Graphene oxide membranes and related methods
A technology of graphene and graphene sheets, applied in chemical instruments and methods, membranes, membrane technology, etc., can solve problems such as hindering technical limitations or economic constraints, not suitable for a wide range of chemical environments, and time-consuming
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
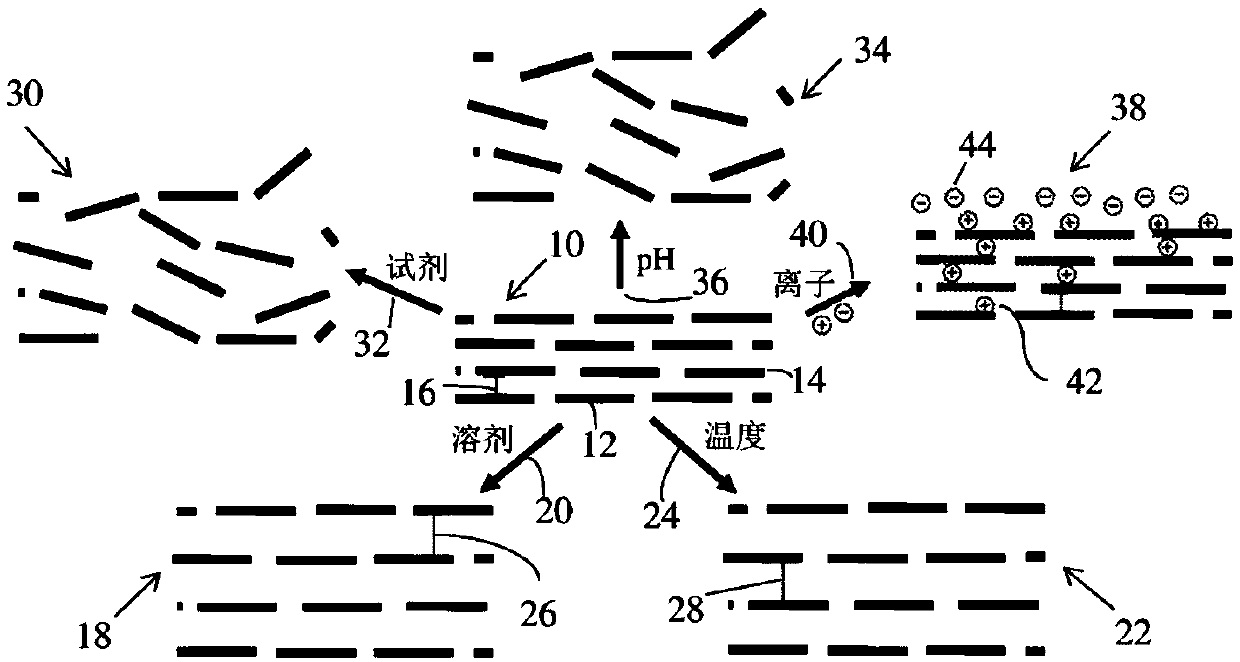
[0162] This example describes the formation and properties of cross-linked graphene oxide (ie, GO) films.
[0163] The structure of GO was studied. From these experiments, two key features were identified: first, graphene oxide films are unstable in water when the flakes are held together only by van der Waals forces; It also serves as a size exclusion mechanism for GO membranes. The interlayer spacing of GO films is determined by the attractive van der Waals forces between flakes and is affected by the humidity of the environment during film formation. For graphene oxide, the interlayer distance as measured by the 2θ peak of X-ray diffraction is typically to Unoxidized graphite exhibits ABA stacking of graphene layers and associated lower ca. layer spacing. Reduced graphene oxide also shows lower-order 2-theta peaks, but not necessarily packing as ABA. In all cases, there are no chemical bonds, either horizontally or vertically, between the individual flakes. When h...
