Patents
Literature
62results about How to "No stomata" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electron beam welding method for variable-section gas turbine casing
ActiveCN102416525AImprove manufacturing levelConvenient welding methodElectron beam welding apparatusSpot weldingVacuum chamber
The invention relates to an electron beam welding method for a variable-section gas turbine casing, relating to a welding method for a gas turbine casing and solving the problem that the existing welding method for a cylinder and a horizontal flange of the same section in the gas turbine casing cannot meet welding requirements for the cylinder and the horizontal flange of the variable section. The method comprises: 1, selecting an electron beam welding machine; 2, cleaning; 3, arranging the cleaned casing and a tool clamp onto a workbench in a vacuum chamber of the welding machine, assemblingthe casing onto a tool, positioning two variable-section horizontal flanges and a cylinder, and carrying out spot welding; and 4, carrying out electron beam welding. The multi-section welding is adopted for the variable-section horizontal flanges with different thicknesses, the welding of the horizontal flanges of different thicknesses for the variable-section casing can be realized through adjusting and selecting the current, voltage, gun distance and other parameters of the welding machine, and the product quality and the production efficiency can be improved greatly. The method can be applied in welding of the variable-section gas turbine casing.
Owner:HARBIN TURBINE
Alloy coating for crystallizer surface laser cladding and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to the field of laser cladding, in particular to an alloy coating for crystallizer surface laser cladding and a preparation method thereof. The componenst of the alloy coating are prepared according to the mechanical property and effectiveness condition of the crystallizer and the characteristics of crystallizer surface laser cladding. The alloy coating is prepared from nickel-based self-melt alloy powder comprising the following elements in percentage by mass: Ni 55-57, Cr 16-19, W 8-10, Mo 8-10, Al 0.8-1.0, Ti 2.5-3.5, C 0.2-0.3, Si 2.5-3.5 and B 2-2.5. After being cladby laser, the crystallizer surface has a high-quality coating, thereby meeting the requirements of a crystallizer on a basic performance of quick heat conduction on one hand and increasing the wear resistance and hot erosion resistance of the crystallizer surface.
Owner:SIASUN ROBOT & AUTOMATION LIMITED BY SHARE
Equipment and method for casting plurality of aluminum alloy ingots with small diameters by using vertical direct chilling casting (DC)
The invention provides equipment and a method for casting a plurality of aluminum alloy ingots with small diameters by using vertical direct chilling casting (DC) and relates to the equipment and the method for casting the aluminum alloy ingots, which aim to solve the problems of low consistency of metal temperatures, low water cooling uniformity and high possibility of ingot suspension or tension fracture and flow running in each crystallizer in the process of casting the aluminum alloy ingots with the small diameters by the conventional technology for casting the plurality of aluminum alloy ingots with the small diameters by using the vertical DC. The method comprises the following steps of: communicating all branch outlets on runners with a plurality of upper end inlets of hot top caps correspondingly one by one; communicating the lower end outlet of each hot top cap with a crystallizer inlet of the crystallizer, wherein the distances between a flow storage slot and the runners of all crystallizers are same; heating a heat preserving sleeve to the temperature of between 100 and 150 DEG C; opening the outlet of a smelting furnace, feeding molten aluminum alloy into all the crystallizers through the runners, and performing water cooling; stopping for 5 to 10 seconds after the liquid level of the molten aluminum alloy in the runners reaches a preset position; and moving an ingot guiding device downwards. The surface of each ingot is smooth, does not have cracks and has small segregation tumors, and each ingot does not have air pores, is not loose and has small grains.
