Method for extracting hematopoietic stem cells in placenta by using multifunctional placenta tissue processing device
A hematopoietic stem cell and processing device technology, applied in the field of placental tissue processing, can solve the problems of less interstitial cells, easy pollution, and labor time-consuming, etc., and achieve the effect of efficient cleaning and cell recovery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0042] Embodiment 1: This embodiment is a method for extracting hematopoietic stem cells in the placenta using a multi-functional placental tissue processing device, which is specifically completed according to the following steps:
[0043] 1. Clean the placenta:
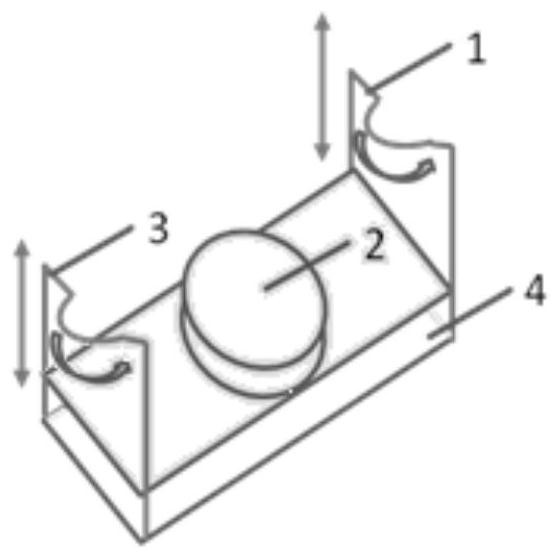
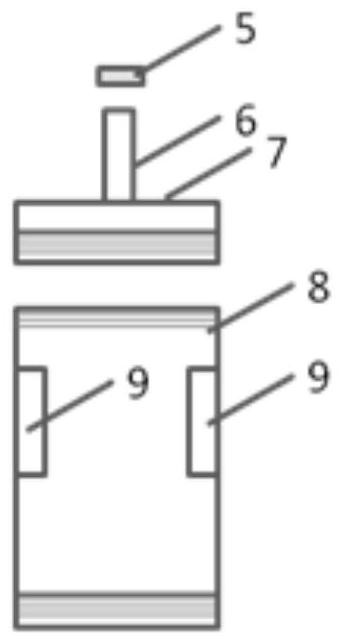
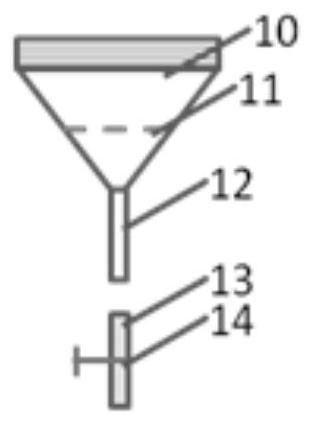
[0044] ①. The lower end of the processor cylinder 8 of the placenta processing device is threadedly connected with the upper end of the conical treatment liquid receiver 10 of the cleaning liquid receiver, and the aseptically collected placenta is put into the processor cylinder 8, and the sterile physiological The saline is injected into the processor cylinder 8 through the closed silica gel cap 5, and the processor cylinder 8 is sealed; the volume ratio of the volume of the sterile saline to the processor cylinder 8 is 1:(16~40); the placenta The volume ratio of the volume to the processor cylinder 8 is 1:(10~20);
[0045] ②. Place the connecting pipe 6 and the cleaning fluid guide pipe 12 on the arc-shaped parts...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0069] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is: the diameter of the arc portion of the first belt 1 is 20 cm, and the diameter of the arc portion of the second belt 3 is 20 cm. Others are the same as the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0070] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2 is that the diameter of the platform of the electromagnetic stirrer 2 with a platform is 20 cm. Others are the same as those of the specific embodiment one or two.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com