induced orientation of the highly polar glycine molecules in large preexisting solute clusters, helping them organize into a crystalline structure. A method to induce crystallization and to prepare polymorphs and / or morphologies of materials by using a static electric field to cause nucleation and crystal growth to occur in a supersaturated solution in such a way as to obtain a crystal structure that would not normally appear without the use of the static electric field. Aqueous glycine solutions were prepared by combining solid glycine and water. Supersaturated solutions were generated by heating the tubes to 62-64° C. and holding them at that temperature in an ultrasonicator overnight. Once the glycine was completely dissolved, the solutions were slowly cooled to room temperature. A chamber was constructed consisting of two brass electrodes separated by a 5 mm insulating gap, with a hole drilled down through the center, parallel to the gap-electrode interface, with a diameter large enough to accommodate the test tube. A DC voltage was applied across the electrodes, large enough to produce electric fields in the range of 400,000 to 800,000 V / m. Tests tubes containing the aged solutions were placed in the high-voltage chamber. Exposure of the aged solutions to fields of 600,000 V / m resulted in crystallization typically within 30-90 min. The onset of nucleation was observed visually by the formation of a needle-shaped crystallite.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HLDG 19
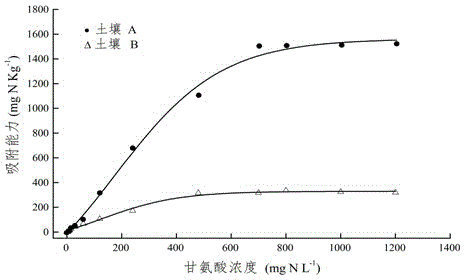
Method for measuring contribution rate of soil adsorbed amino acid to plant nitrogen nutrition
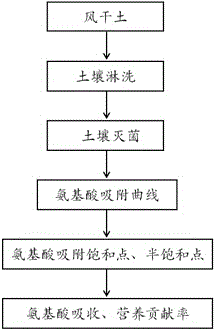
The invention provides a method for measuring a contribution rate of soil adsorbed amino acid to plant nitrogen nutrition, and belongs to the technical field of biogeochemistry. The method comprises the following steps: airing and grinding collected soil, performing sieving, and using the processed soil for later use; performing repeated leaching on soil with a strong potassium sulfate salt solution; placing leached soil in an autoclave to carry out high temperature and high pressure steam sterilization treatment; adding 15N-labeled glycine solutions with different concentrations into the soil subjected to sterilization treatment to carry out adsorption tests; performing oscillation, centrifugation and filtration, and calculating a glycine adsorption curve in the soil according to the glycine concentration difference in the solution before and after adsorption; according to the glycine adsorption curve, selecting soils at the adsorption saturation point and the adsorption half saturation point of the curve; performing cultivation tests on paddy rice seedlings in a sterile culture room, harvesting paddy rice after 21 days, and calculating the contribution rate of absorption of amino nitrogen and amino acid to paddy rice nitrogen nutrition. The method has a very important function of revealing fertility of soil organic nitrogen and nitrogen cycle of an ecological system.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
Compositions of zirconium chloride complex and its method of manufacture
InactiveUS20060222612A1Highly active andHighly effectiveCosmetic preparationsGroup 4/14 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesGlycine solutionChloride
The invention discloses a process for preparing highly active aluminum zirconium tetrochlorohydrate glycine powder by forming aluminum chloride glycine and zirconium chloride glycine solution individually, and then blending such aluminum chloride glycine and zirconium chloride glycine together to form aluminum zirconium tetrochlorohydrate glycine.
Owner:HAIMEN CITY PAYUAN CHEM
Method for measuring impurity content of faropenem polymers in faropenem sodium raw materials and preparations
ActiveCN101852782ASignificantly progressiveVolume controlOrganic chemistryComponent separationColumn temperatureImpurity
The invention particularly relates to a method for measuring the content of faropenem polymers in faropenem sodium raw materials and preparations by high-efficiency liquid chromatography, which belongs to the field of medicine analysis. The measuring method of the invention is gel chromatography. The high-efficiency liquid chromatogram is used for detection, and the chromatogram conditions are as follows: (1) the gel permeation chromatography has the exclusion molecular weight between 600 and 800 Daltons; (2) the mobile phases as two mobile phases, wherein the mobile phase A is a water phase solution with the pH value between 5.0 and 8.5 and the concentration between 0.01 and 0.2 mol / L, and the mobile phase B is water or a sodium dodecyl sulfate water solution or a glycin solution between 0.005 and 0.02 percent; (3) the column temperature is the room temperature; (4) the flowing rate is between 0.5 and 1.0 ml / min; and (5) the detection wavelength is between 210 and 300 nm. The method of the invention has the advantages of strong specificity, good repetitiveness and high automation degree, and the polymers in the faropenem sodium raw materials and the preparations can be accurately qualified.
Owner:LUNAN PHARMA GROUP CORPORATION
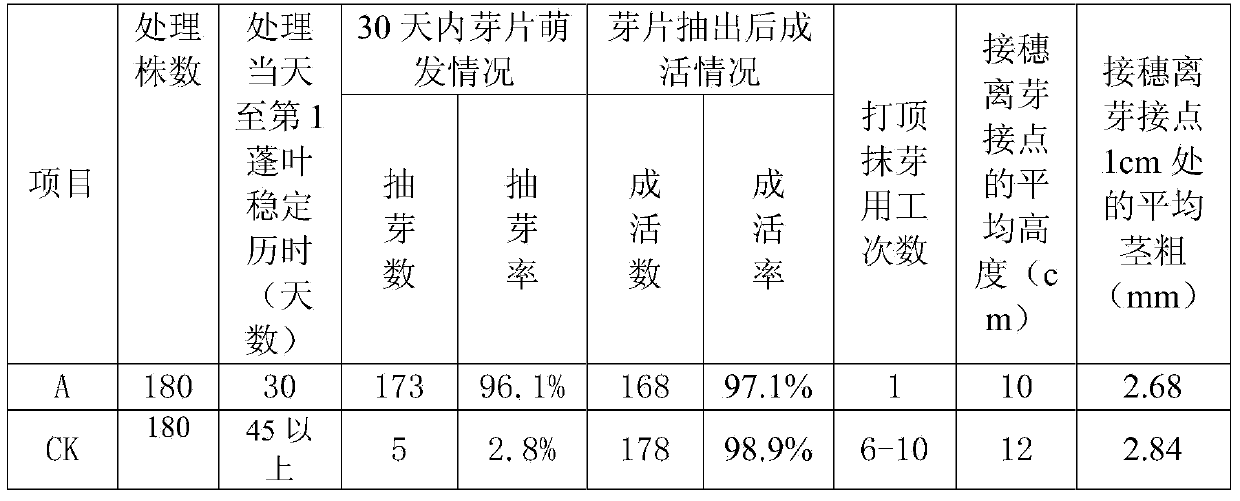
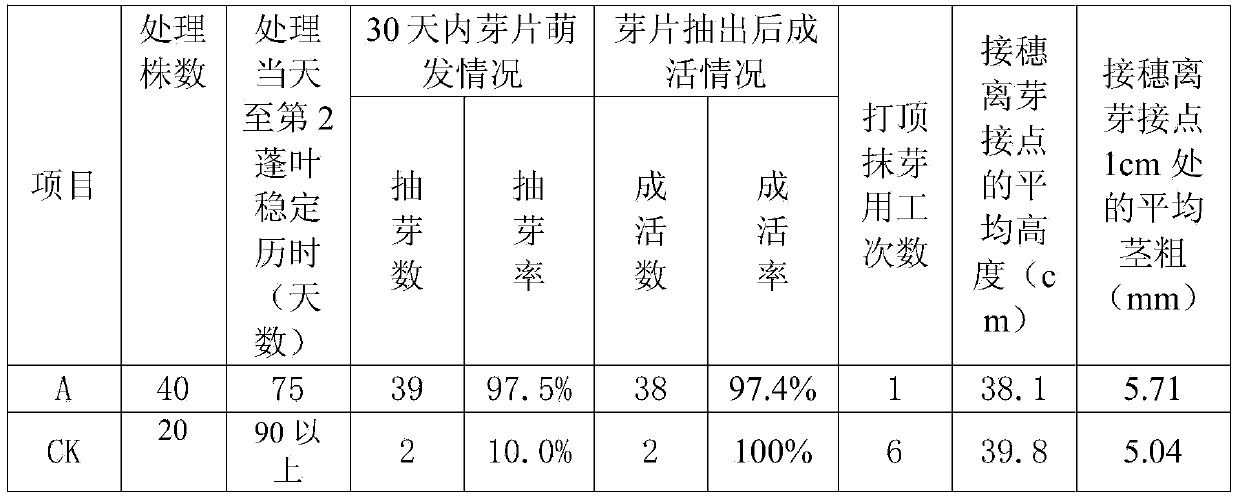
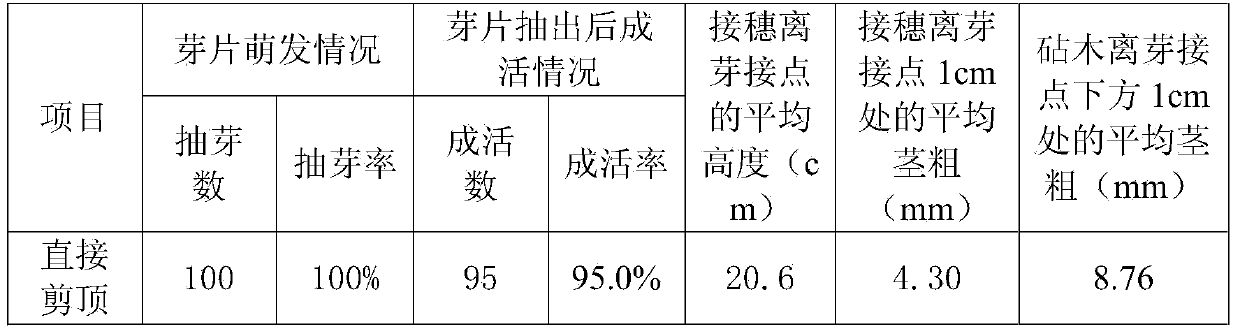
Method for increasing budding and growing consistency of bud grafting seedlings of rubber seeds
ActiveCN103947448ASolve back drySolve problems such as uneven germination and growthHorticultureBud growthGrowth management
The invention relates to a method for increasing the budding and growing consistency of bud grafting seedlings of rubber seeds. The method is characterized in that bud grafting is carried out by taking rubber seedlings which are germinated for1-2 weeks, the top parts of root stocks are cut when second cluster leaves are stable, and water and fertilizer are applied to the root parts of the root stocks before the top parts of the root stocks are cut; after the top parts of the root stocks are cut and before the bud grafting is carried out, culture substrate in a seedling culturing container is maintained to be wet, the water and the fertilizer are applied to root parts of the bud grafting seedlings until the bud grafting seedlings are budded, seedling-strengthening water and fertilizer are applied to the root parts of the bud grafting seedlings after the bud grafting seedlings are budded and leaves are unfolded, and glycine solution is sprayed and applied to the leaf surfaces; after grafted first cluster leaves are stable, and the water and the fertilizer are applied to the root parts of the root stocks until the bud grafting seedlings can be selectively taken out from a nursery after the second cluster leaves are stable; disease and insect damage prevention management is carried out during the period. According to the method for increasing the budding and growing consistency of the bud grafting seedlings of the rubber seeds, disclosed by the invention, the operation is simple and convenient, the efficiency is high, a top advantage removing measure is combined with a tube stroking measure, the problems that the bud grafting seedlings are withered and the budding growth is irregular are effectively solved, the budding and growing consistency of rubber bud grafting seedlings is promoted, convenience is provided for a follow-up growth management, the seedling culturing production cycle is shortened, the seedling culturing production efficiency is increased, and the quality of a nursery stock is increased.
