Method for calculating energy spectrum behind charged particle protection layer
A charged particle and protective layer technology, which is applied in the field of calculating the energy spectrum behind the charged particle protective layer, can solve the problems of shortened working life, long calculation time, slow calculation speed, etc., to achieve extended working life, fast calculation speed and easy operation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0029] Specific implementation mode one: the specific process of a method for calculating the energy spectrum behind the protective layer of charged particles in this embodiment is as follows:
[0030] The radiation-sensitive component for spacecraft of the invention is mainly affected by space comprehensive radiation environment factors such as protons, electrons and heavy ions with different energies. The invention is based on the original energy spectrum of original charged particles commonly used in engineering, on the basis of distinguishing positive ions and negative ions, and aiming at different thicknesses of protective layers, the purpose of quickly calculating the energy spectrum after the protective layer is achieved.
[0031] The invention relates to a primary energy spectrum based on orbital primary charged particles commonly used in engineering, and its application objects include materials, devices, electronic systems and structures. The feature of this technolo...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0049] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the differential energy spectrum of the orbit incident particle is determined in the step 1; the specific process is:
[0050] Determine the satellite orbit height and satellite orbit inclination according to the satellite orbit;
[0051] According to the altitude of the satellite orbit and the inclination of the satellite orbit, the electrons in the Earth's radiation belt, the protons in the Earth's radiation belt, the protons of the solar cosmic ray, the ions of the solar cosmic ray and the ions of the galactic cosmic ray are respectively determined;
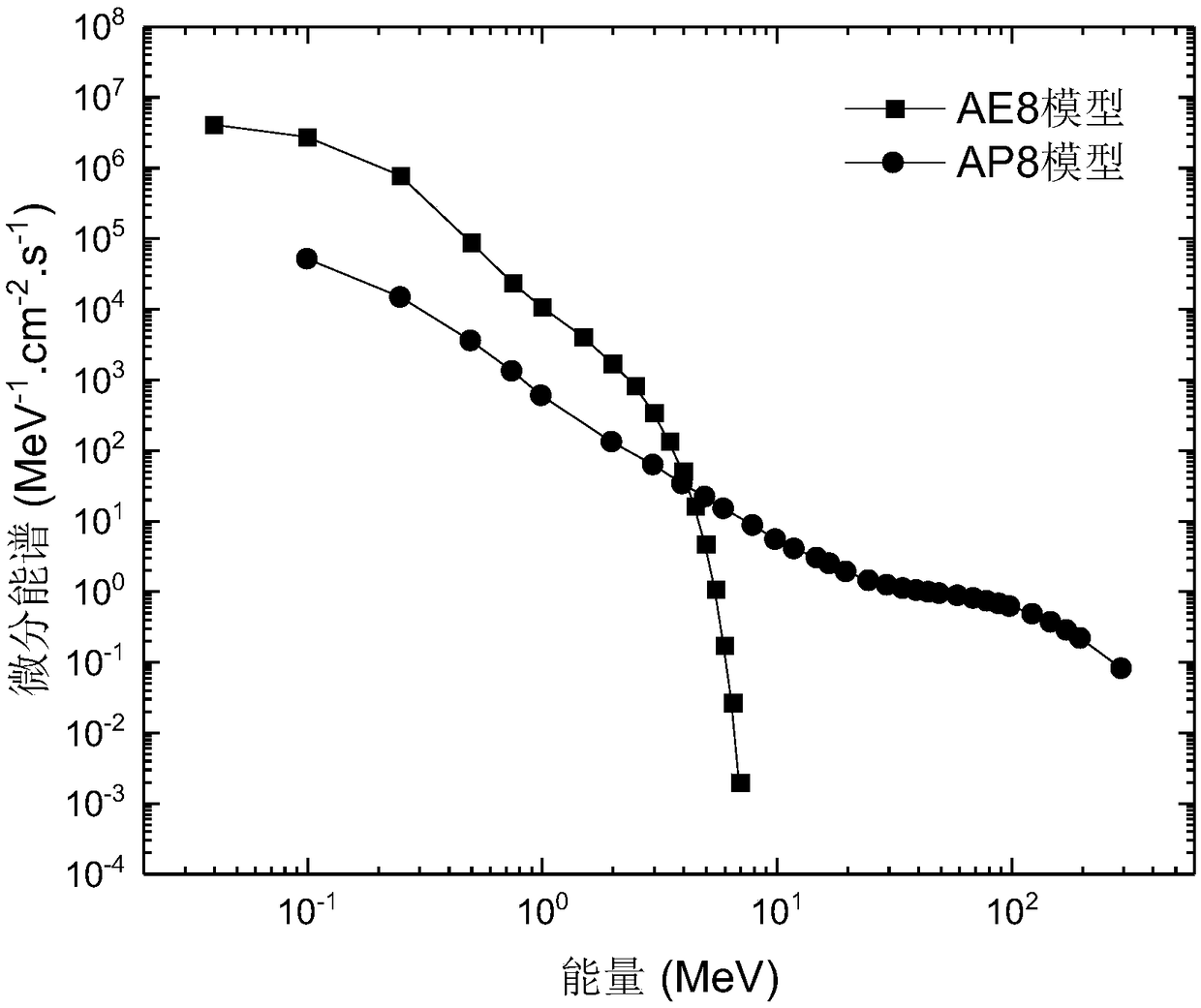
[0052] Select the AE8 or AE9 model according to the electrons in the Earth's radiation belt, and obtain the differential energy spectrum f(E′ of the orbital incident electrons 1 );
[0053] Select the AP8 or AP9 model according to the protons in the Earth’s radiation belt, and obtain the differential energy spectrum f(E′ of orbital incident p...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0059] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that if the incident particle is an electron in the step four, the range has nothing to do with the thickness of the protective material, and the thickness t of the protective material determined according to the step two is calculated. The differential energy spectrum f(E 1 ') energy E 1 ′ and the range and the thickness of the protective material, the specific formula is:
[0060]
[0061] Among them, R i (E 1 ) is the remaining range of incident electrons in the earth’s radiation belt in the protective material, calculated by software such as EGS and GEANT; R i is the remaining range; E 1 is energy (Earth radiation carries electron energy).
[0062] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com