Rare earth-free low-alloy super-high-toughness magnesium alloy and preparation method thereof
An ultra-high-strength, low-alloy technology, applied in the field of magnesium alloys and their preparation, can solve the problems of low yield strength of magnesium alloys, and achieve the effects of high mechanical properties, abundant raw material reserves and excellent surface quality.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
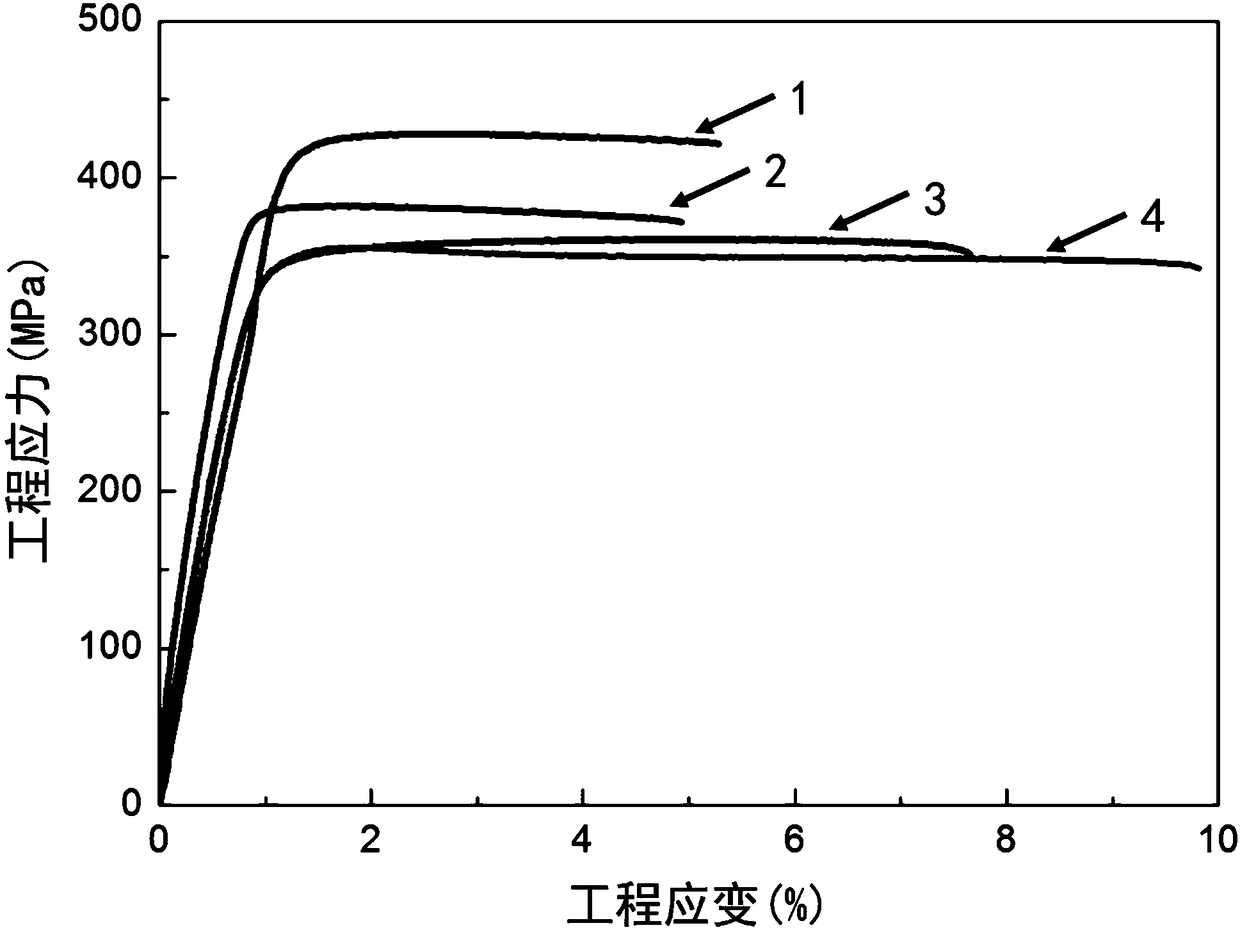
[0018] Embodiment 1: This embodiment is a rare earth-free low-alloy ultra-high-strength magnesium alloy, which is composed of Mg and alloy elements, and the mass fraction of alloy elements is ≤ 2.5%, and the balance is Mg; the alloy elements are composed of Al, Composed of Ca and Mn, the mass fraction of Al is 0.2%-2.0%, the mass fraction of Ca is 0.2%-2.0%, and the mass fraction of Mn is 0.4%.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0019] Specific embodiment 2: The present embodiment as described in specific embodiment 1 is a method for preparing a rare earth-free low-alloy ultra-high-strength magnesium alloy, which is specifically completed according to the following steps:
[0020] 1. Casting: using pure Mg, pure Al, Mg-Ca master alloy and Mg-Mn master alloy as raw materials, successively smelting and casting to obtain a cast alloy; the mass fraction of Al in the cast alloy is 0.2% to 2.0%, The mass fraction of Ca is 0.2%-2.0%, the mass fraction of Mn is 0.4%, the balance is Mg, and the total mass fraction of Al, Ca and Mn≤2.5%;
[0021] 2. Homogenization treatment: place the cast alloy in a resistance heating furnace for homogenization treatment, and obtain the alloy after homogenization treatment;
[0022] 3. Extrusion deformation: preheat the homogenized alloy and the extrusion die respectively to obtain the preheated alloy and the preheated extrusion die, and then put the preheated alloy into the p...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0026] Specific implementation mode three: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode two is: in step one, in SF 6 +CO 2Under a mixed protective atmosphere, first place pure Mg in a crucible, heat up to 680-760°C, keep warm at a temperature of 680-760°C to completely melt pure Mg, and then add pure Al, Mg-Ca intermediate alloy and Mg-Mn in sequence The alloy is mechanically stirred at a temperature of 680-760°C for 15min-30min, then left to stand for 15min-30min to obtain an alloy melt, and then the alloy melt is made into an ingot by a metal mold water cooling solidification process to obtain a cast alloy. Others are the same as in the second embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com