Additive manufacturing method for laser-assisted laser cladding
A laser cladding and additive manufacturing technology, which is applied in the directions of additive manufacturing, additive processing, and process efficiency improvement. The effect of forming quality and improving the degree of densification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
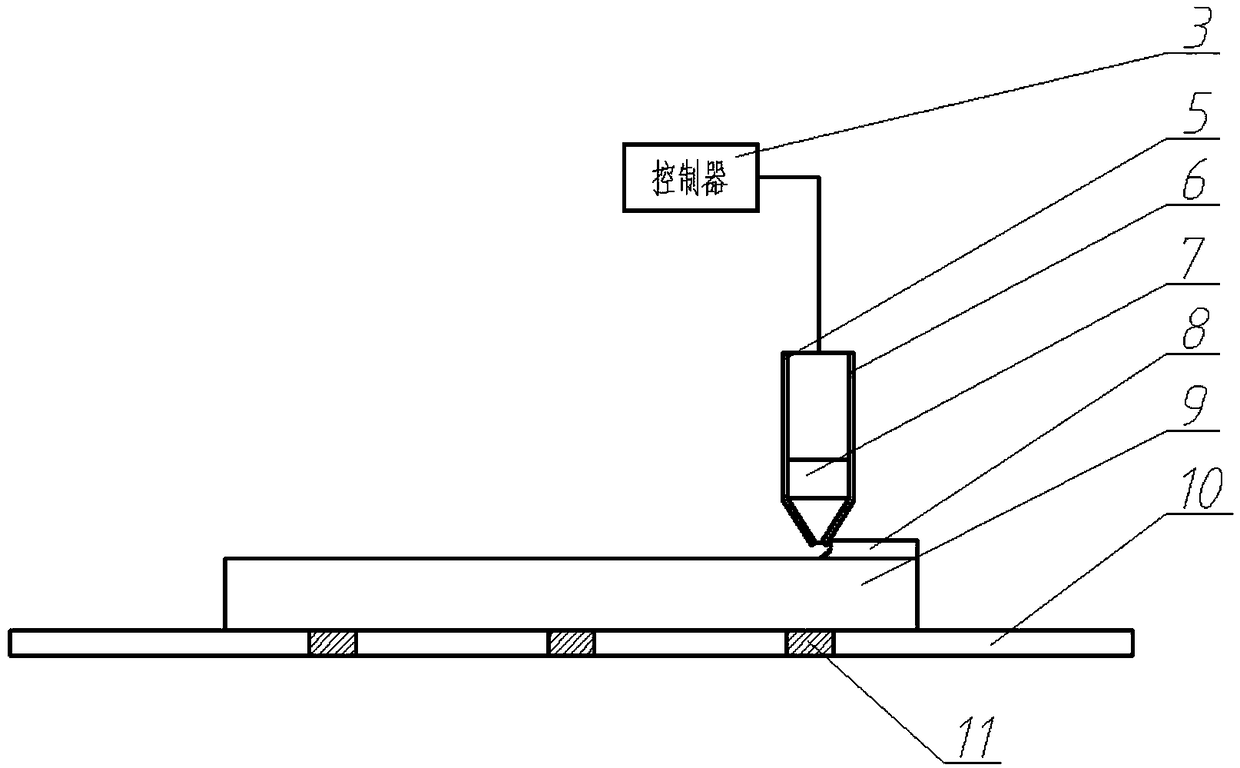
[0025] Such as figure 1 As shown, fix the TC4 substrate on the workbench with a fixture, use the laser cladding device, adopt the above laser cladding process parameters, along the Figure 4 The path shown in the plan is to carry out laser cladding on the surface of the substrate. After the first layer of cladding is completed, the above-mentioned laser cladding process parameters are still used, and the following steps are still followed: Figure 4 The planned path shown for the second layer of cladding.