Owner:RUBBER RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Preparation method for poly(ethylene glycol) modified recombinant human interleukin-2
InactiveCN103193879AGood molecular weight uniformityStrong antiviral activityDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsPolyethylene glycolP-Toluenesulfonic acid
The invention provides a preparation method for poly(ethylene glycol) modified recombinant human interleukin-2, belonging to the field of biological medicine. The method comprises the following steps: activating mPEG with an activator so as to obtain an activated mPEG molecule; and reacting the activated mPEG molecule with recombinant human interleukin-2, adding a glycine solution to terminate a reaction and separating and purifying an obtained product; wherein the activator is one selected from the group consisting of succinic anhydride and N-hydroxysuccinimide, p-toluenesulfonic acid-chlorine, N,N'-carbonyl diimidazole, N,N'-disuccinimidocarbonate, p-nitrophenyl carbonate, benzotriazole carbonate, phenylsuccinimide carbonate and N-acetoxysuccinimide. The preparation method provided by the invention is simple and convenient to operate and is easy for quality control and enlarged production.
Owner:SHENZHEN YATAIXING IND
Preparation method for novel jelly
The invention discloses a preparation method for novel jelly. The preparation method includes the following steps of 1, material taking, wherein raw materials are prepared according to a formula; 2, jelly cooking; 3, filtering, wherein cooked jelly water is directly filtered through a screen of 100 meshes to obtain a transparent clarified glycine solution, and then the transparent clarified glycine solution is pumped into a cooling pot through a pump; 4, cooling and blending; 5, filling, wherein the prepared jelly water is automatically pumped into a sealing machine material barrel from a storage pot, and cups are automatically filled with the jelly water to be full; 6, sealing, wherein the jelly cups full of the jelly water are subjected to reverse moulding and then subjected to heat sealing; 7, normal-pressure sterilization, wherein the jelly cups are sterilized in hot water at 82-85 DEG C; 8, cooling, wherein the sterilized jelly water is cooled through cold water so that the surface of jelly can be rapidly cooled to 35 DEG C or so; 9, drying; 10, product inspection; 11, packaging and encasing; 12, finished product warehousing. The prepared jelly has the advantages of being good in taste, low in calorie, healthy, harmless and the like.
Owner:FUJIAN TIAN XIAN BAO BAO FOOD
Simple preparation method of copper glycine
InactiveCN102766062AWide variety of sourcesFast chelationOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationBASIC CUPRIC CARBONATEWater baths
The invention provides a novel simpler method for synthesizing copper glycine, comprising the following steps of: 1, respectively porphyrizing equimolar CuSO4.5H2O and K2CO3, mixing and grinding; 2, rapidly pouring the above mixture into 50mL of warm water, rapidly stirring, and letting the two substances fully react; 3, filtering or precipitating to obtain basic cupric carbonate; 4, mixing the basic cupric carbonate powder and a glycine solution according to the mole ratio of 1: 4.5 in a water bath of 65-70 DEG C; and 5, stirring and chelating for about 30 minutes. The method provided by the invention requires simple steps and has high chelating rate. When the substances are added into the hot water bath, the reaction is immediately performed. It only takes 30min to chelate to the maximum value. In addition, the yield is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI QIBAO HIGH SCHOOL
Method for preparing monodispersed alpha-Fe2O3 nanoparticles
InactiveCN103332752AStrong penetrating powerGood biocompatibilityMaterial nanotechnologyFerric oxidesBiocompatibility TestingFe2o3 nanoparticles
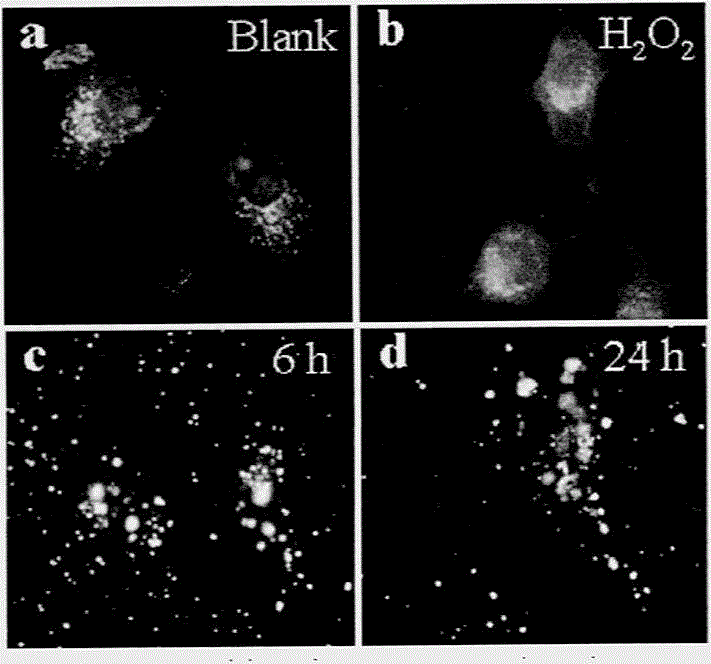
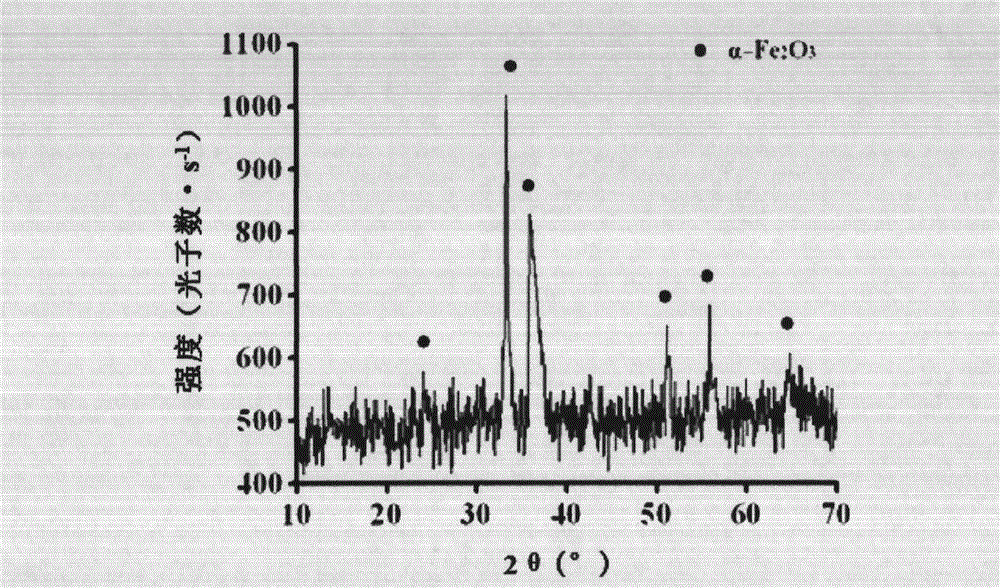
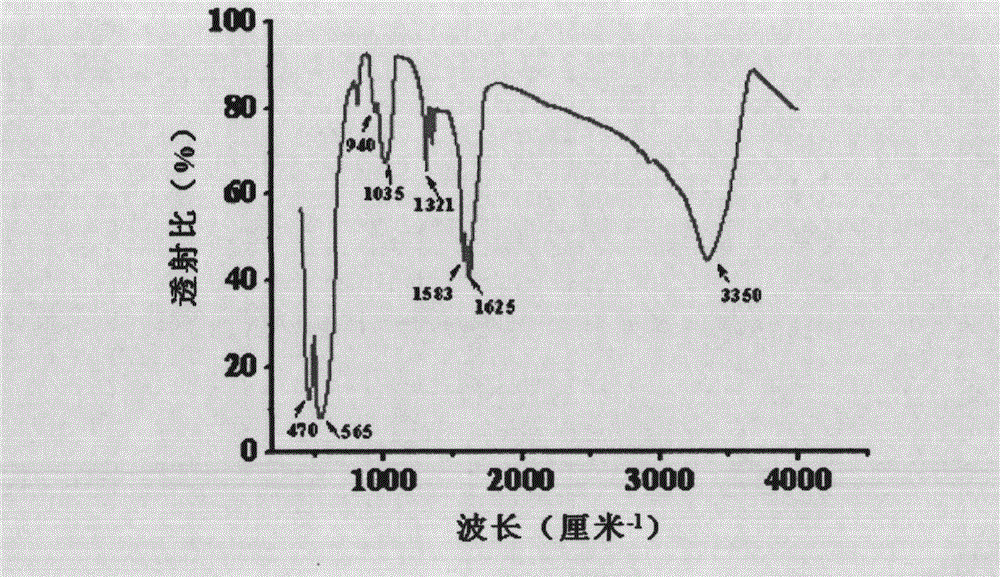
The invention discloses a method for preparing monodispersed alpha-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. The method comprises the following steps of firstly preparing a ferric nitrate solution and a glycine solution; then adding the above solutions into a hydrothermal reactor; then adding ultrapure water and absolute ethyl alcohol into the hydrothermal reactor; mixing the above materials uniformly; putting the reactor in a temperature-programmed controller; carrying out programmed temperature to make the temperature stabilized at 175-185 DEG C; reacting for 10-14 h at the temperature; cooling the reactor to a room temperature after the reaction is finished; washing the obtained reaction product with absolute ethyl alcohol and ultrapure water; and finally drying the reaction product with an oven. The method disclosed by the invention is simple and economic and has good repeatability; the prepared alpha-Fe2O3 nanoparticles have a hexagonal system structure, an average particle size of 50 nm and very large cell absorption efficiency and high biocompatibility and have particularly large application prospects in aspects such as conveying drugs or targeted therapy, etc.
Owner:HUNAN PROVINCIAL TUMOR HOSPITAL
Method for leaching Cu from alkaline glycinate solution
InactiveCN107400777AAvoid high acid consumptionAvoids copper leaching problems due to elemental sulfur passivationProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisSulfur
The invention discloses a method for leaching Cu from an alkaline glycinate solution. The method comprises steps as follows: (1) pulping Cu ore powder, adding glycine or a glycine solution prepared in advance to ore pulp, adding lye, adjusting pH of the pulp, stirring the pulp for leaching Cu, or adding glycine to a strong alkali solution to prepare an alkaline glycinate solution, adding the prepared alkaline glycinate solution to the ore pulp, adjusting pH of the pulp, and stirring the pulp to leach Cu; (2) performing solid-liquid separation on the mixed solution after leaching to obtain a Cu-containing liquid and waste residues; (3) treating the Cu-containing liquid: adding NaS or NaHS to the Cu-containing liquid to generate CuS precipitate, performing solid-liquid separation, performing a reduction reaction on the CuS-containing solid to obtain Cu, or treating the Cu-containing liquid by solvent extraction-electrodeposition to obtain Cu. The method has the beneficial effect that the problems of high acid consumption caused by leaching under the acidic condition and Cu leaching passivation by elemental S can be solved by leaching Cu in an alkaline environment.
Owner:NORTHWEST RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY INST
Method for controlling temperature of glycine cooling crystallization crystal point
InactiveCN106442607AOptimizing the crystallization processControl supersaturationInvestigating phase/state changeTemperature controlGlycine solution
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical crystallization and particularly relates to a method for controlling the temperature of a glycine cooling crystallization crystal point. The method specifically includes the steps that glycine and deionized water are added into a crystallizer according to a certain proportion, a proper additive is added after the materials are completely dissolved, after the additive is completely dissolved, temperature-controlled cooling and crystallization are conducted at a certain stirring speed and a certain cooling speed, and the temperature of the glycine crystal point is observed and recorded. The method for controlling the temperature of the glycine cooling crystallization crystal point can effectively control the supersaturation degree of a glycine solution and control the temperature of the glycine crystal point, and accordingly provides bases for optimizing the glycine crystallization technology.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Preparation method of copper glycinate
InactiveCN102643206AWide variety of sourcesFast chelationOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationWater bathsBasic copper carbonate
The invention provides a new simpler method for synthesizing copper glycinate, which comprises the following steps: stirring to chelate cupric subcarbonate powder and glycine solution in a mol ratio of 1:4.5 in a water bath at 65-70 DEG C for 30 minutes, adding ethanol, cooling to crystallize, and centrifuging to obtain the copper glycinate solid.
Owner:SHANGHAI QIBAO HIGH SCHOOL
Processing technology of dried mutton
InactiveCN108634168APlay the role of removing the smell of muttonUnique flavorFood scienceInjection volumeGlycine solution
The invention discloses a processing technology of dried mutton. The processing technology comprises the following steps: step 1, selecting of raw mutton; step 2, injecting of a deodorizing pickling solution: injecting the deodorizing pickling solution into the mutton treated in the step 1, wherein the deodorizing pickling solution contains the following components in percentage by weight: 55-65%of ginger juice, 15-21% of a glucose solution and 14-30% of a glycine solution, wherein the concentration of the ginger juice is 10-15% / L, the concentration of glucose is 2-7% / L, the concentration ofglycine is 1-3% / L, and the injection volume is 5-7ml of deodorizing pickling solution per 10g of mutton; step 3, pickling; step 4, high-pressure steam boiling; step 5, baking; and step 6, cooling andvacuum packaging: cooling diced meat subjected to baking in the step 6 to room temperature and performing vacuum packaging. The scheme can effectively improve the peculiar smell of the dried mutton.
Owner:贵州务川仡苗特色食品有限公司
Fluorescent microsphere and antibody coupling method
PendingCN111077316AImprove coupling efficiencyHigh strengthFluorescence/phosphorescenceBinding siteGlycine solution
The embodiment of the invention discloses a fluorescent microsphere and antibody coupling method. The method comprises the following steps: (a) activating fluorescent microspheres, and resuspending toobtain a microsphere suspension; (b) adding an antibody solution into the microsphere suspension for reaction, carrying out ultrasonic treatment, and continuing the reaction; (c) after the reaction is finished, adding a confining liquid into a reaction liquid for confining, centrifuging, and collecting precipitates; and (d) putting the precipitates into a glycine solution, and carrying out ultrasonic dispersion to obtain a fluorescent microsphere and antibody coupled compound. In the coupling method, the fluorescent microspheres are activated, and sufficient contact of reactants is ensured through the ultrasonic treatment so that coupling efficiency and coupling strength of the fluorescent microspheres and the antibodies can be significantly improved, microsphere surfaces and antibody protein binding sites can be fully combined, stability of the prepared compound can be effectively improved, and an agglutination phenomenon can be avoided; in addition, sensitivity of fluorescence detection can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING PEPMAGIC BIOTECH CORPORATION LTD
A kind of fermentation process of mycophenolic acid
ActiveCN109929890BPromote generationGuaranteed stabilityMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologySporeling
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial fermentation, and in particular relates to a fermentation process of mycophenolic acid. The fermentation process comprises preparing the glycerol spores by penicillium brevicompactum, then performing seed culture and fermentation culture and timely supplementing glucose and glycine in the fermentation liquid during the fermentation culture.According to the fermentation process, sunflower seed cake powder is added to a fermentation medium, which can not only reduce the dosage of an antifoaming agent, but also promote the growth of mycelium and promote the formation of metabolites. At the same time, a glycine solution can be supplemented by the program addition method in the fermentation process, so that the concentration of the glycine in the fermentation liquid can be maintained within a suitable range, the production of the metabolites can be continuously promoted, and the influence of the excessive concentration in the initial medium on the produced bacteria can be avoided. The process can effectively improve the fermentation level of the penicillium brevicompactum and increase the yield of the mycophenolic acid.
