Complex network node influence maximization method based on depth auto-encoder
A complex network and autoencoder technology, applied in the field of maximizing the influence of complex network nodes based on deep autoencoders, can solve the problem of high time complexity, inability to mine node influence characteristics in complex networks, and unsuitable for large-scale networks and other problems to achieve the effect of avoiding the amount of calculation, reducing the feature dimension, and reducing time consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
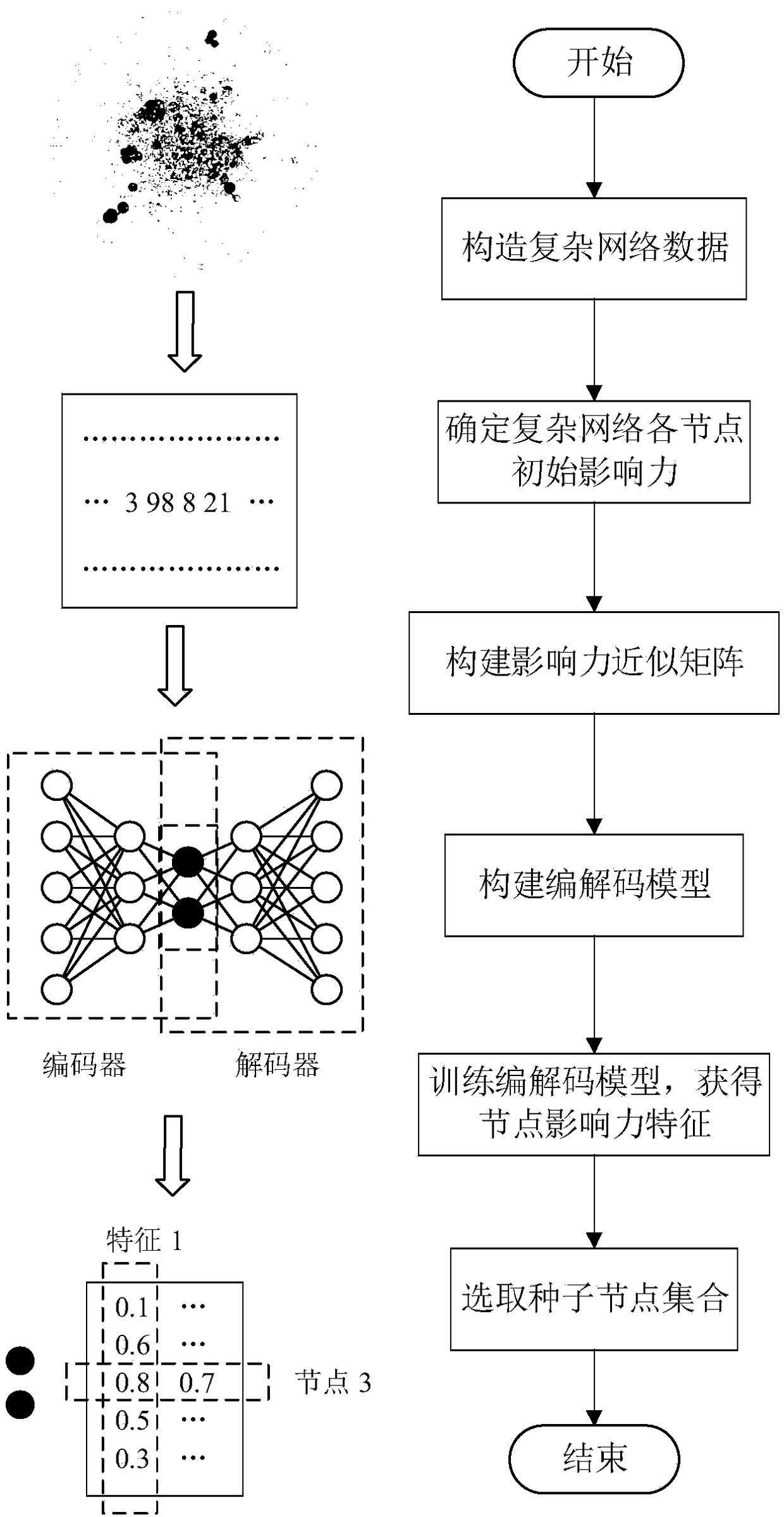
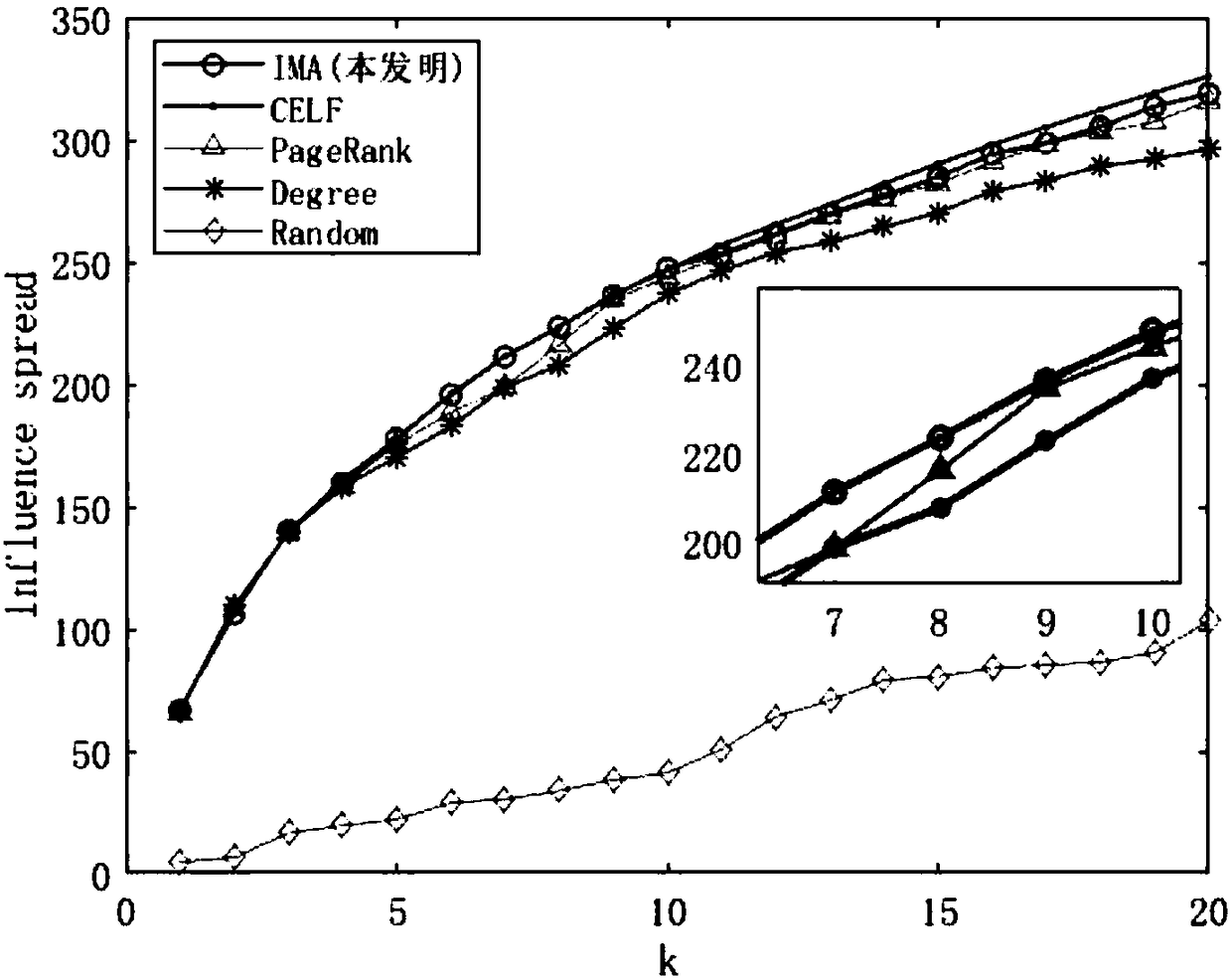
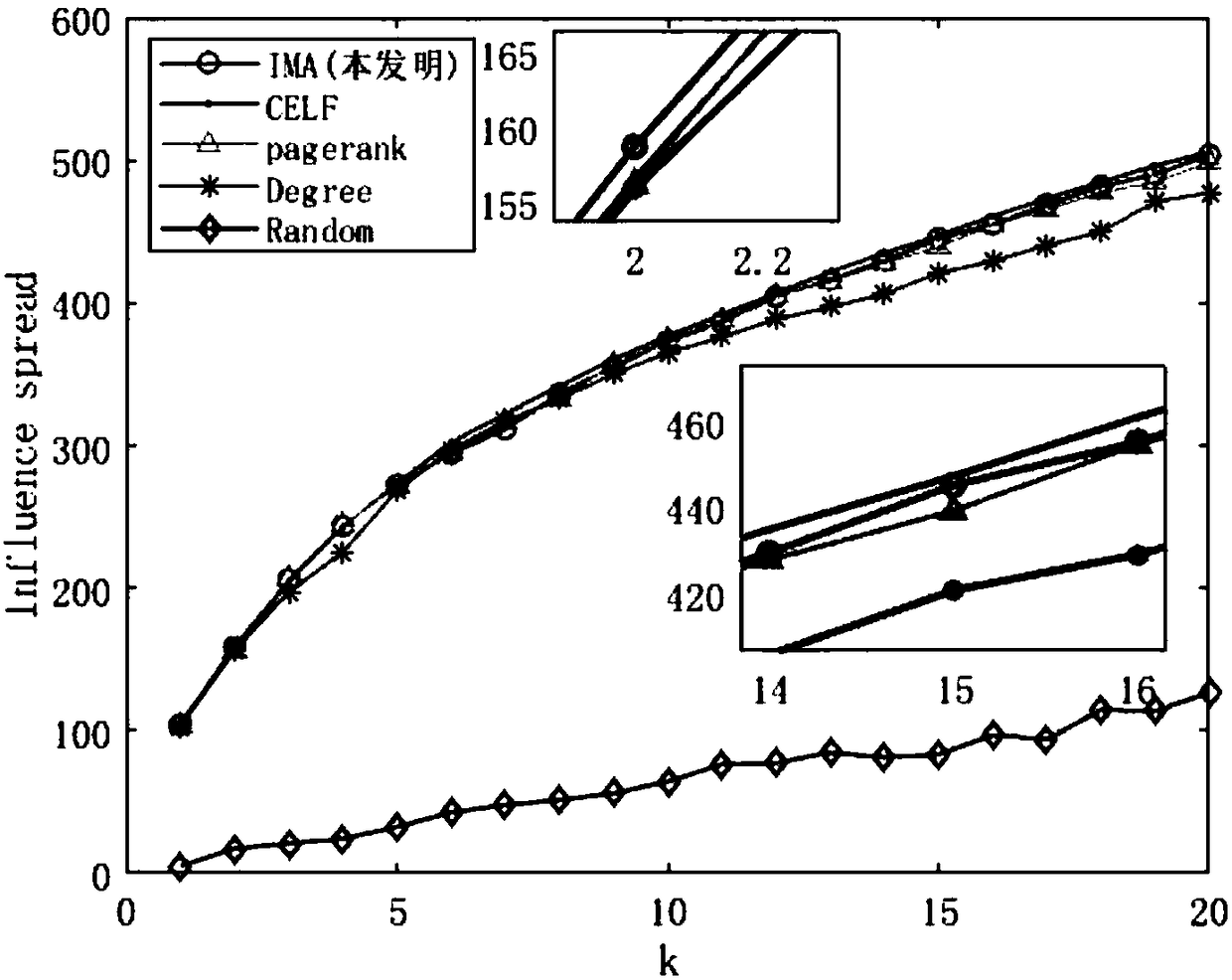
[0028] Complex networks are abstracted from various complex systems in the real world. Studying complex networks can help understand the deep relationship between individuals in the network, and influence analysis in complex networks plays a vital role in complex networks. Existing technologies cannot mine the influence characteristics of nodes in complex networks, and there is a certain blindness in the process of selecting nodes, and most of them are based on greedy algorithms, which have very high time complexity and are not suitable