Owner:HARBIN ZHONGFEI NEW TECH CO LTD
High-density zinc oxide based target and preparation method thereof
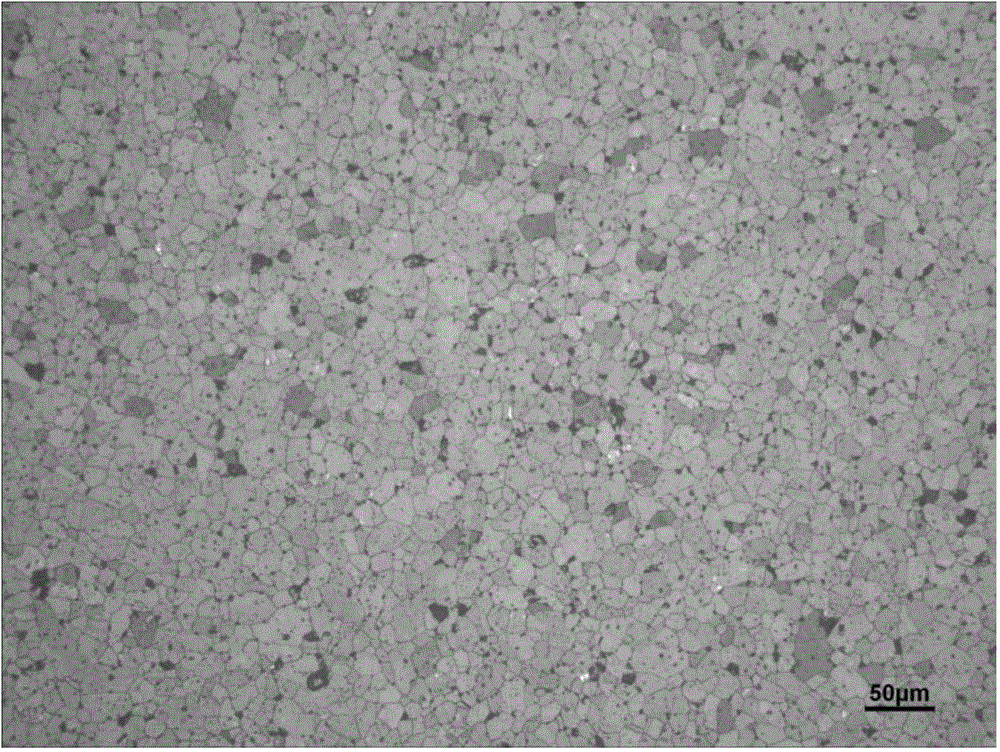
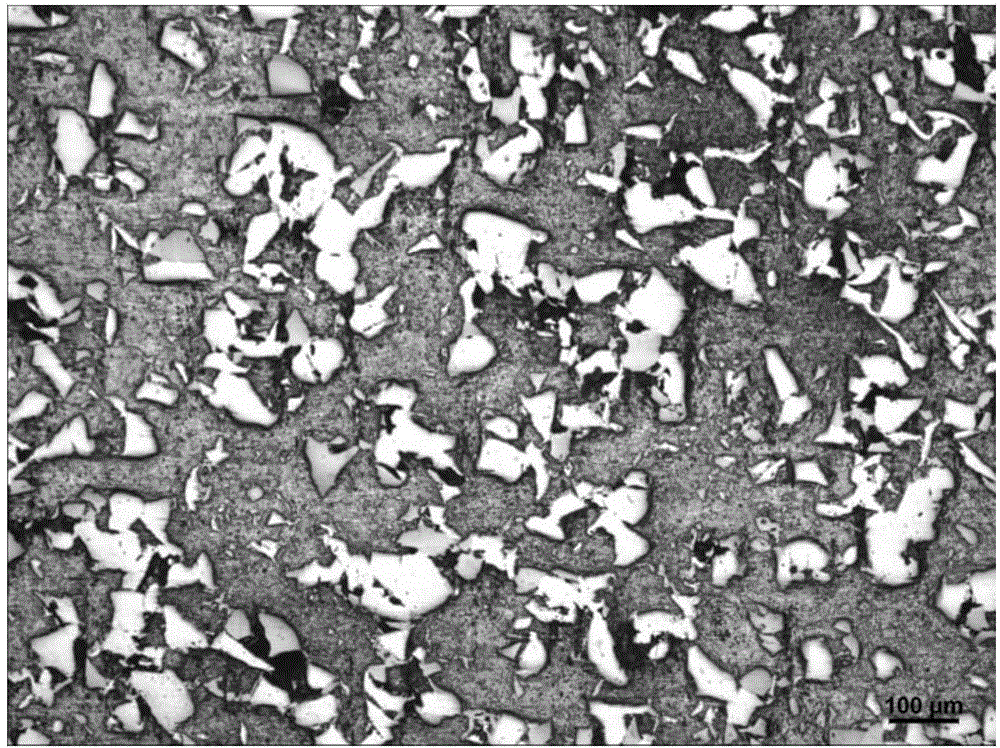
The invention discloses a high-density zinc oxide based target and a preparation method thereof. The method sequentially comprises the following steps: mixing materials: adding a binder and water into raw materials, mixing uniformly, so as to obtain uniform slurry, and carrying out drying and powdering on the slurry, so as to obtain dry powder particles with uniform particle size distribution; carrying out binder removal and degassing: loading the dry powder particles into a package of a corresponding size, and carrying out binder removal and degassing treatment; carrying out hot isostatic pressing: soldering and sealing the package which is subjected to binder removal and degassing, and then, carrying out hot isostatic pressing treatment; annealing: carrying out annealing treatment on package removed ingot blank. The zinc oxide based target obtained by adopting the method has the advantages that the relative density is not lower than 99% of theoretical density, the density is uniform, the average crystal grain size is not greater than 30 microns, and the zinc oxide based target is free from air pores and loosening.
