Building energy-saving house
A technology for building energy conservation and housing, applied in building components, building insulation materials, thermal insulation and other directions, can solve problems such as poor thermal insulation performance, difficult thermal insulation effect, energy waste, etc., and achieve the effect of improving insulation performance and improving thermal insulation performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
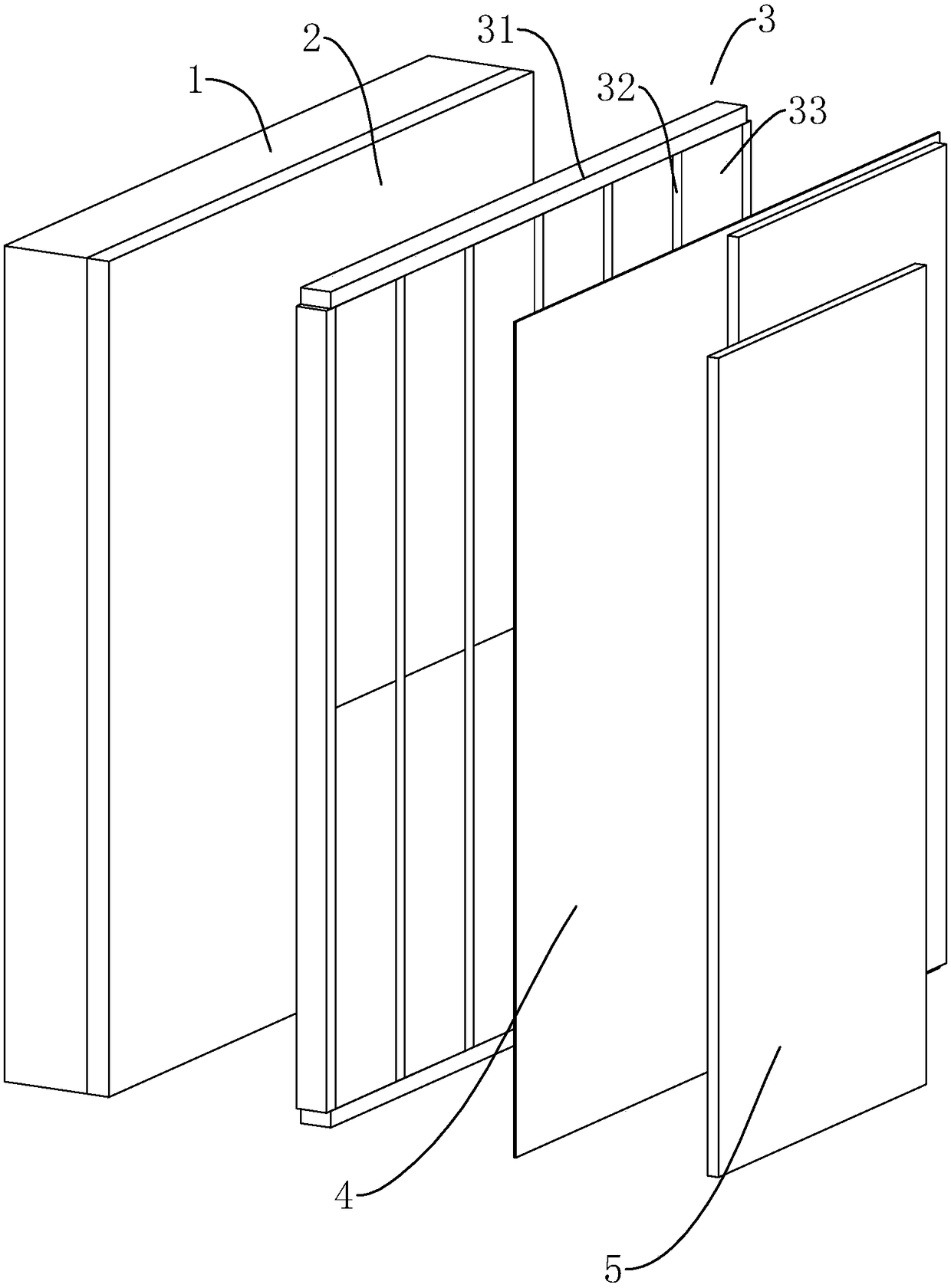
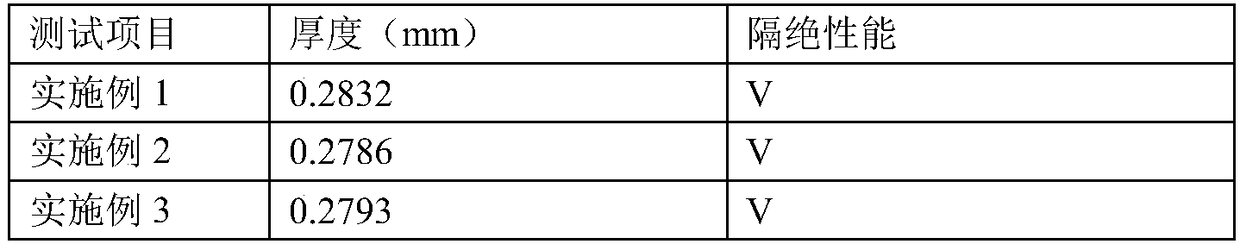
[0037] Such as figure 1 As shown, a building energy-saving house includes a concrete exterior wall body 1 . On the inner side of the concrete outer wall 1, a waterproof insulation layer 2 and an inner wall skeleton 3 fixedly connected to the ceiling and floor of the house at the upper and lower ends are arranged, and the side of the inner wall skeleton 3 away from the waterproof insulation layer 2 is laid with gypsum. board 5, and then while the concrete outer wall body 1 plays the role of separating the inside and outside sides of the house, the waterproof insulation layer 2 can achieve a preliminary heat preservation effect while preventing the water from leaking from the outside of the house to the inside; at the same time After the inner wall skeleton 3 is fixed on the inner side of the concrete outer wall body 1 of the house, the gypsum board 5 fixed on the inner side of the inner wall skeleton 3 makes a partition space be formed between the concrete outer wall body 1 and...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Compared with embodiment one, the plastic film layer of embodiment two comprises the following components by weight:
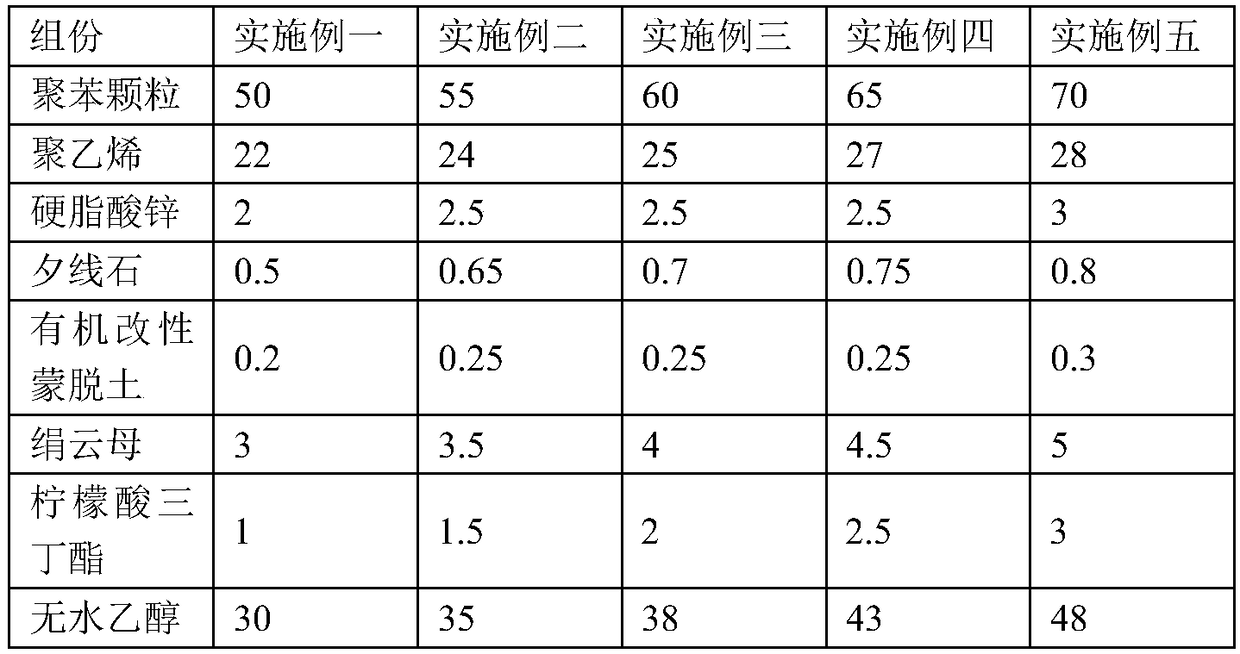