for large-scale network data processing and complex mining. Influence characteristics of network nodes. The present invention conducts research on this, and proposes a method for maximizing the influence of complex network nodes based on a deep autoencoder. refer to figure 1 , the implementation steps of the present invention are as follows:
[0029] (1) Construct complex network data: abstract the complex network in the real world into a top...
Embodiment 2
[0046] The method of maximizing the influence of complex network nodes based on deep autoencoder is the same as that in Embodiment 1. The estimated value of influence propagation within the scope of two layers is obtained in step 3 of the present invention, and the two-layer influence propagation of each node in the complex network needs to be set. The range equation is used to estimate the two-layer influence propagation range of complex network nodes, and its influence estimate is calculated by the following LIE equation:
[0047]
[0048] in, is the set of neighbor nodes of node v, S represents the set of nodes, k represents the number of nodes, Indicates the neighbor nodes of all nodes in the set S, Indicates the node set of the set S within the spread range of two layers of influence.
[0049] It can be seen that the estimated value of the spread of influence within the scope of the two layers of the present invention is the initial number of activated nodes σ 0 ...
Embodiment 3
[0052] The method for maximizing the influence of complex network nodes based on deep autoencoders is the same as that of Embodiment 1-2, and the construction of the codec model described in step 5 of the present invention specifically includes the following steps:
[0053] (5a) Construct the encoder: use the ReLu function f(x)=max(0,x) as the activation function of the encoder, input the influence approximation matrix M into the encoder equation, and use a single element x i , For example, calculate the deep feature z of node influence, Methods as below:
[0054] z=f(Wx i +b)
[0055] where W and b are the weights and biases in the encoder, respectively.
[0056] (5b) Constructing the decoder: use the ReLu function f(x)=max(0,x) as the activation function of the decoder, input the node influence deep feature z obtained in 5a) to the decoder, and obtain the heavy The element x′ in the influence approximation matrix of the structure i :
[0057] x' i =f(W'z+b')
[00...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com