Owner:GUANGDONG BLUE TREASURE PHARMA
Industrial production and preparation process of glycine chelated manganese
ActiveCN103739509ANothing producedProcess safetyOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationGlycine solutionSulfate
The invention relates to an industrial production and preparation process of glycine chelated manganese. The industrial production and preparation process comprises the following steps: enabling manganese sulfate monohydrate and a sodium hydroxide solution to generate a manganese hydroxide white solid under certain conditions, filtering, drying, then adding sulfuric acid, dropping a glycine solution for reaction, concentrating for 2-4h when the vacuum degree of filtrate is above 0.07MPa after the end of reaction, adding 60-70 parts by weight of acetone into the solution and precipitating the solid; and performing centrifugal filtration, using a double-cone vacuum drying machine, and drying at the temperature of 80 DEG C for 2h-3h when the vacuum degree is above 0.06MPa to obtain a glycine chelated manganese product. The industrial production and preparation process provided by the invention has the advantages of simple synthesis route, safety and reliability of the process, short reaction period, high yield, good product quality and no production of pollutants.
Owner:山东祥维斯生物科技股份有限公司
Method and device for preparing strontium carbonate crystals through self-diffusion at room temperature
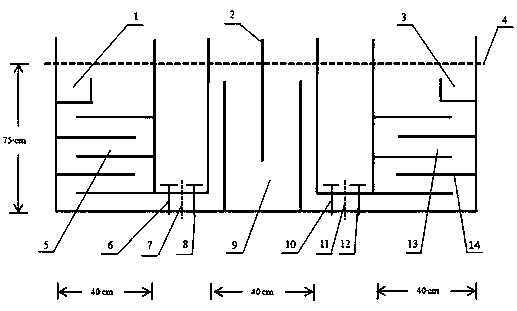
InactiveCN109133136AReduce consumptionImprove production efficiencyStrontium carbonatesStrontium carbonateSelf-diffusion
The invention relates to a method and a device for preparing strontium carbonate crystals through self-diffusion at room temperature. According to the method, with strontium dichloride hexahydrate andammonium hydrogen carbonate as reactants and glycine as a biomimetic control agent, granular strontium carbonate crystals are prepared; the method comprises the following specific steps: in a reaction device, adding a first batch of the strontium dichloride hexahydrate and the ammonium hydrogen carbonate, then adding 0.020% of a glycine solution, reacting for 24h by standing at room temperature,supplementing a second batch of the reactants and a third batch of the reactants, respectively continuing reacting for 24h by standing, filtering a reaction product, washing for three times by using distilled water, and drying for 1h at 105 DEG C to obtain the granular strontium carbonate crystals with the grain diameter of 110-440nm, wherein the product purity is higher than or equal to 99% and the yield is 96-98%. The reaction device consists of a reactor 1 (5), a reactor 2 (9) and a reactor 3 (13). The method and the device have the advantages of high preparation efficiency, simple and convenient operation, high technological stability, low energy consumption, low production cost and the like.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
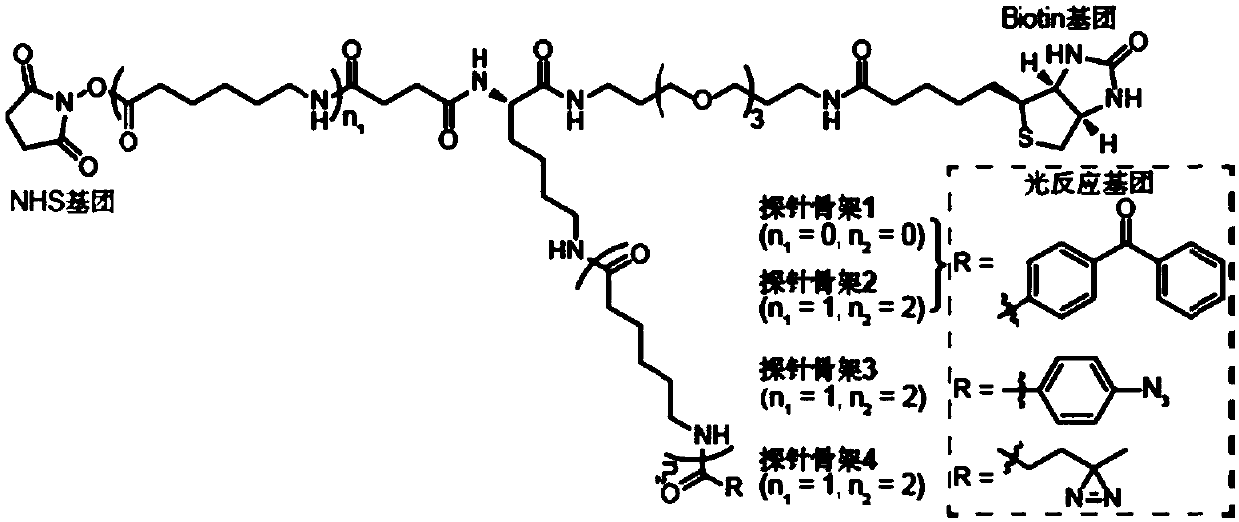
Probe as well as synthesis method and application thereof
ActiveCN110873772AAchieve enrichmentAchieve identificationComponent separationPeptidesProtein targetCell membrane
The invention provides a probe as well as a synthesis method and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) removing Boc from a compound A, and reacting with a compound B to obtain a compound C; (2) condensing the compound C obtained in the step (1) with N-hydroxysuccinimide to obtain a probe skeleton; and (3) mixing bait protein with the obtained probe skeleton, connecting, adding a glycine solution to terminate the reaction, and filtering to obtain the probe. The synthesis method disclosed by the invention is simple and convenient to operate, low in cost and environment-friendly; according to the prepared probe, an SH2 structural domain is used as bait protein; analysis of weak interaction and instantaneous interaction between proteins is facilitated; especially,enrichment and identification of the SH2 structural domain and tyrosine phosphorylated protein are facilitated, the enrichment and identification capacity of target proteins and compounds thereof nearhuman or animal tissue samples and cell membranes is remarkably improved, and background interference of other non-specific adsorption proteins is reduced.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA
Fermented soybean meal feed for penaeus vannamei
InactiveCN107223809AComprehensive and balanced nutritionIncrease profitClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffDiseaseFermentation
The invention discloses a fermented soybean meal feed for penaeus vannamei. The fermented soybean meal feed consists of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 60-70 parts of fermented soybean meal, 5-10 parts of fish meal, 10-15 parts of cuttlefish paste, 4-8 parts of mussel powder, 2-5 parts of egg powder, 2-5 parts of yeast powder, 2-5 parts of shrimp shell powder, 3-5 parts of pumpkin powder, 2-3 parts of honey dry powder, 0.5-1 part of calcium peroxide, 0.005-0.008 part of vitamins, 1-2 parts of magnetite powder, 1-1.5 parts of mineral substances and 1-3 parts of an additive. A preparation method of the fermented soybean meal comprises the following steps of inoculating soybean meal with bacillus subtilis, performing aerobic fermentation for 8-10 hours, then performing inoculating with lactobacilli, performing anaerobic fermentation for 2-3 days, soaking fermented products with a glycine solution for 2-3 days, and performing drying so as to obtain the fermented soybean meal. Through the adoption of the fermented soybean meal feed disclosed by the invention, the growth speed and the disease resistance of the penaeus vannamei can be obviously increased.