Owner:ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY & MATERIALS CO LTD
Chromium-aluminum-silicon alloy target material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104419859AHigh densityNo stomataVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingChromiumHot isostatic pressing
The invention provides a chromium-aluminum-silicon alloy target material and a preparation method thereof. The alloy target material is prepared from the following components in atom percentage: 5-75 percent of chromium, 10-90 percent of aluminum and 1-20 percent of silicon. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing alloy powder, carrying out cold isostatic pressing treatment, degassing, carrying out heat isostatic pressing treatment and mechanically processing. The chromium-aluminum-silicon alloy target material has the advantages of high compactness, no pores or segregation, uniform texture, fine crystalline grain and the like, and is suitable for sputtering coatings of multiple cutters and molds.
Owner:北京安泰六九新材料科技有限公司 +1
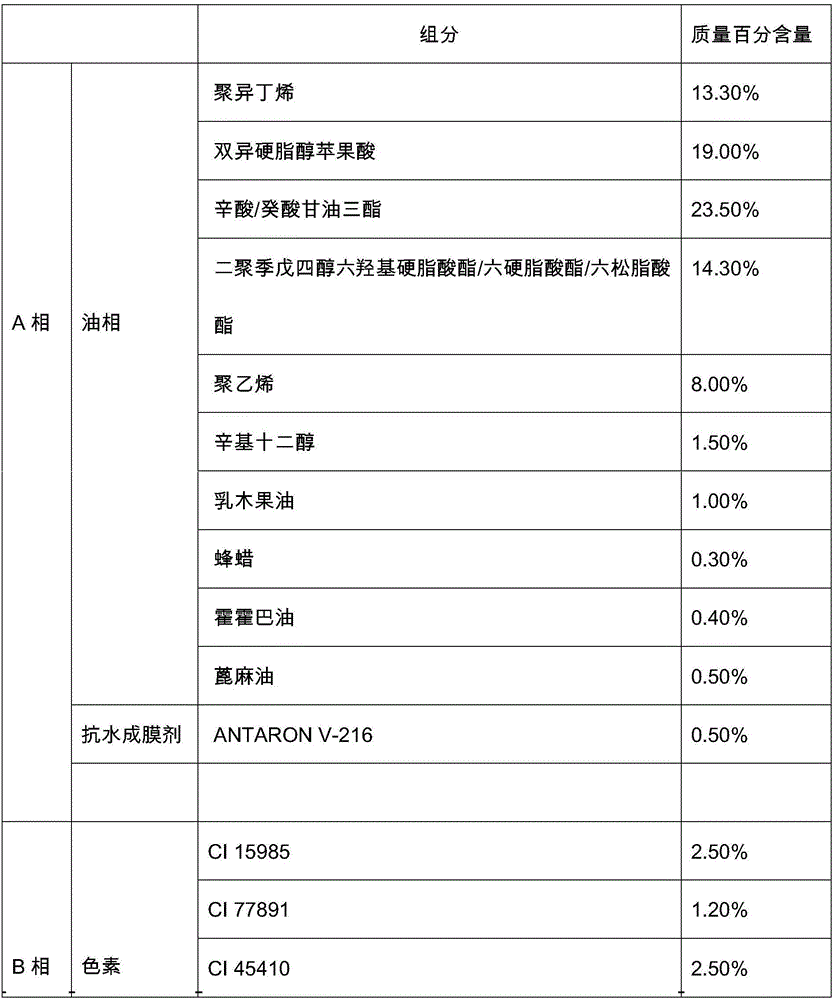
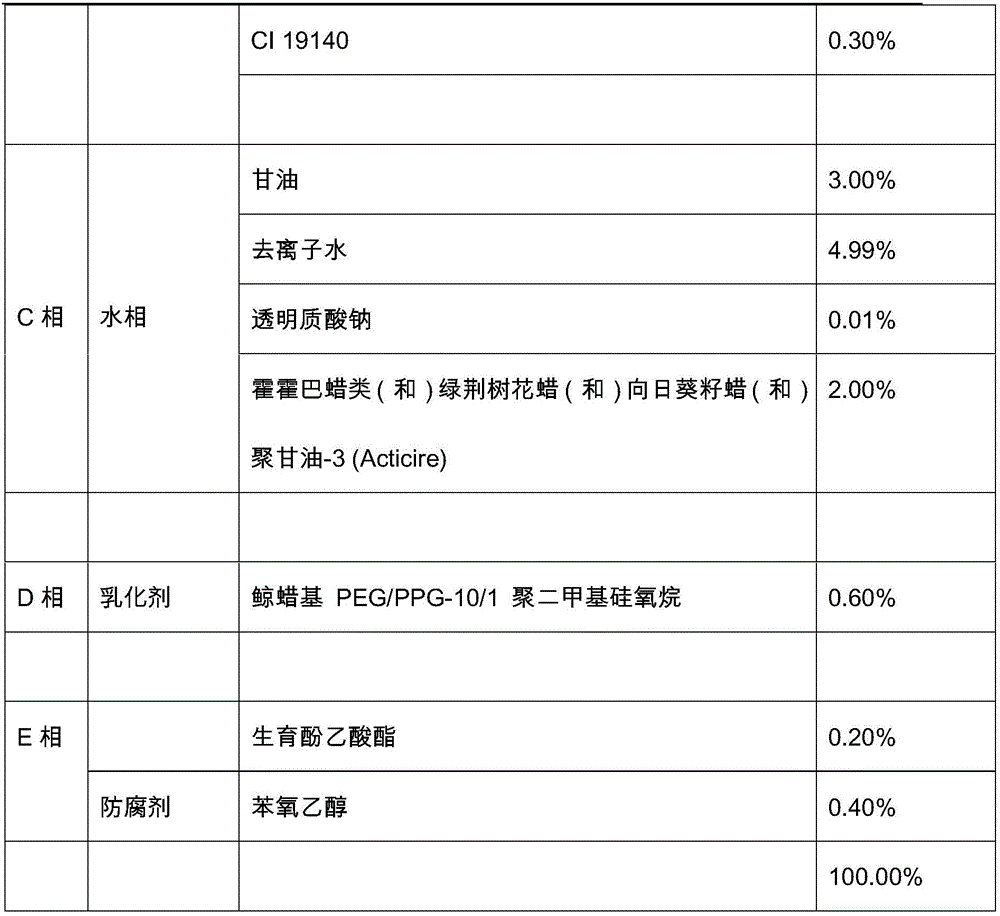
Water-rich lipstick and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a water-rich lipstick which comprises the following components by weight percent: 1-10% of an emulsifier, 1-25% of water-phase component and 65-98% of oil-phase component, wherein the lipstick can further be added with pigments, pearlescent components and water-soluble active components as required. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the lipstick. The water-rich lipstick provided by the invention is soft and smooth in paste, bright in gloss, beautiful and attractive in color, contains natural flowing water capable of effectively reducing lip lines, deeply moisturizing lips, preventing the lips from water loss and keeping the lips constantly moist and lustrous, and suitable for people with different skin colors and different ages.
Owner:广州品赫化妆品有限公司
Wear-resisting and high-hardness flux core wire
InactiveCN107252994AHigh hardnessHigh strengthWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaSilicon alloyRare earth
The invention discloses a wear-resisting and high-hardness flux core wire. The wear-resisting and high-hardness flux core wire is composed of a flux core and a low-carbon cold-rolling steel tape sheath wrapped on the outer side of the flux core. The flux core comprises, by weight, 20-25 parts of low-carbon ferrochromium, 1.5-3 parts of titanium powder, 1-2 parts of nickel powder, 5-8 parts of calcium-silicon alloys, 2-4 parts of magnesium-aluminum alloys, 3-5 parts of electrolytic manganese, 1-2 parts of ferromolybdenum, 2.5-4 parts of ferroniobium, 1-2 parts of ferrovanadium, 3-5 parts of rare earth iron alloys, 3-5 parts of carbonate, 3-4 parts of graphite, 120-150 parts of iron powder, 0.5-1.5 parts of tungsten powder and 2-4 parts of calcium fluoride. The wear-resisting and high-hardness flux core wire has good welding performance, deposited metal tissue is compact, air holes and cracks are avoided, combination with base metal is good, performance is stable, and deposited metal has good wear resistance, corrosion resistance, high hardness and other performance.
