Microfluid extraction expansion reactor for 3D printing and applications of microfluid extraction expansion reactor
A 3D printing and microfluidic technology, applied in the improvement of process efficiency, additive processing, etc., can solve the problems of low throughput, unrealistic, and high processing cost of microfluidic chips, achieve rapid separation, shorten time, and avoid extractants Effects of contact with air
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
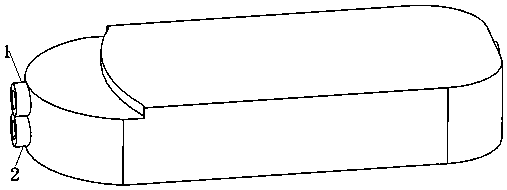
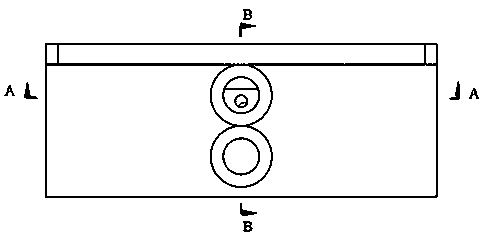
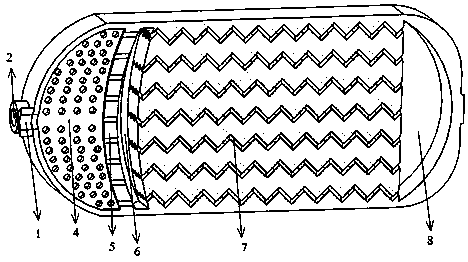
[0045] Such as Figures 1 to 6As shown in 9 and 10, the 3D printed microfluidic extraction expansion reactor includes water phase inlet 1, oil phase inlet 2, mixed liquid collection chamber I3, droplet cutting sieve plate 4, mixed liquid collection chamber partition 5, Mixed liquid collection chamber II6, mixed reaction microchannel 7, mixed liquid collection chamber III8 and mixed liquid outlet 9, one side of the microfluidic extraction expansion reactor is provided with a mixed liquid collection chamber I3 communicated with the water phase inlet 1 and connected with the oil phase The oil phase chamber connected to the inlet 2, the bottom of the mixed liquid collection chamber I3 is provided with a droplet cutting sieve plate 4, and the bottom of the mixed liquid collection chamber I3 communicates with the oil phase chamber through the droplet cutting sieve plate 4, and the side of the mixed liquid collection chamber I3 After passing through the partition plate 5 of the mixed...
Embodiment 2
[0050] The 3D printed microfluidic extraction expansion reactor in Example 1 was applied in the process of extraction, recovery of indium and separation of iron.
[0051] Such as Figure 7 As shown, the 3D printed microfluidic extraction scale-up reactor is applied in the extraction recovery of indium and separation of iron:
[0052] The sulfuric acid system solution containing 2.32g / L indium and 1.42g / L iron (using H 2 SO 4 Solution Adjust the pH value of the aqueous phase solution to 0.5) as the aqueous phase stock solution 11, and D2EHPA (dioctyl phosphate) diluted with 260# solvent oil (the volume ratio of 260# solvent oil to D2EHPA is 7:3) as the oil phase The stock solution 11 is pumped into the water phase inlet 1 and the oil phase inlet 2 of the microfluidic extraction expansion reactor 14 through the flow pump I12 and the flow pump II13 with a maximum flow rate of 100ml / min respectively (both the set flow rate is 0.6ml / min). Mix in middle, stay for 210s, then extrac...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Such as Figures 1 to 6 As shown in 9 and 10, the 3D printed microfluidic extraction expansion reactor includes water phase inlet 1, oil phase inlet 2, mixed liquid collection chamber I3, droplet cutting sieve plate 4, mixed liquid collection chamber partition 5, Mixed liquid collection chamber II6, mixed reaction microchannel 7, mixed liquid collection chamber III8 and mixed liquid outlet 9, one side of the microfluidic extraction expansion reactor is provided with a mixed liquid collection chamber I3 communicated with the water phase inlet 1 and connected with the oil phase The oil phase chamber connected to the inlet 2, the bottom of the mixed liquid collection chamber I3 is provided with a droplet cutting sieve plate 4, and the bottom of the mixed liquid collection chamber I3 communicates with the oil phase chamber through the droplet cutting sieve plate 4, and the side of the mixed liquid collection chamber I3 After passing through the partition plate 5 of the mixe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com