Embodiment 2
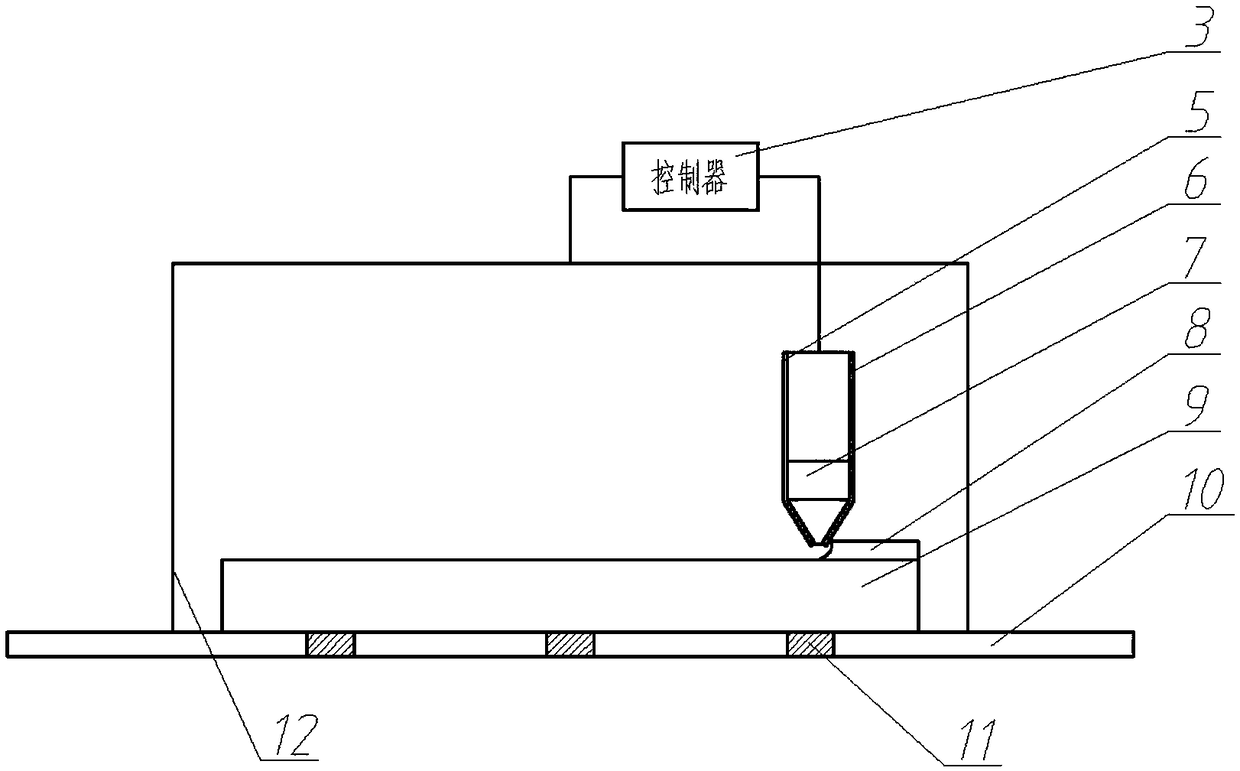
[0027] Such as figure 2 As shown, the TC4 substrate is fixed on the workbench with a fixture, the heating device is heated to 500.11°C, and kept at this temperature, and then the laser cladding device is used, and the above laser cladding process parameters are adopted, along the lines as Figure 4 The path shown in the plan is to carry out laser cladding on the surface of the substrate. After the first layer of cladding is completed, the above-mentioned laser cladding process parameters are still used, and the following steps are still followed: Figure 4 The planned path shown for the second layer of cladding.
