Monoclonal antibody resisting EV-D68 virus and preparation and application thereof
A technology of EV-D68 and monoclonal antibody, which is applied in the direction of antiviral agents, antiviral immunoglobulins, antibodies, etc., and can solve problems such as the difference in activity between antibodies and natural antibodies
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Embodiment 1: The preparation process of the monoclonal antibody against EV-D68 virus is described in detail.
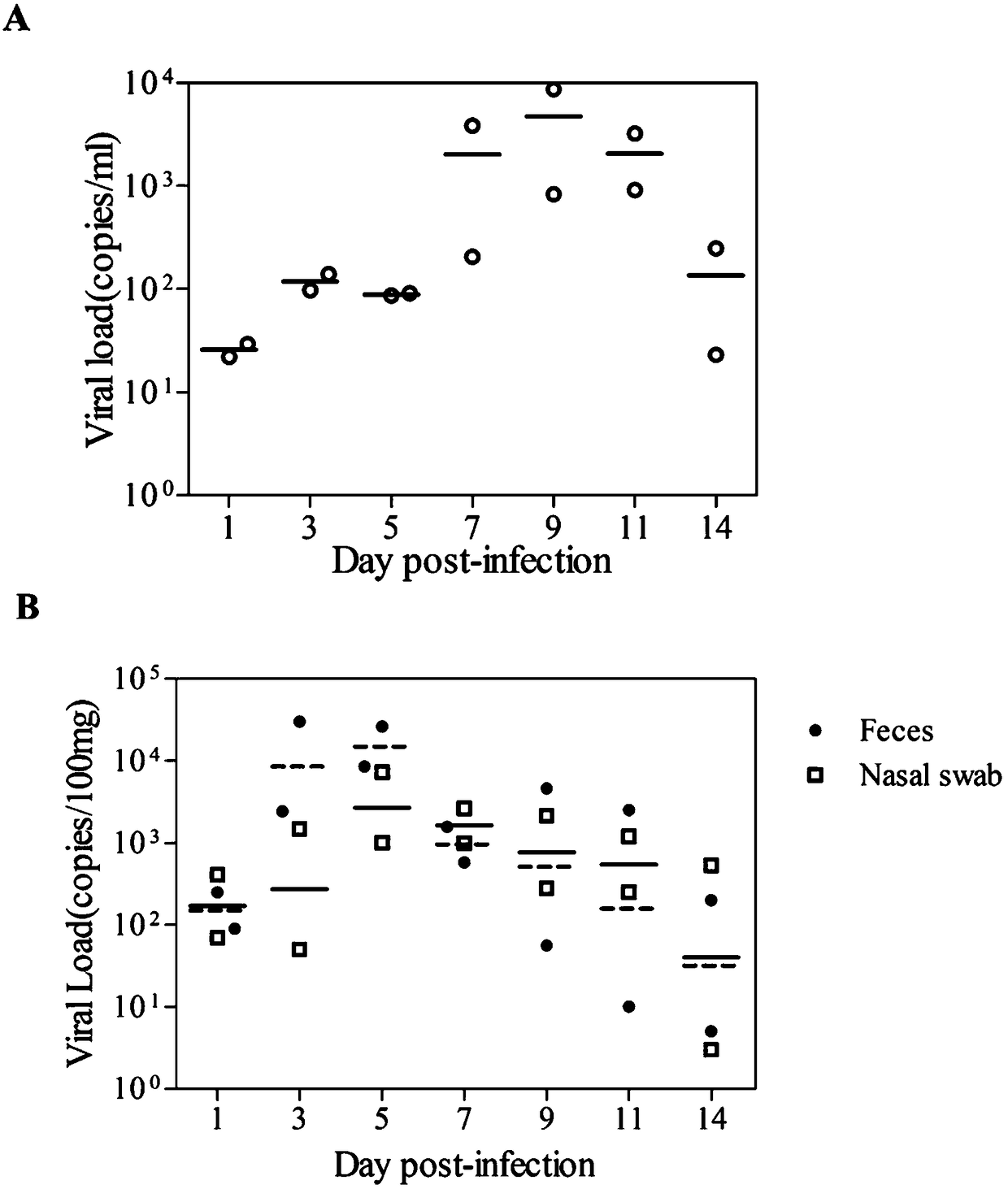
[0040] Infection of rhesus monkeys with EV-D68 virus
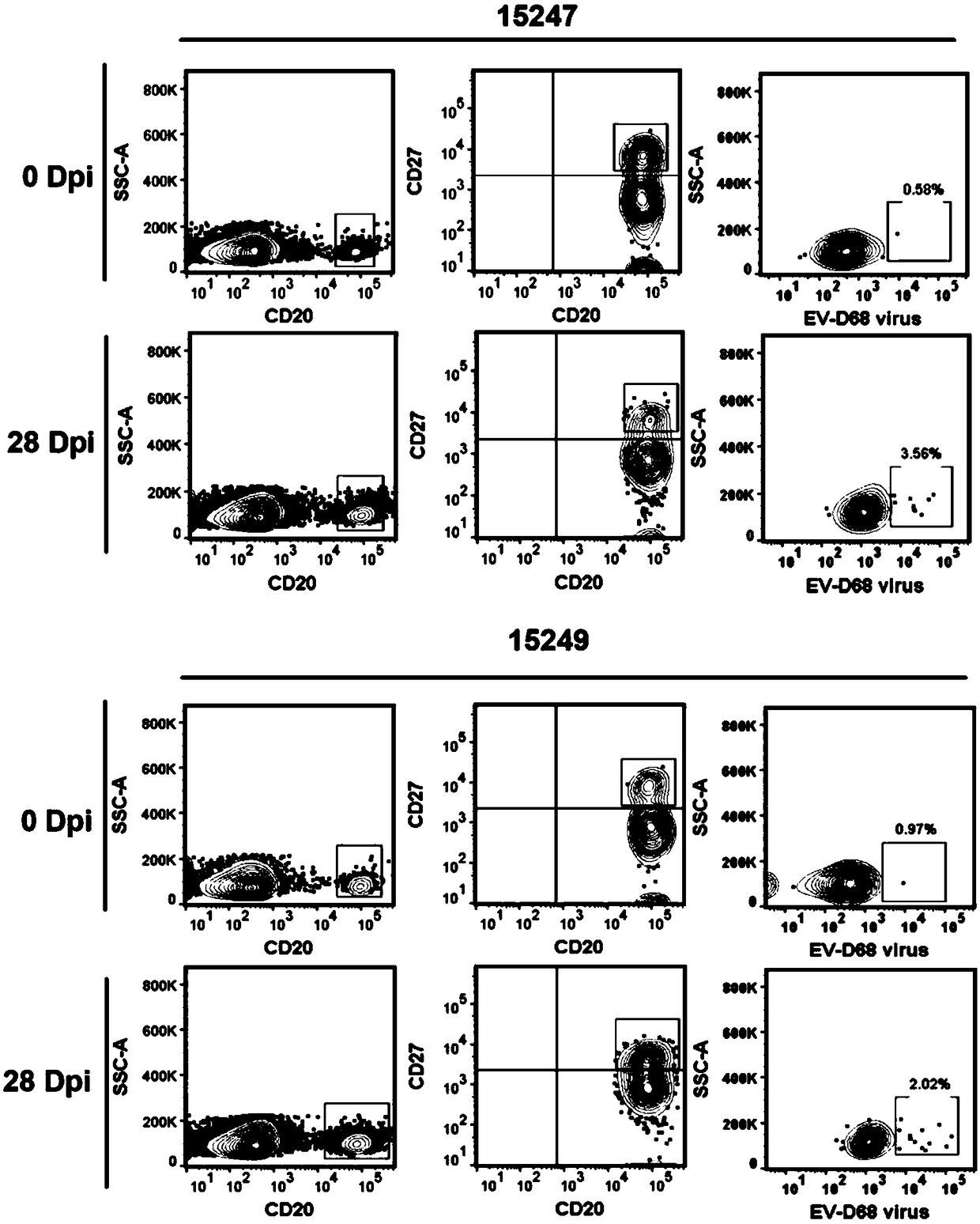
[0041] 1) All animal experiments conform to the 3R principle, namely replacement (Replacement), reduction (reduction), optimization (Refinement); animal experiments are approved by IACUC (Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee), Institute of Medical Biology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Two healthy 6-month-old rhesus monkeys, weighing 1.2kg±0.3kg, were injected with EV-D68 virus with a titer of 104.5CCID50 via upper respiratory tract nasal drip. Before the experiment, the EV-D68 virus antibody test of the two rhesus monkeys was negative.
[0042] 2) At 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, and 14 days after rhesus monkey infection, samples were taken to detect feces, nasal swabs, and blood viral load; at 0, 7, 14, 21, and 28 Daily detection of neutralizing antibody levels;
[0043] 3) Analysis of the results:...
Embodiment 2
[0210] Example 2: The monoclonal antibody A6-1 obtained in Example 1 was used to identify EV-D68 virus.
[0211] WB verification of antibody specificity
[0212] 1) Sample preparation: Add 80 μl of purified EV-D68 whole virus to 20 μl of 5× loading buffer, mix well and cook at 100°C for 5 minutes;
