In-situ preparation method for manufacturing high-entropy alloy by gradient powder feeding laser additive material
A laser additive and high-entropy alloy technology, which is applied in the field of alloy materials, can solve the problems of coarse grains, poor forming of printed parts, serious heat accumulation of printed parts, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] An in-situ preparation method for laser additive manufacturing of high-entropy alloys, comprising the following steps:
[0030] Step 1, raw material preparation, the spherical powder of Nb, Mo, W, Ti, Zr with a purity of 99.9%, the particle size of the spherical powder is in the range of 50-150 μm, and the spherical powder of Nb, Mo, W, Ti, Zr in an equal molar ratio Mixing, mixing the mixed spherical powder in a three-dimensional mixer for 3 hours, the cylinder speed is 30r / min, drying the uniformly mixed spherical powder in a vacuum dryer for 6 hours, the temperature is 90 degrees Celsius, and the vacuum degree is Relative pressure -0.95MPa, the first raw material powder is obtained after drying; dry the Mo spherical powder with a purity of 99.9% in a vacuum dryer for 6 hours, the temperature is 90 degrees Celsius, the vacuum degree is relative pressure -0.95MPa, and the drying is completed After obtaining the second raw material powder;
[0031] Step 2, additive pre...
Embodiment 1
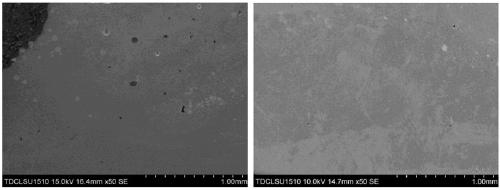
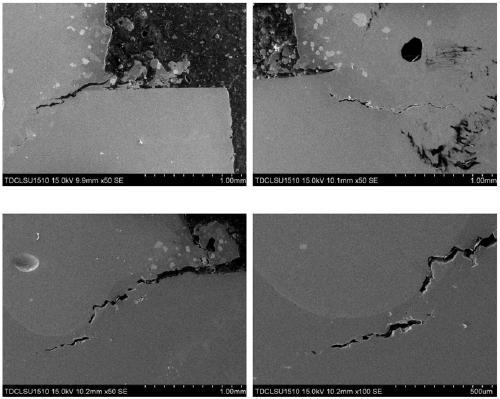
[0039] Compared with the comparative example, the macroscopic transition of Example 1 is smoother, and there is no obvious dividing line. This phenomenon indicates that the interface between the printed layer and the substrate in Example 1 forms a gentle transition in composition. It helps to reduce the thermal expansion coefficient difference on both sides of the interface between the printing layer and the substrate, thereby reducing the cracking tendency of the interface between the printing layer of the substrate and the thermal cycle during the printing process.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com