Processing method for enabling cellulose fibers to achieve antibacterial functions based on supercritical CO2 fluid technology
A technology of cellulose fiber and fluid technology, which is applied in the processing field of cellulose fiber with antibacterial function based on supercritical CO2 fluid technology, which can solve the problems of single function, relatively small content of functional content, complicated finishing process, etc., and achieve Increase the effective volume, good sustained-release effect, good hand feeling effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1: Supercritical CO 2 Method for Fluid Loading Antibacterial Drug Limonic Acid to Viscose Fiber
[0035] First wash the viscose fabric with ethanol and deionized water, dry and balance for 24 hours and weigh, take ramic acid by weighing 11% of the viscose fabric weight and put it into the medicine tank of the high-pressure equipment, and add 0.1% of the viscose fabric weight of ethanol, and then into the viscose fabric. Cool the CO 2 The gas CO flowing out of the cylinder 2 Cool to liquid.
[0036] The pressure of the high-pressure equipment is first set to 8Mpa, the temperature is 70°C, and the carbon dioxide becomes a supercritical fluid. After impregnation and equilibrium for 15 minutes, the pressure rises to 20MPa at a speed of 0.5MPa / min; Descending until the end of the experiment, the viscose fibers loaded with limonic acid were obtained. The drug loading of viscose fiber was 6.9%.
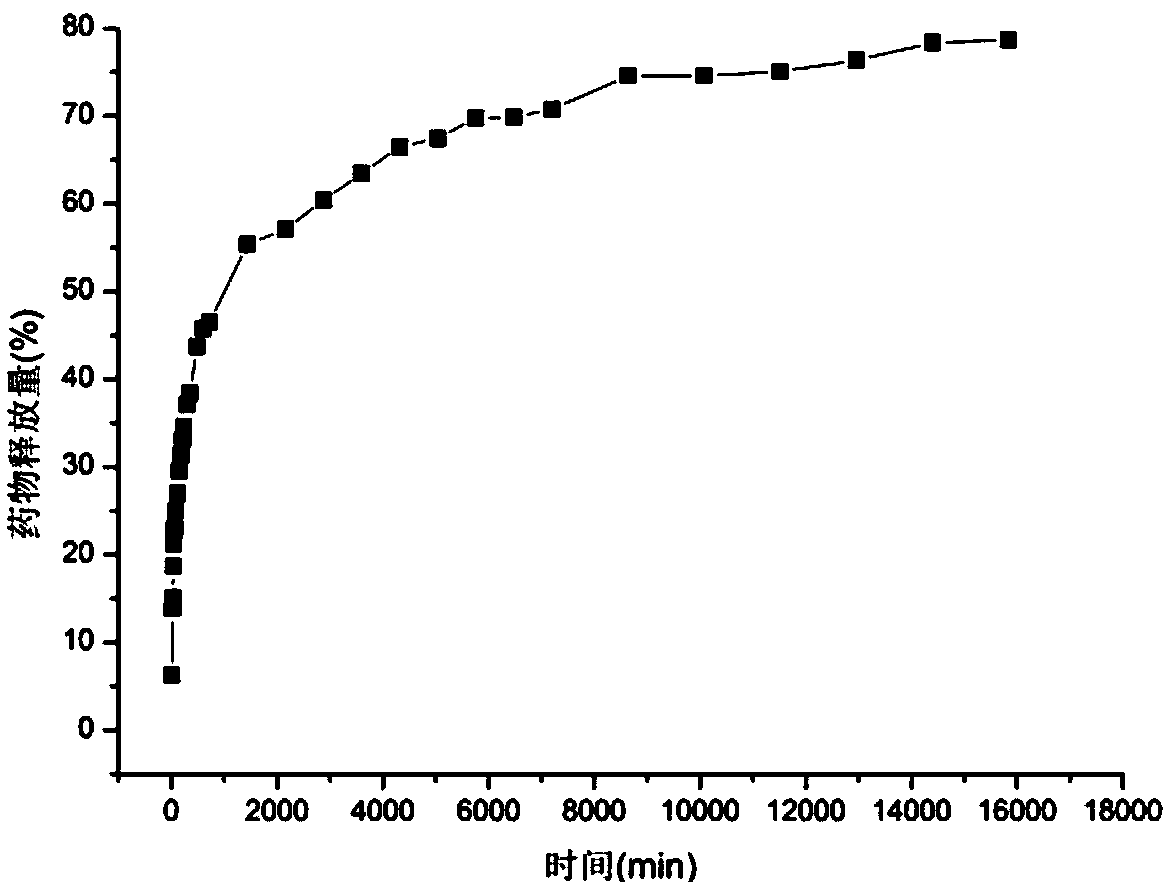
[0037] In order to analyze the slow-release properties of viscose f...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2: Supercritical CO 2 Method for Fluid Loading Antibacterial Drug Tropone to Cotton Fiber
[0044] Weigh an appropriate amount of cotton fiber, soak it in an aqueous solution of N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide (NMMO) with a mass fraction of 70% for 40 minutes at a bath ratio of 1:25, and take out the cotton fiber at a water bath temperature of 80°C. .