Owner:天长市通联焊业有限公司
Process for surfacing stainless steel sealing face on ductile cast iron valve base
InactiveCN102785004AImprove work efficiencyStrong heat resistanceArc welding apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesButt weldingGas metal arc welding
The invention discloses a process for surfacing a stainless steel sealing face on a ductile cast iron valve base. The process includes firstly preheating and cleaning up the valve base; adopting pulse gas metal arc welding; performing full-automatic welding, pulsed direct current, anode reversed connection, and protection through argon and carbon dioxide mixed gas, wherein the flow is 18-25L / min and the welding speed is 8-15cm / min; cladding a stainless steel welding cladding with the thickness of 2.5-6mm at a to-be-welded position of the valve base after the welding; and then placing the valve base at the temperature of 350-400 DEG C for 2 hours. The process has the advantages that the welded sealing face is reliable in strength and stable in performance, and has no defects such as air holes and cracks; the utilization rate of welding materials is high, the process is simple, convenient to operate, and capable of achieving automation; and compared with spinning, boxing and stainless steel ring embedding processes, a plurality of processes such as marking, blanking, plate rolling, butt welding and spinning are omitted, and the process is suitable for automatic welding and batch production.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU ZHENGDIE VALVE CO LTD
High-carbon high-chrome high-vanadium wearable surfacing self-shielded flux-cored wire
InactiveCN105798484AHigh hardnessImprove wear resistanceWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaManganeseFerrosilicon
The invention discloses a high-carbon high-chrome high-vanadium wearable surfacing self-shielded flux-cored wire. According to the flux-cored wire, the core is prepared from the following components in mass percentage: 5-25% of high carbon ferro-chrome, 30-60% of chromium carbide, 15-35% of ferrovanadium, 0.5-5% of ferromolybdenum, 1-4% of electrolytic manganese, 1-4% of ferrosilicon, 1-4% of ferroboron, 1-5% of graphite, 1-5% of aluminium magnesium, 0-3% of zircon sand, 0-4% of marble, 0-3% of barium fluoride, 0-5% of barium carbonate, 0-3% of sodium fluosilicate, and 0-5% of fluorite; the skin of the flux-cored wire is a mild-carbon steel strip, the diameter is 1.6-4.0mm, and the counterweight ratio is 44-53%. According to the flux-cored wire disclosed by the invention, the rigidity and wearability of surfacing alloy can be greatly improved and the toughness of the surfacing alloy cannot be reduced; and the prepared surfacing alloy can be widely applied to surfacing repair of parts with severe low and intermediate stress abrasion at low temperature, intermediate temperature and high temperature and manufacture of new parts.
Owner:GRIPM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Process for clearing metal grinding materials for derusting by using special steel wires for steel wire rope
The invention discloses a process for clearing metal grinding materials for derusting by using special steel wires for a steel wire rope, which is carried out according to the following steps: (1), disassembling the steel wire rope into single steel wires and classifying according to the diameters; (2), cutting the steel wires into cylindrical steel wire cutting segments by using a steel wire segment cutting machine; (3), putting the cylindrical steel wire cutting segments into a round casting machine, and repeatedly and circularly casting for 30-100 minutes at a speed of 75meter / second until the cutting segments are round to form steel grits; (4), carrying out roundness separation on the steel grits in a round separation machine; (5), screening the steel grits subjected to the screening by the round separation machine to screen scraps; and (6) packaging and putting in storage. With the adoption of the process method, the produced metal grinding materials have high quality and long service life and are suitable for surface clearing and derusting of various workpieces.
Owner:TIANJIN XINCHAO AST STEEL & ABRASIVE FOUNDRY
Gypsum model precise casting technology
InactiveCN107812888AReduced risk of crackingReduce casting costsFoundry mouldsFoundry coresAbnormal tissue growthPorosity
The invention provides a gypsum model precise casting technology and relates to the technical field of casting technologies. The gypsum model precise casting technology comprises the following steps that gypsum slurry is prepared; grouting is carried out, a box frame in which a module is installed is placed into a grouting chamber, then vacuumizing is carried out to 0.05-0.06 MPa, and the slurry is stably poured into the box frame; roasting is carried out, step temperature rise is adopted, and heat is preserved for a certain period of time in each section, so that the temperature of the innerwall and the temperature of the outer wall are consistent; casting and casting cleaning are carried out; and after a gypsum model is dried completely, gravity casting is carried out, and for large thin-wall precise castings, great careful clearing, repairing and correcting are carried out after casting. According to the gypsum model precise casting technology, the crack risk of the castings can bereduced greatly, size precision is high, the casting cost is low, the casting quality is good, and defects of air holes, shrinkage holes, shrinkage depression, rising and the like are avoided.