Owner:周海峰
Jelly with blood lipid reduction effect and preparation method of jelly
InactiveCN107319447AGood blood fat-lowering effectEasy to acceptFood ingredient functionsBlack teaLiquid surfaces
The invention relates to a preparation method of jelly with a blood lipid reduction effect. The preparation method comprises steps as follows: a tea and sugar water solution and black tea fungus mycoderm are poured into a sterilized container and left to stand for fermentation, when a film on a liquid surface reaches 0.5 cm thick or thicker, the black tea fungus mycoderm is cut, jelly powder, proteoglycan and white granulated sugar are mixed, the mixed mixture is spread into a monascus vinegar powder solution and heated until the mixture is completely dissolved in the monascus vinegar powder solution, and a glycine solution is obtained; the glucine solution and mycoderm units of black tea fungi are mixed, bottling, sealing and cooling are performed sequentially after mixing, and the jelly with the blood lipid reduction effect is obtained. The invention further relates to the jelly with the blood lipid reduction effect. The jelly with the blood lipid reduction effect contains various vitamins, amino acid and minerals and has a unique flavor and a good healthcare effect.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Method for using a static electric field to induce crystallization and to control crystal form
InactiveUS7879115B2Polycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsTesting tubesDc voltage
Applying a strong static DC electric field to supersaturated aqueous glycine solutions resulted in the nucleation of the γ polymorph attributed to the electric-field induced orientation of the highly polar glycine molecules in large preexisting solute clusters, helping them organize into a crystalline structure. A method to induce crystallization and to prepare polymorphs and / or morphologies of materials by using a static electric field to cause nucleation and crystal growth to occur in a supersaturated solution in such a way as to obtain a crystal structure that would not normally appear without the use of the static electric field. Aqueous glycine solutions were prepared by combining solid glycine and water. Supersaturated solutions were generated by heating the tubes to 62-64° C. and holding them at that temperature in an ultrasonicator overnight. Once the glycine was completely dissolved, the solutions were slowly cooled to room temperature. A chamber was constructed consisting of two brass electrodes separated by a 5 mm insulating gap, with a hole drilled down through the center, parallel to the gap-electrode interface, with a diameter large enough to accommodate the test tube. A DC voltage was applied across the electrodes, large enough to produce electric fields in the range of 400,000 to 800,000 V / m. Tests tubes containing the aged solutions were placed in the high-voltage chamber. Exposure of the aged solutions to fields of 600,000 V / m resulted in crystallization typically within 30-90 min. The onset of nucleation was observed visually by the formation of a needle-shaped crystallite.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES HLDG 19
A kind of industrialized production preparation process of glycine chelated manganese
ActiveCN103739509BProcess safetyShort reaction cycleOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationGlycine solutionSulfate
A kind of industrial production preparation process of glycine chelated manganese, the steps are as follows: Manganese sulfate monohydrate is mixed with sodium hydroxide solution under certain conditions to form manganese hydroxide white solid, filtered and dried, then sulfuric acid is added, and glycine solution is added dropwise to react After the reaction is completed, the filtrate is concentrated for 2-4 hours at a vacuum degree of 0.07 MPa or more, and 60-70 parts by weight of acetone is added to the solution to precipitate a solid; centrifugal filtration, using a double-cone vacuum dryer, and drying at a vacuum degree of 0.06 MPa or more at 80°C for 2 hours to 3 hours , to obtain glycine chelated manganese products. The invention has the advantages of simple synthesis route, safe and reliable process, short reaction cycle, high yield, good product quality and no pollutant generation.
Owner:山东祥维斯生物科技股份有限公司
Coupling method of fluorescent latex microspheres and protein
PendingCN111077314AImprove the activation effectImprove coupling efficiencyFluorescence/phosphorescenceBinding siteGlycine solution