[0045] Wash the treated cotton fibers with ethanol and deionized water, dry and balance for 24 hours, weigh them, weigh 7% of the cotton fiber weight, and put tropolone into the medicine tank of the high-pressure equipment, and add cotton fibers 0.08% by weight of methanol, and then put into the cotton fiber. Use a cooling tank to cool the gaseous carbon dioxide flowing out of the carbon dioxide cylinder into a liquid. The pressure of the high-pressure equipment is set to 18Mpa and the temperature is 80°C. of cotton fibers. The drug loading of cotton fiber is 5.6%.
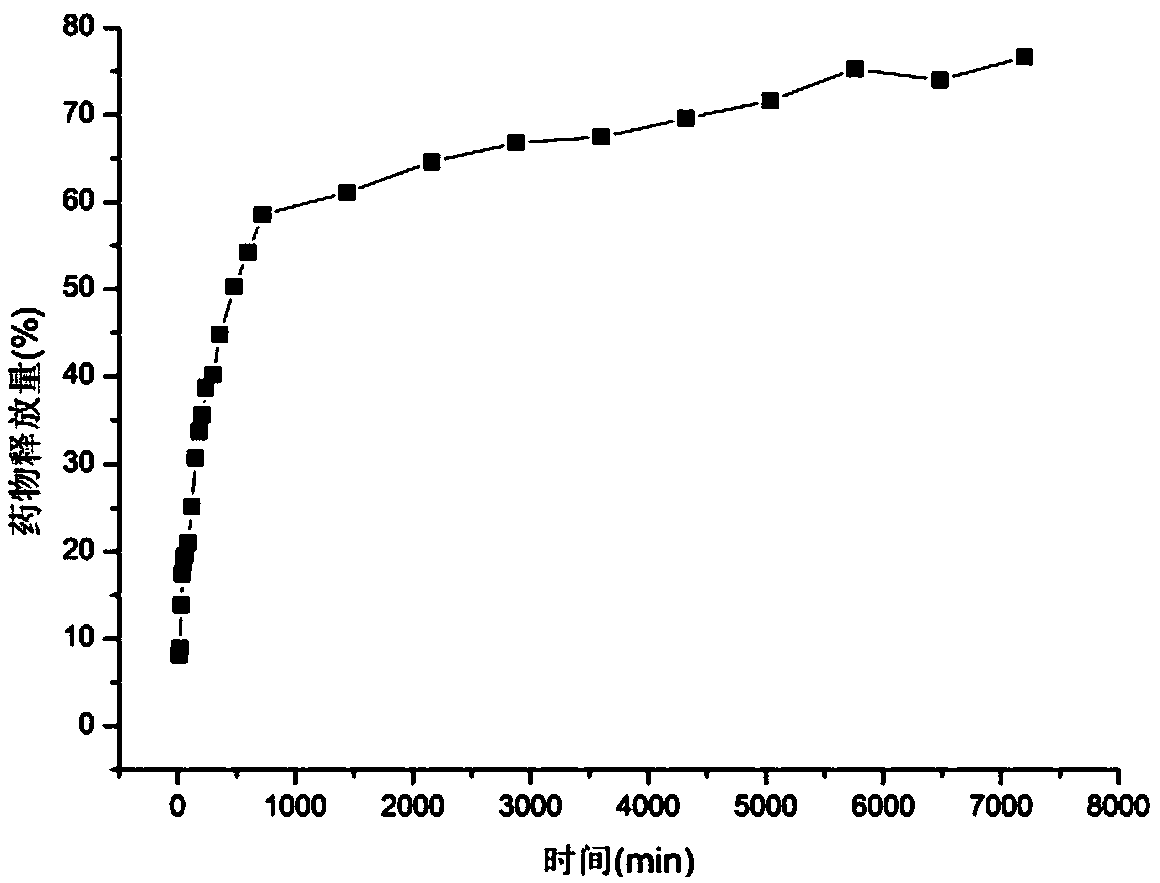
[0046] In order to analyze the slow-release pr...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Example 3: Supercritical CO 2 Method for Fluid Loading Antibacterial Medicine Hippuric Acid to Tencel Fiber
[0051] First, take an appropriate amount of Tencel fabric, wash it with ethanol and deionized water, dry it and weigh it for 24 hours, weigh hippuric acid according to the weight of Tencel fabric at 12%, prepare a 20% ethanol solution with water, and then prepare 0.04mol / L AOT / ethanol solution, put into a clean container to prepare a microemulsion.