Embodiment 3
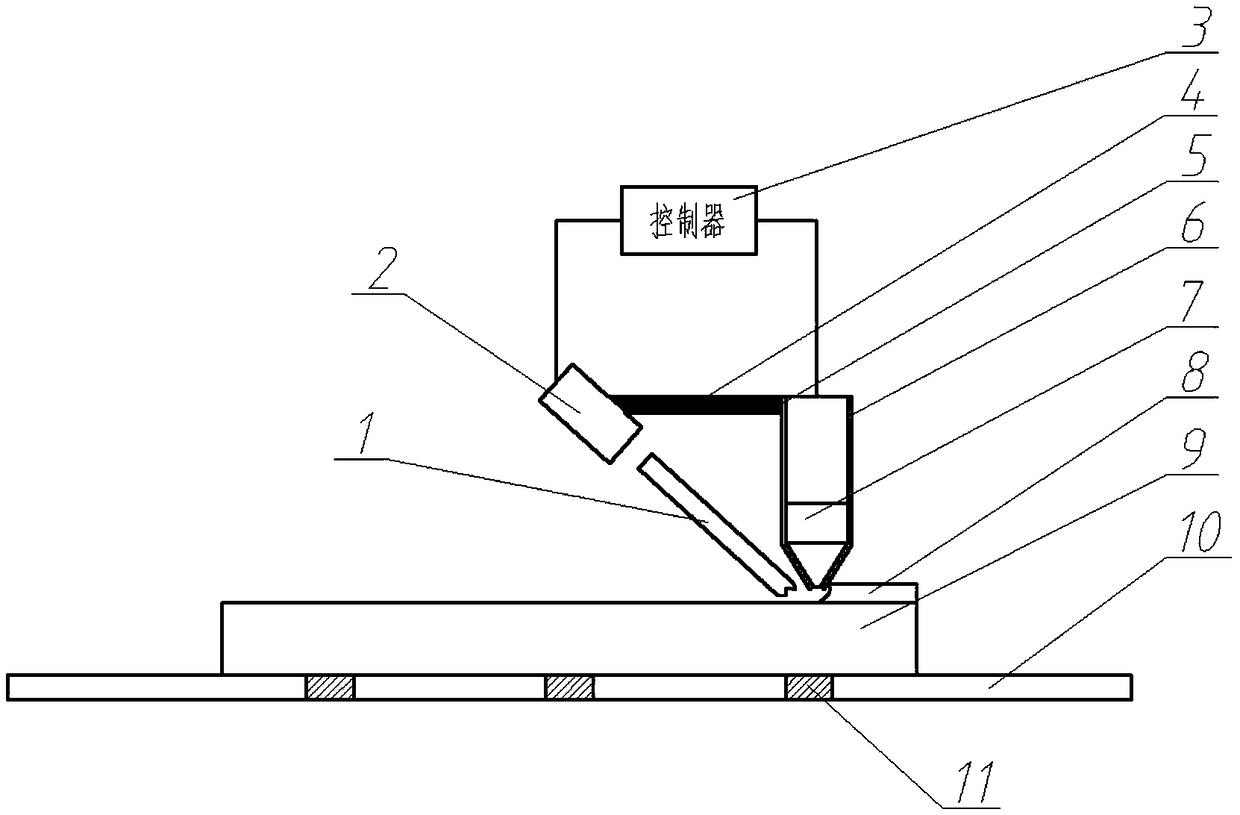
[0029] Technical scheme of the present invention, such as image 3 As shown, 1) fix the TC4 substrate on the workbench with a fixture; 2) first use a continuous laser beam to locally heat the initial position of the substrate surface to the dynamic recrystallization temperature of the substrate at 500.11 °C; 3) immediately use laser melting The cladding device adopts the above laser cladding process parameters to carry out laser cladding on the same position, and adopts the same operation steps, along the Figure 4 The pre-planned path shown is to complete the first layer of cladding; in order to ensure simultaneous laser heating and laser cladding at the same position, where the laser-heated light outlet is connected with the laser cladding head, the two parts are together during processing 4) Then use a continuous laser beam to locally heat the initial position of the cladding layer surface to the dynamic recrystallization temperature of the cladding layer 500.11 ° C; 5) Imm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com