The embodiment of the invention discloses a coupling method of fluorescent latex microspheres and protein. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out activation treatment and resuspensionon the fluorescent latex microspheres to obtain a fluorescent latex microsphere solution; diluting the protein by adopting a glycine solution, then adding the diluted protein into the fluorescent latex microsphere solution, carrying out ultrasonic reaction, then carrying out rotary uniform mixing reaction, and carrying out co-labeling on glycine and the protein; after the reaction is finished, adding confining liquid into the reaction liquid for confining, centrifuging, and collecting precipitates; and putting the precipitates into a glycine solution, and carrying out ultrasonic dispersion toobtain a fluorescent latex microsphere and protein coupled compound. According to the coupling method, coupling efficiency and coupling strength of the fluorescent latex microspheres and the protein can be improved so that surfaces of the microspheres are fully combined with binding sites of proteins, stability of the prepared compound can be effectively improved, and an agglutination phenomenon is avoided; in addition, sensitivity of fluorescence detection can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING PEPMAGIC BIOTECH CORPORATION LTD
Process method for recovering copper from low-grade copper oxide ore
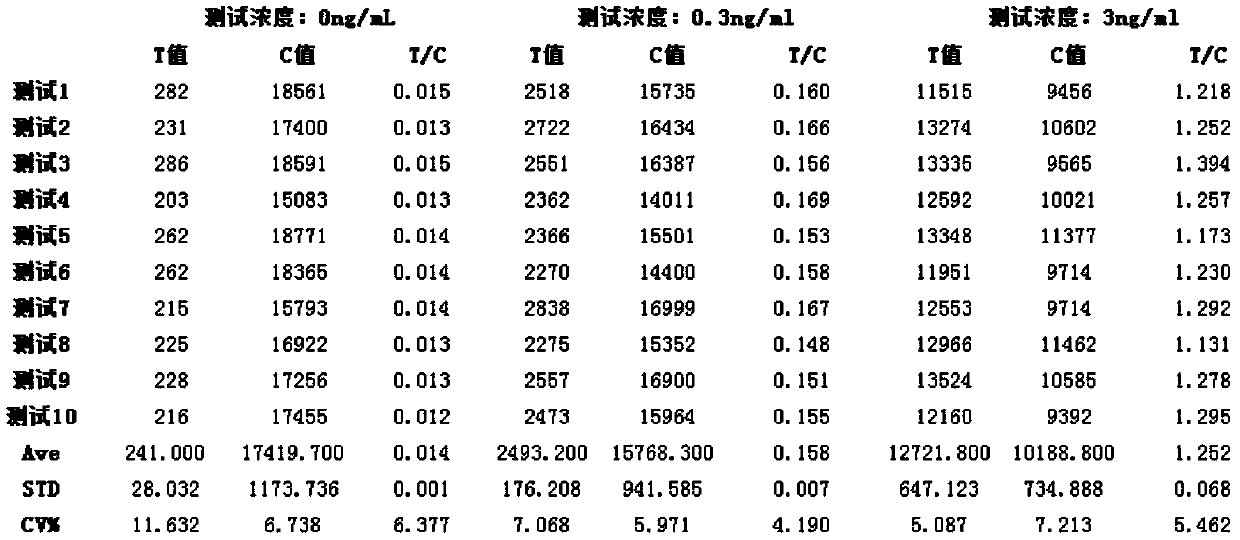
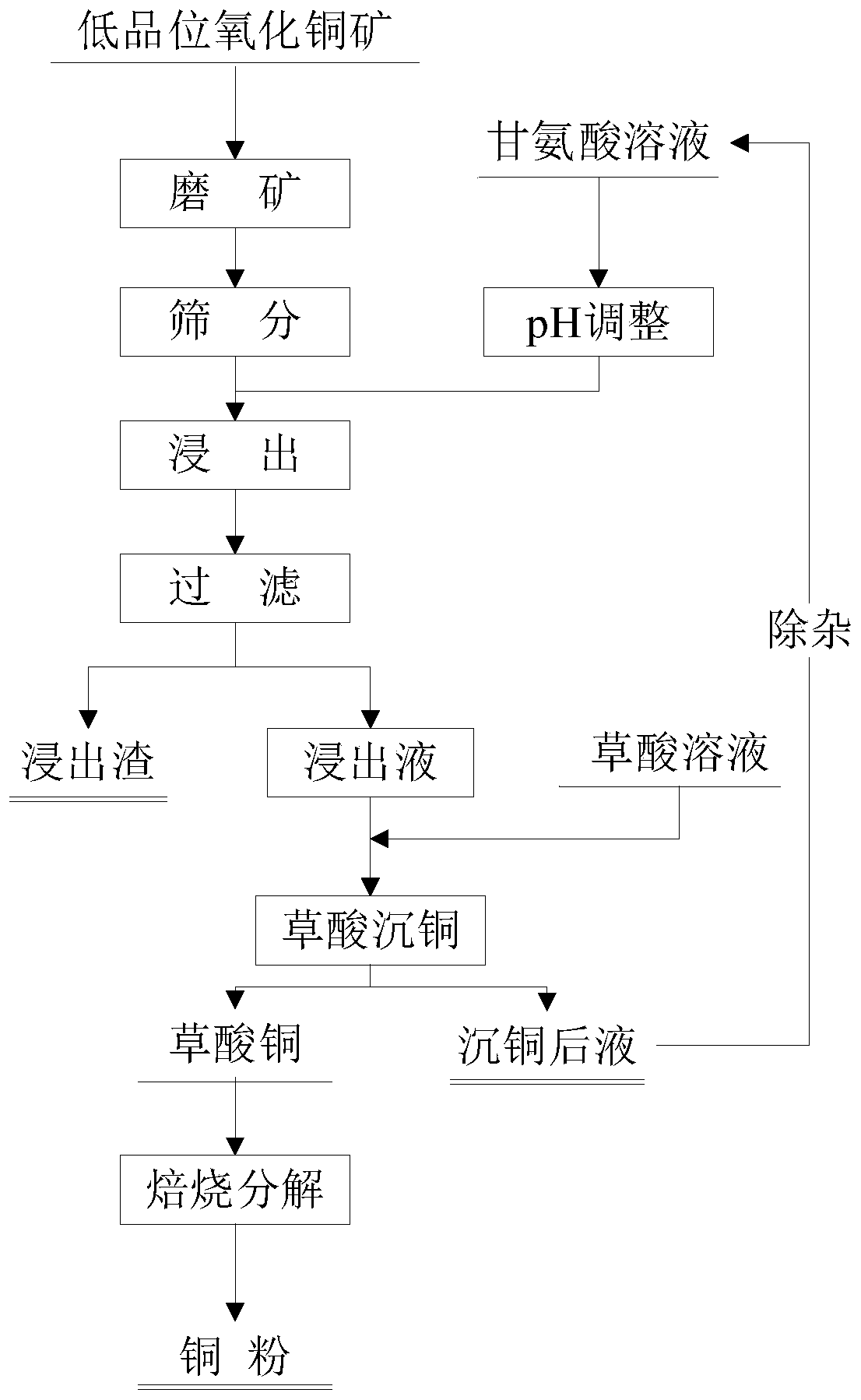
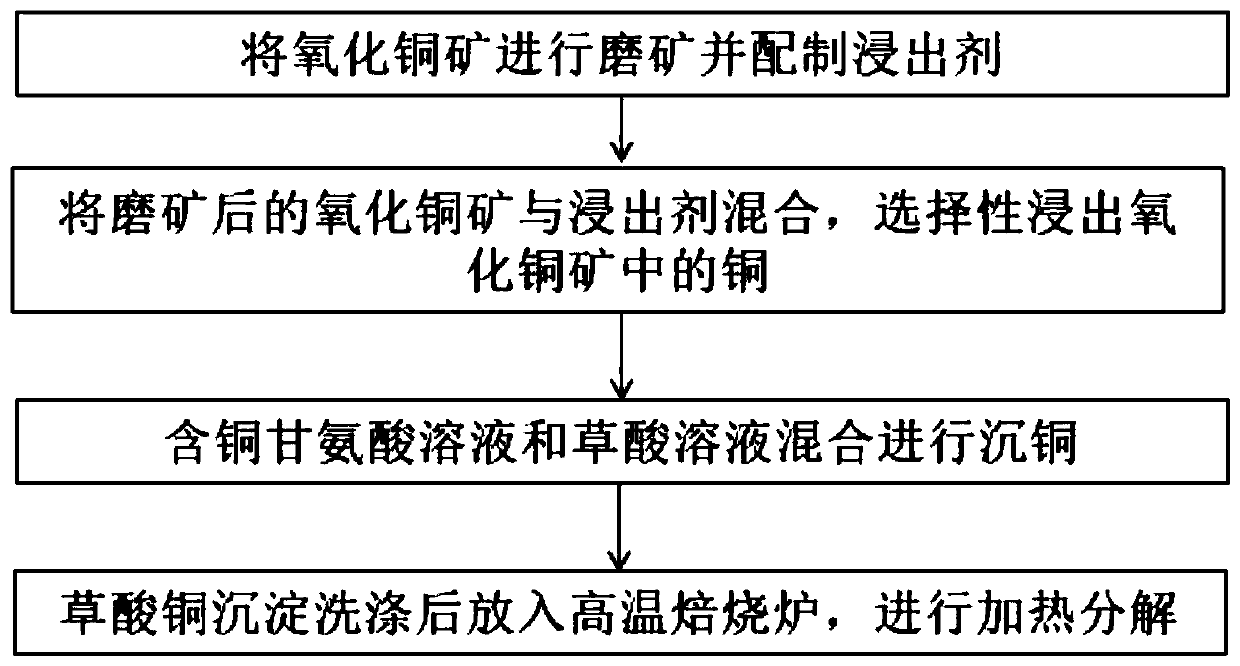
ActiveCN111500860AAvoid leachingImprove separation efficiencyProcess efficiency improvementOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATECalcite
The invention relates to a process method for recovering copper from low-grade copper oxide ore, belongs to the technical field of copper recovery, and solves the problems of difficulty in beneficiation and enrichment, high cost and the like of the low-grade copper oxide ore. In the process method for recovering copper, the copper grade in the low-grade copper oxide ore is 0.4-2.0 %, and the low-grade copper oxide ore contains at least one alkaline gangue mineral of quartz, dolomite, gibbsite, calcite and mica. The process method for recovering copper comprises the following steps: S1, grinding the copper oxide ore and preparing a leaching agent, wherein the leaching agent is a glycine leaching agent; S2, mixing the copper oxide ore subjected to grinding with the leaching agent, selectively leaching copper in the copper oxide ore, and carrying out filtering to obtain a copper-containing glycine solution; S3, mixing the copper-containing glycine solution and oxalic acid solution for copper deposition; and 4, washing the copper oxalate precipitate, putting the washed copper oxalate precipitate into a high-temperature roasting furnace, and carrying out heating decomposition to obtaincopper powder. The efficient selective leaching and recovering of copper in the low-grade copper oxide ore can be realized.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Making method of dried bracken
InactiveCN106259858AComprehensive nutritional protectionStay greenFruit and vegetables preservationFlavorVitamin C
The invention discloses a making method of dried bracken. The making method comprises the following steps: harvesting bracken at first; after cleaning, soaking in a sodium carbonate and ethanol solution; rinsing in a boiling solution prepared from white vinegar, rice wine, pectin, sodium chloride and water; drying the bracken by combining vacuum drying and microwave drying; and spraying a glycine with certain concentration in an assisted manner. Compared with the prior art, the making method can protect nutrition of the bracken, reconstitution properties of the dried bracken are quite good, after the dried bracken is reconstituted, the original shape and emerald green color of the bracken can be recovered rapidly, and the reconstituted bracken is nearly the same as fresh bracken harvested from the forest, but is better in flavor. Loss of vitamin C of the dried bracken prepared by the preparation method is 28.7-29.5% of the original content, and loss of iron element is 1.48-1.65% of the original content.
Owner:HEFEI YUANZHENG AFE SCI TECH
Electroporation method for streptococcus mutans
InactiveCN101205546AImprove efficiencyGood repeatabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCompetent cellGlycine solution
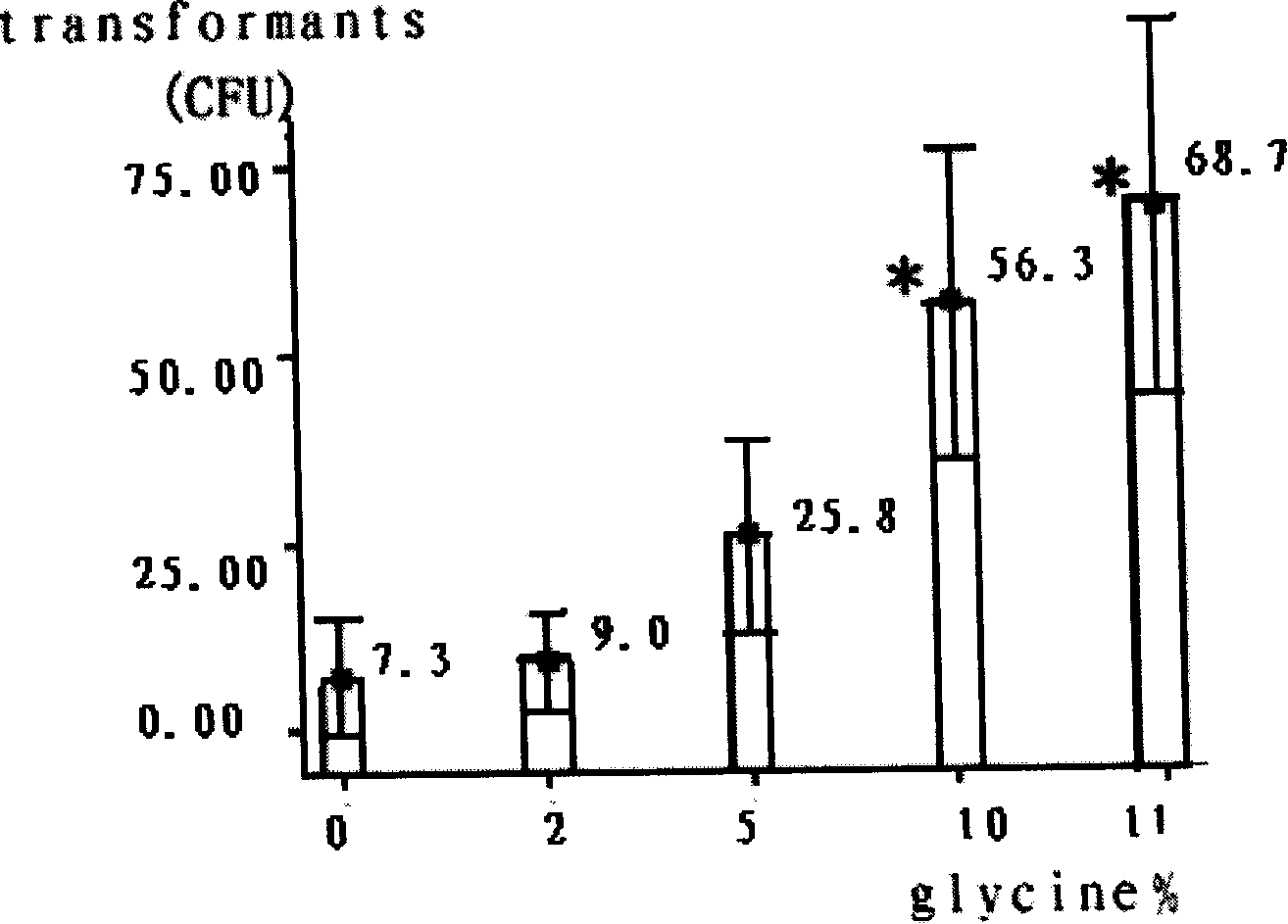
