Optical waveguide mode converter used for improving optical waveguide transmission characteristic
A technology of mode converter and transmission characteristics, applied in the direction of optical waveguide light guide, optical waveguide coupling, light guide, etc., can solve problems such as large scattering loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
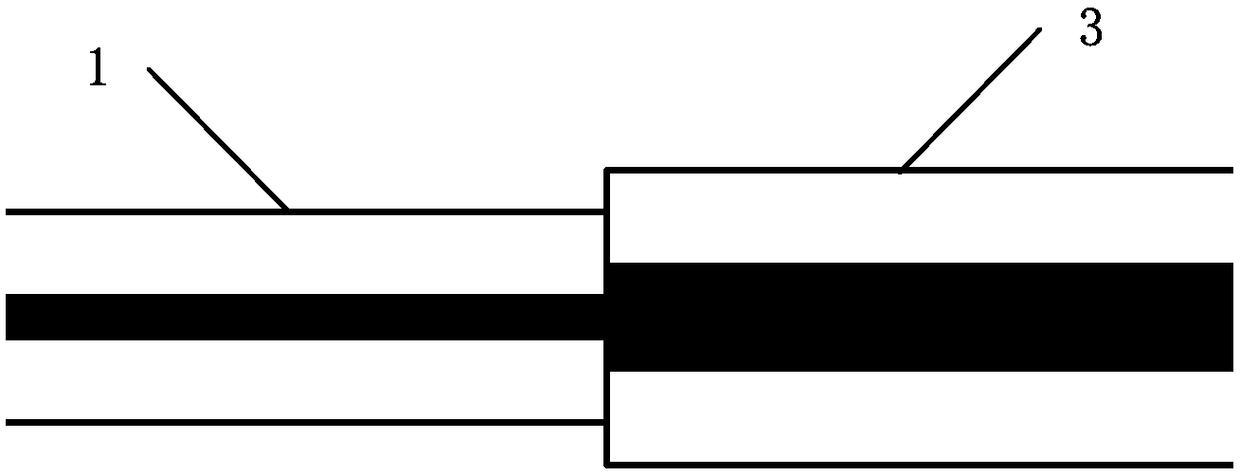
[0044] see Figure 4 , this embodiment proposes an optical waveguide mode converter that improves the transmission characteristics of the optical waveguide. The converter includes a single-mode optical fiber (1), a section of coreless optical fiber with a ball lens (2) and a rectangular optical waveguide (3), and the end face of the single-mode optical fiber (1) is connected with a section of coreless optical fiber with a ball lens (2) , keep an effective distance L between the end face of the optical waveguide (3) and the ball lens 2 . The axial centers of the single-mode optical fiber (1), the axial centers of the coreless optical fiber (2) and the optical waveguide (3) are kept on the same horizontal straight line. Its working principle: almost all the optically transformed Gaussian beams are coupled into the fundamental mode of the optical waveguide, which can not only reduce the scattering loss of the optical waveguide due to roughness, but also solve the problem of mod...
Embodiment 2
[0046] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, and the special features are as follows:
[0047] The mode converter parameter is, the length of the coreless fiber (2) is L 1 , the radius of the fiber optic ball is R, and the refractive index of the ball lens material is n 1 , the distance between the end face of the optical waveguide (3) and the ball lens is L 2 , the refractive index of the gap material between the ball lens and the optical waveguide (3) is n 2 , n 1 >n 2 , the value range of the parameter: L 1 200-236μm, R is 125-140μm, L 2 It is 947-1200μm.
[0048] join Image 6 , the coreless fiber with ball lens is packaged into a specially designed adapter (4), the width of the adapter is greater than 2 times the radius R of the ball lens, the incident end of the adapter has a stepped groove (5), and the size of the groove is the same as The size of the fiber jumper matches, so that the flat end of the fiber ball and the output end of the fiber ju...
Embodiment 3
[0051] see Figure 4 , this embodiment proposes a structural schematic diagram of an optical waveguide mode converter for improving optical waveguide transmission characteristics and its working principle.
[0052] An optical waveguide mode converter for improving the transmission characteristics of the optical waveguide, comprising a single-mode optical fiber (1), a section of coreless optical fiber with a ball lens (2) and a rectangular optical waveguide (3). The flat end of the coreless fiber (2) can be parallel-jointed or fused with the output end of the single-mode fiber (1), and the length of the coreless fiber is L 1 , the vertex of the spherical surface is facing the input end of the optical waveguide (3) and the distance L 2 , the spherical radius is R, and the refractive index of the spherical lens material is n 1 , the refractive index of the gap material between the ball lens and the optical waveguide is n 2 . The axis of the single-mode fiber, the axis of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com