Embodiment 2
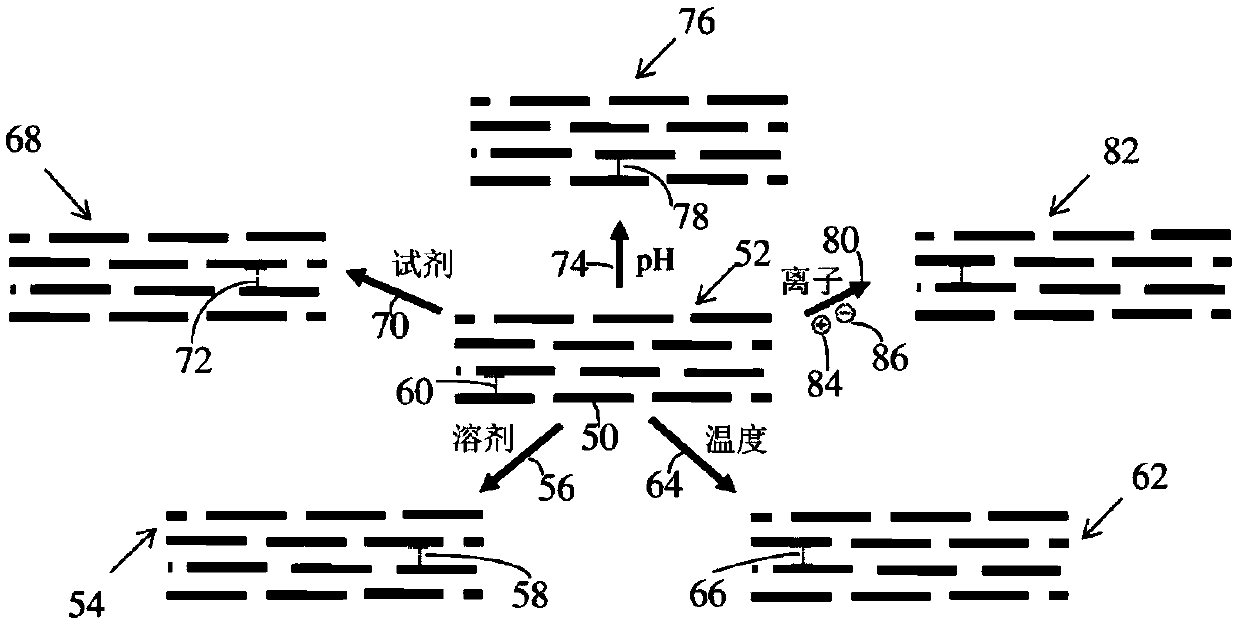
[0180] This example describes the compatibility of cross-linked graphene oxide films in a variety of environments. Crosslinked graphene oxide films were found to be compatible with chlorinated solvents, elevated temperatures in aqueous solvents, elevated temperatures in non-polar solvents, oxidizing agents, and high pH.
[0181] Durable graphene oxide films can be prepared using chemically durable linking groups. For example, these graphene oxide films can be soaked overnight in pure dichloromethane (DCM). In contrast, commercial polyethersulfone membranes degrade immediately upon contact with only a few drops of DCM.
[0182] Even in water, today's polymeric NF membranes are typically rated at 25°C with a reported maximum operating temperature of 50°C. However, the temperature and solvent tolerance of the robustly cross-linked graphene oxide films was demonstrated at elevated temperatures. Briefly, X-ray diffraction data is used to give the interplanar spacing between shee...
Embodiment 3
[0190] This example describes the formation in Example 1 and is shown in Figure 14 Highly cross-linked foam in .
[0191] Highly cross-linked foams were formed by functionalizing GO sheets with acid chlorides. Briefly, 20 mg of GO, 20 mL of dimethylformamide and 1 mL of oxalyl chloride were reacted for 4 hours. The resulting solution was dried by rotary evaporation for 30 minutes of some hydrochloric acid by-product and further diluted with 80 mL of DMF. Add 1 mL of NEt while stirring 3 to induce cross-linking. After 3 minutes, the mixture was vacuum filtered through a polyvinylidene fluoride or polytetrafluoroethylene filter and washed with methanol to remove residue and precipitate triethylammonium hydrochloride (white salt). The layered GO films have macropores.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com