Method for enriching heavy metals in eutrophic water body by means of configuration of submerged plants
A submerged plant, eutrophication technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, biological water/sewage treatment, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
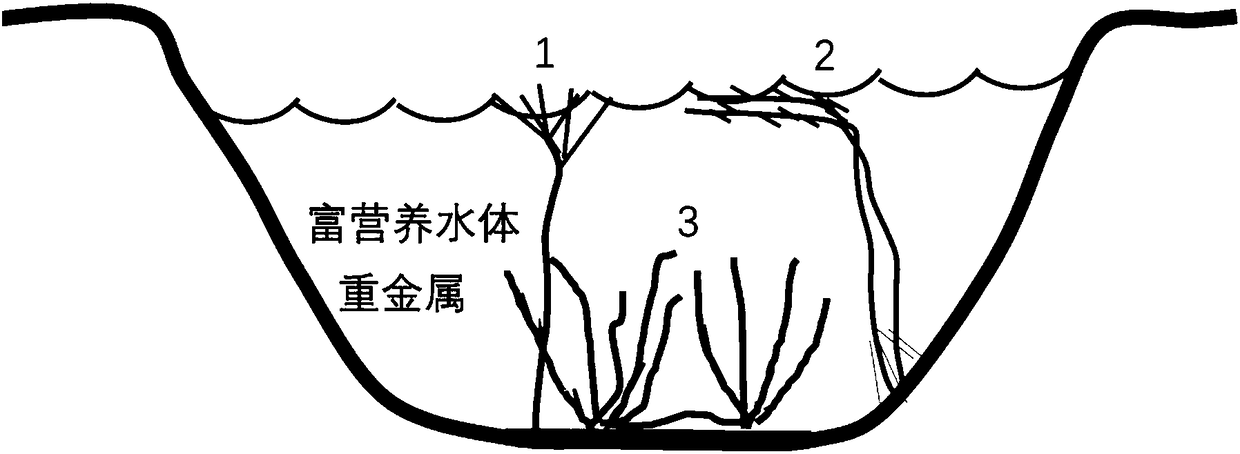
[0020] A method for efficiently enriching heavy metals in eutrophic water bodies by utilizing the arrangement of submerged plants, the steps of which are as follows:
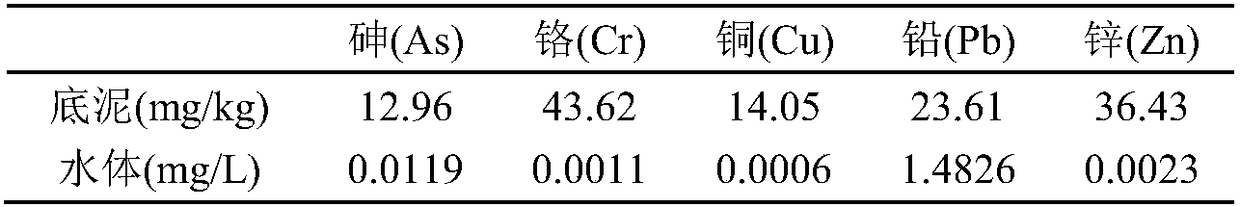
[0021] (1) Screen out dominant submerged plants from eutrophic water bodies: Three dominant submerged plants were screened out from eutrophic water bodies in the wild, namely hornwort (C.demersum), bitter grass (V.natans) and M. spicatum (M. spicatum);
[0022] (2) Propagate and amplify superior submerged plants using seed bank technology: take hornwort and chrysoprhiza spicosa tops at 10 or 12 or 14 or 15 cm, and cut grass with roots to a height of 10 or 11 or 13 or 15 cm, insert lake mud and Massive growth and expansion in the sediment mixed with sand and soil at a ratio of 2:1, the water depth is 60 or 70 or 80 or 90 or 100cm;
[0023] (3) Allocation of submerged plants with different advantages: the spatial configuration is canopy-type submerged plants hornwort and chrysostrum spicosa and rosette-type subme...
Embodiment 2-6
[0033] Its implementation steps are identical with embodiment 1.
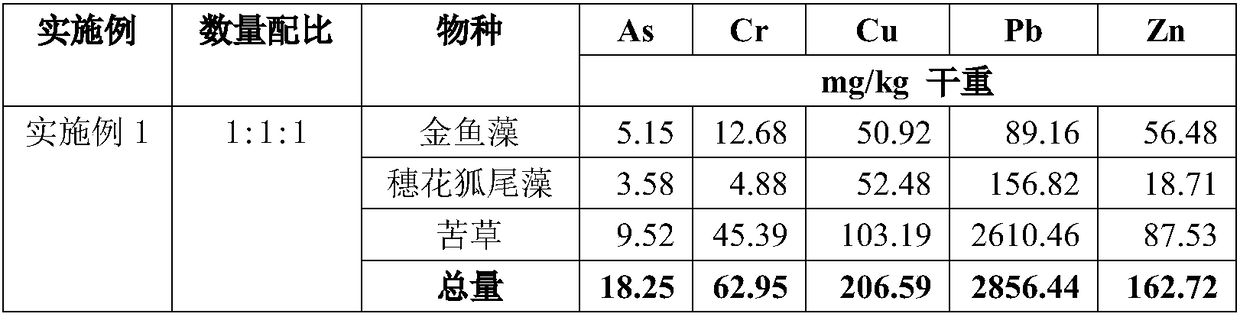
[0034] From the results of Examples 2-6, it can be concluded that when hornwort: P. spicaculata: Erythrina fragrans = 1:2:2, the ability to enrich various heavy metals in eutrophic water bodies is the strongest. When the number of hornwort algae is large, the growth of chrysanthemum rosette is limited by light, so the ability to accumulate heavy metals is also weakened.
[0035]
[0036] The above examples show that arsenic, chromium, copper, lead and zinc in nutrient-rich water can be efficiently enriched by using the 1:2:2 quantity configuration of three different growth-type species of hornwort, chrysanthemum spikulatus, and Erytheria spica. This kind of heavy metal has played the role of not only economy and environmental protection, but also ecological beauty.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com