[0049] 55 parts of polyphenylene particles, 24 parts of polyethylene, 2.5 parts of zinc stearate, 0.65 parts of sillimanite, 0.25 parts of organically modified montmorillonite, 3.5 parts of sericite, 1.5 parts of tributyl citrate and 35 parts of anhydrous ethanol.
[0050] The manufacturing method of plastic film layer comprises the following steps:
[0051] Step 1: Take 55 parts of polystyrene particles, 24 parts of polyethylene, 2.5 parts of zinc stearate, 0.65 parts of sillimanite, 0.25 parts of organically modified montmorillonite and 3.5 parts of sericite, mix and stir for 10 minutes, and then add 35 parts of absolute ethanol in a constant temperature water bath at 50°C for 2 hours to obtain a mixture;
[0052] Step 2: Add 1.5 parts of tributyl citrate to the mixture, stir at a constant temperature of 80°C and a stirring speed of 3600r / h for 1 ho...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Compared with embodiment one, the plastic film layer of embodiment three comprises the following components by weight:
[0057] 60 parts of polyphenylene particles, 25 parts of polyethylene, 2.5 parts of zinc stearate, 0.7 parts of sillimanite, 0.25 parts of organically modified montmorillonite, 4 parts of sericite, 2 parts of tributyl citrate and 38 parts of anhydrous ethanol.
[0058] The manufacturing method of plastic film layer comprises the following steps:
[0059] Step 1: Take 60 parts of polystyrene particles, 25 parts of polyethylene, 2.5 parts of zinc stearate, 0.7 parts of sillimanite, 0.25 parts of organically modified montmorillonite and 4 parts of sericite, mix and stir for 10 minutes, and then add 38 parts of absolute ethanol in a constant temperature water bath at 50°C for 2 hours to obtain a mixture;
[0060] Step 2: Add 2 parts of tributyl citrate to the mixture, stir at a constant temperature of 80°C and a stirring speed of 3600r / h for 1 hour to ob...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com