[0213] 2) Carry out SDS-PAGE gel protein electrophoresis of EV-D68 whole virus;
[0214] 3) After electrophoresis, take out the gel, cut off the stacking gel, and soak the separating gel in the transfer buffer; prepare a PVDF membrane of the same size as the gel, 2 filter papers, and soak in the transfer buffer; Stack neatly in the order of filter paper, PVDF membrane, gel, and filter paper, try to drive away the air bubbles during the stacking process, cover the negative plate, 25V, 1.3A and transfer the membrane for 20 minutes;
[0215] 4) Sealing: After the membrane transfer is completed, take out the PVDF membrane, put it into a glass plate, add 40ml of freshly prepared block...
Embodiment 3
[0219] Example 3: The monoclonal antibody A6-1 obtained in Example 1 was used to inhibit EV-D68 virus infection.
[0220] 1. Virus contact inhibition experiment
[0221] 1) Hela and Vero cells in the logarithmic growth phase were used, after trypsinization, the complete cell culture medium was used for pipetting and mixing, and the dilution was 4×10 5 cells / ml, add to 12-well cell culture plate according to 500 μl / well, and wait for the cells to grow into a monolayer for later use;
[0222] 2) Neutralize the virus with different dilutions of monoclonal antibodies, add the neutralized virus-antibody mixture to a 96-well cell culture plate grown into a single layer, react at room temperature for 1 hour, and wash the plate 3 times with PBS remove excess virus;
[0223] 3) Harvest the cells in the above 12-well plate, extract the total RNA of the cells, and perform quantitative detection of the virus gene copy number by qRT-PCR.
[0224] 4) Analysis of the results: From the res...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com