Viscoelastic agent for ophthalmology
A viscoelastic and ophthalmological technology, applied in medical science, medical formula, surgery, etc., can solve problems such as intraocular lens turbidity, and achieve the effects of improving storage stability, improving stability, and improving storage and transportation performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0038] According to another embodiment of the present invention, the viscoelastic agent comprises or consists of the following components:
[0039] - Sodium Hyaluronate: 1.5%-2.5% w / v;
[0040] - Boric acid: 0.7%-0.85% w / v;
[0041] - Borax: 0.04%-0.07% w / v;
[0042] - Sodium chloride: 0.3%-0.7% w / v;
[0043] - The balance is water.
[0044] The viscoelastic agent of the present invention is a viscoelastic agent suitable for ophthalmology, especially, a viscoelastic agent suitable for intraocular.
[0045] The present invention also relates to an ophthalmic implement comprising a viscoelastic as described above.
[0046] The present invention also relates to an ophthalmic implant comprising a viscoelastic as described above.
[0047] The present invention also relates to the method for preparing the viscoelastic agent of the present invention, comprising the steps of:
[0048] - Dissolving pH buffers and osmolarity regulators to obtain sterile buffers,
[0049] - adding...
Embodiment 1
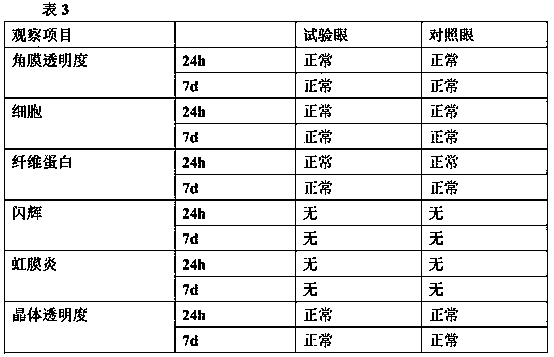
[0055] The viscoelastic agents of the present invention having formulations 1-6 were prepared according to the following steps according to Table 1 below. Firstly, the pH buffer agent and the osmotic pressure regulator powder are dispersed and dissolved with water for injection, and then filtered and sterilized through a 0.22 μm water-based filter membrane to obtain a sterile buffer solution. In a dynamic 100-level environment, add the viscoelastic material calculated and weighed according to the corresponding formula into the sterile buffer solution, shake and mix well, and then stand at 2-8°C to remove air bubbles. Fill the mixed and bubble-free feed solution into the prefilled syringe through the prefilled syringe filling machine under the protection of the oRABS aseptic isolation system.
[0056] Table 1
[0057]
Embodiment 2
[0058] Example 2 Moist heat sterilization of formula 1-6 and shear viscosity before and after sterilization
[0059] Put the viscoelastic agent of formula 1-6 encapsulated in the pre-filled syringe in a pressure-compensated humid-heat sterilizer, set the sterilization temperature at 121°C and F0=8, and use a rheometer before and after sterilization ( Manufacturer TA, model DHR-1) to test, record 0.25s -1 The viscosity data at the shear rate are shown in Table 2.
[0060] Table 2
[0061]
[0062] As shown in Example 2, the viscoelastic agent of the present invention can withstand moist heat sterilization, and after conventional terminal moist heat sterilization, the viscoelastic agent of the present invention still has excellent viscosity, including pH buffering based on boric acid and / or borate The viscoelastic agent of the agent still has the required viscoelasticity and so on.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com