The invention relates to an electroporation transformation method, in particular to an electroporation transformation method to streptococcus mutans. The electroporation transformation method of the invention comprises the following steps: firstly, a streptococcus mutans UA159 strain, exogenous DNAs and electroporation transformation buffers are provided; secondly, competent cells of streptococcus mutans are prepared; thirdly, the competent cells are transformed by electroporation, wherein, the streptococcus mutans in the second step is inoculated into a BHI culture medium and incubated in a shaking table under the condition of 37 DEG C to absorbance OD660nm is equal to 0.5, and then 10 percent glycine solution is added. The electroporation transformation method to the treptococcus mutans disclosed by the invention has the advantages of obvious reinforcement of electroporation transformation efficiency and repeatability of the streptococcus mutans. Moreover, the invention is an effective means for gene transformation research of the streptococcus mutans and can be used for researching a cariogenic mechanism of the streptococcus mutans.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Fermentation process of mycophenolic acid
ActiveCN109929890APromote generationGuaranteed stabilityMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyMetabolite
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial fermentation, and in particular relates to a fermentation process of mycophenolic acid. The fermentation process comprises preparing the glycerol spores by penicillium brevicompactum, then performing seed culture and fermentation culture and timely supplementing glucose and glycine in the fermentation liquid during the fermentation culture.According to the fermentation process, sunflower seed cake powder is added to a fermentation medium, which can not only reduce the dosage of an antifoaming agent, but also promote the growth of mycelium and promote the formation of metabolites. At the same time, a glycine solution can be supplemented by the program addition method in the fermentation process, so that the concentration of the glycine in the fermentation liquid can be maintained within a suitable range, the production of the metabolites can be continuously promoted, and the influence of the excessive concentration in the initial medium on the produced bacteria can be avoided. The process can effectively improve the fermentation level of the penicillium brevicompactum and increase the yield of the mycophenolic acid.
Owner:GUANGDONG BLUE TREASURE PHARMA
Production technology of sour-and-hot taste seafood sauce
The invention discloses a production technology of a sour-and-hot taste seafood sauce. The sour-and-hot taste seafood sauce comprises the following raw materials in compounding ratio: performing immersing with a 0.3% glycine solution on oyster meat for 25-35min, wherein the ratio of the solution to the oyster meat is 1 to 1, fishing out the immersed oyster meat, performing draining, performing immersing with 4-6% salt water for 25-35min, grinding the immersed oyster meat to paste, adding water which is 1.8-2.2 times of the paste, regulating the pH value with a 9-11% NaOH solution to 7.0-7.5, adding bacillus subtilis neutral protease which is 0.1% of the meat, performing warming to 50-55 DEG C, performing hydrolyzing for 1.0-1.7h, regulating the pH value with acetic acid to 5-6, performingheating and boiling over for 8-12h, filtering hydrolysate with a 120-mesh screen mesh, transferring the filtered hydrolysate to a vacuum evaporator, and performing concentration to 0.8-1.2g / 100ml amino nitrogen. The made sour-and-hot taste seafood sauce is composite in taste, and high in nutrient value, the fishy smell is reduced, and the sour-and-hot taste seafood sauce is fresh and delicious inflavor.
Owner:安徽王仁和米线食品有限公司
Coproduction method and coproduction system of glycine and iminodiacetic acid
InactiveCN104817466BTake advantage ofIncrease productivityOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationChromatographic separationIminodiacetic acid
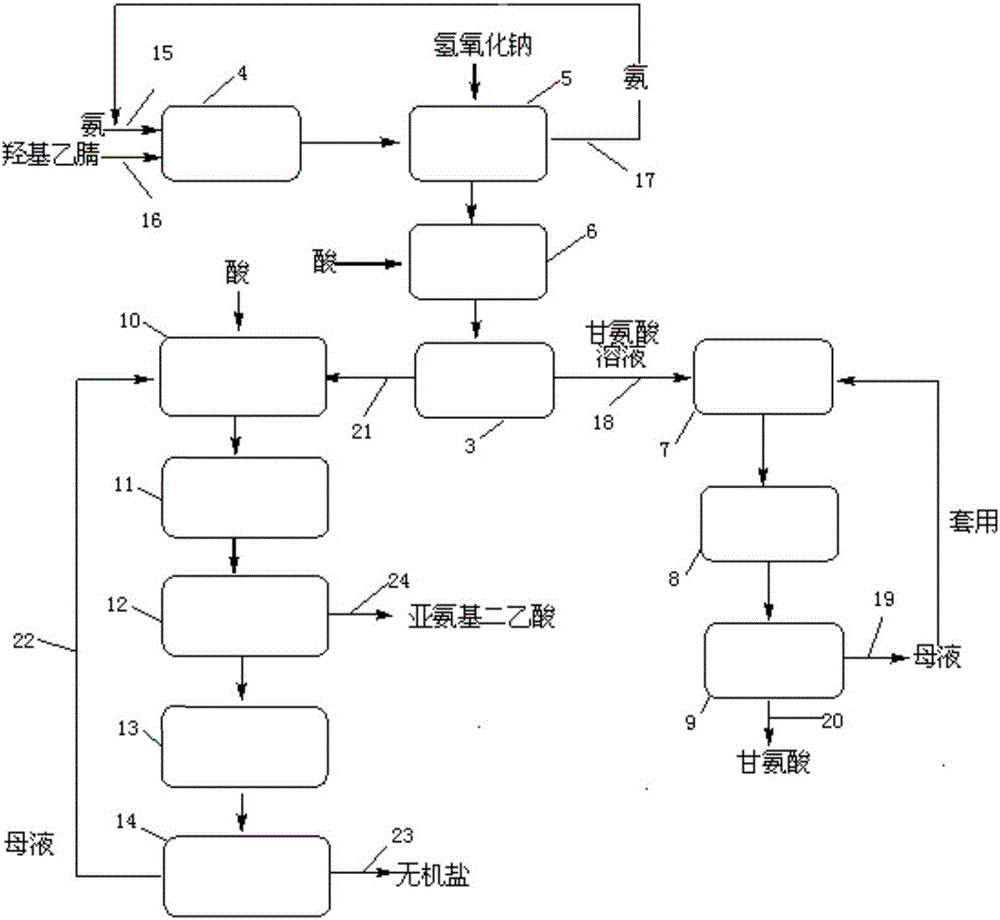
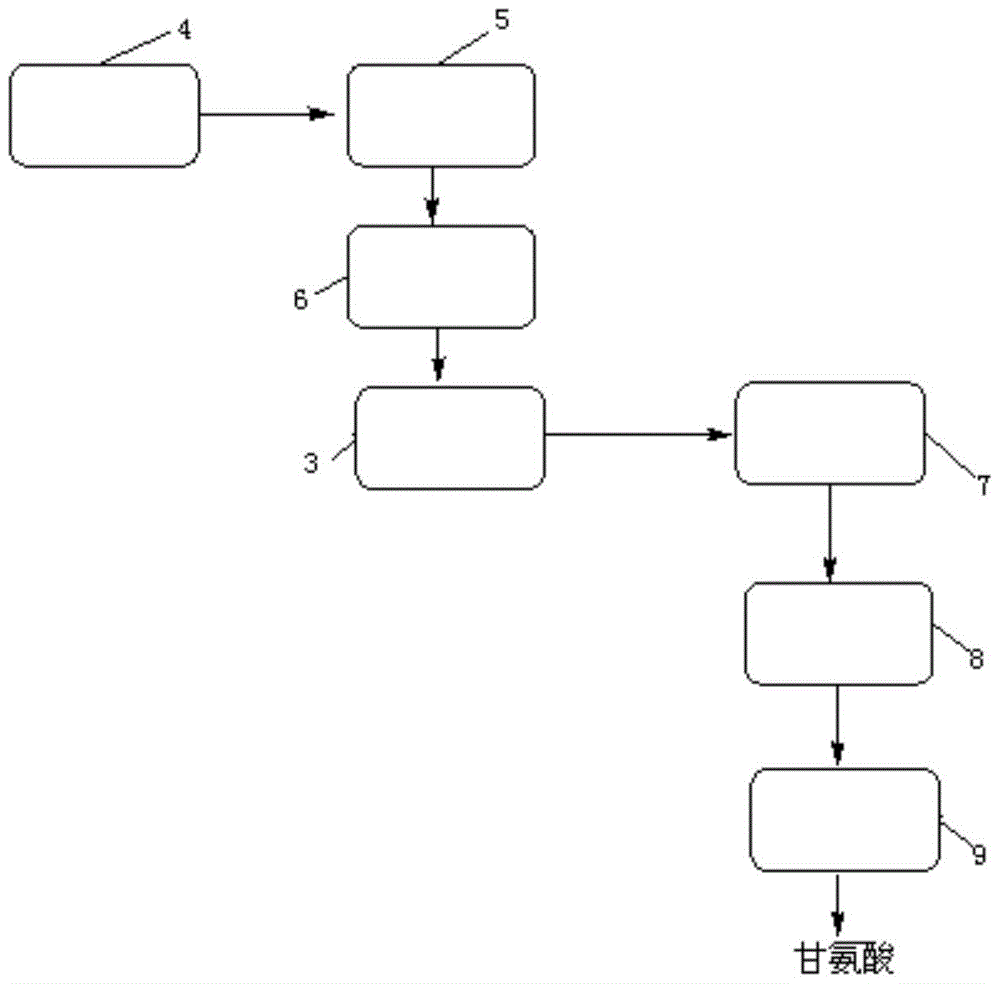
The invention particularly relates to a glycine and iminodiacetic acid cogeneration method and cogeneration system. The method includes the steps: performing alkaline hydrolysis and acidification for mixed liquor containing aminoacetonitrile and iminodiacetonitrile to obtain mixed liquor containing glycine and iminodiacetic acid salt; separating the mixed liquor containing the glycine and the iminodiacetic acid salt by continuous color spectra to respectively obtain glycine liquor and liquor containing the iminodiacetic acid salt. The glycine and iminodiacetic acid cogeneration system comprises a glycine production system unit and an iminodiacetic acid production system unit which are connected through the continuous color spectra jointly possessed by the two units. The glycine and iminodiacetic acid can be simultaneously separated and purified at high purity, by-products are avoided, product yield and purity are improved, and the method is high in production efficiency, simple to operate, green and environmentally friendly.