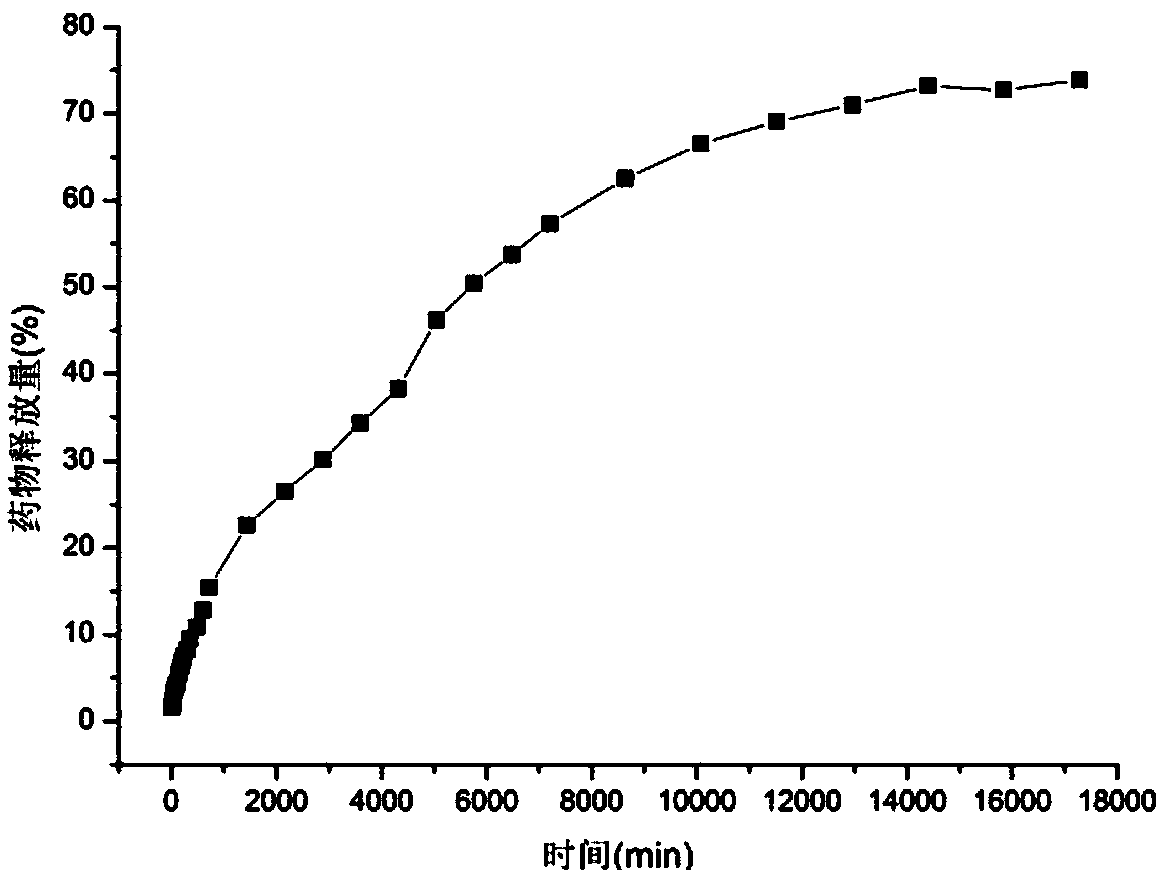
[0052] Put the prepared microemulsion into the medicine tank of the high-pressure equipment, and then put it into the Tencel fabric. Use a cooling tank to cool the gaseous carbon dioxide flowing out of the carbon dioxide cylinder into a liquid. The pressure of the high-pressure equipment is set at 22Mpa, the temperature is 70°C, and the carbon dioxide becomes a supercritical fluid. After the impregnation balance for 3H, the experiment is over, and the tencel fiber loaded with hippuric acid is obtained. . The dr...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| quality score | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com