Owner:CHONGQING UNISPLENDOUR CHEM
Biotinylated chromatin immunoprecipitation method and kit thereof
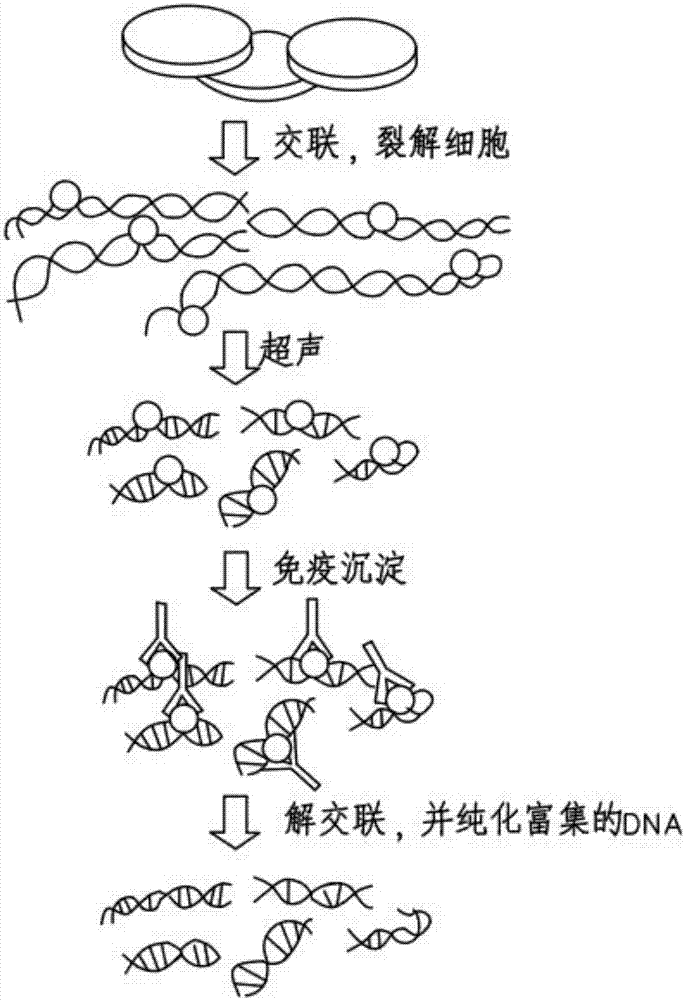
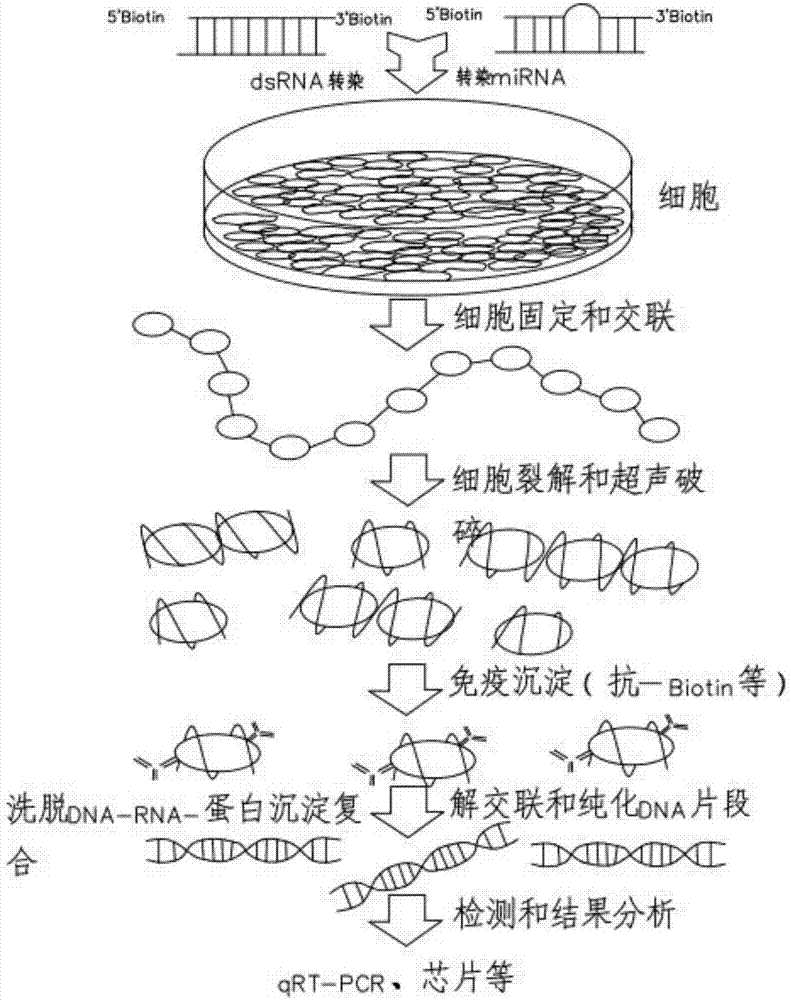
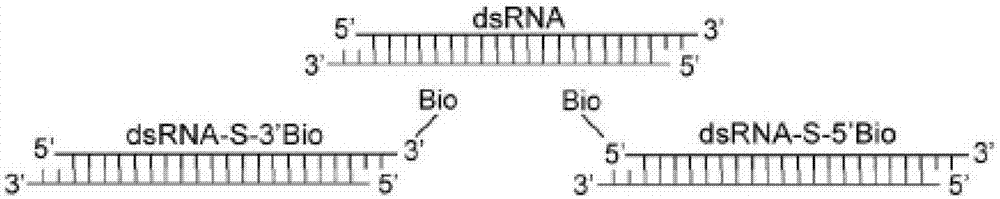
InactiveCN107488713AResearch and Validate InteractionsEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingGlycine solutionBiotin
The invention discloses a biotinylated chromatin immunoprecipitation kit. The kit comprises the following components: protein A+G agarose / salmon sperm DNA, a glycine solution, a chromatin immunoprecipitation dilution buffer, a washing buffer, 0.5M EDTA, 5M NaCl, 1M trismetyl aminomethane with a pH value being 6.5, a SDS cracking buffer, a biotin antibody, and a RNA enzyme inhibitor. The kit has the beneficial effects that the traditional immunoprecipitation is improved, a targeting DNA-RNA compound is obtained, interacting between RNA and DNA is researched and verified, the invention provides the corresponding biotinylated chromatin immunoprecipitation kit, which is convenient for usage by scientific researchers.
Owner:TONGJI HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com