Owner:泰兴市长江密封材料有限公司
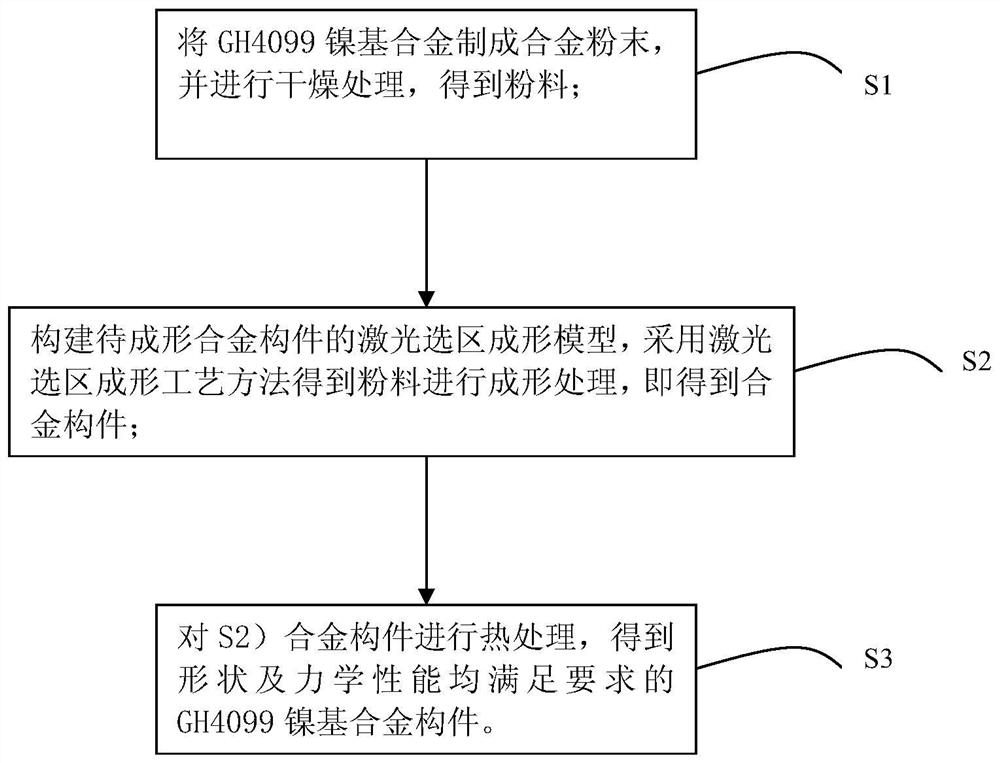
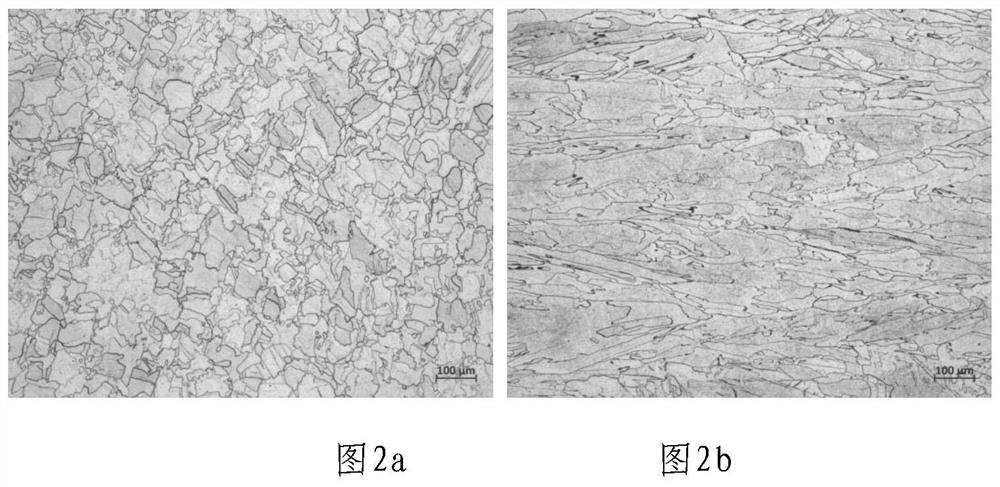
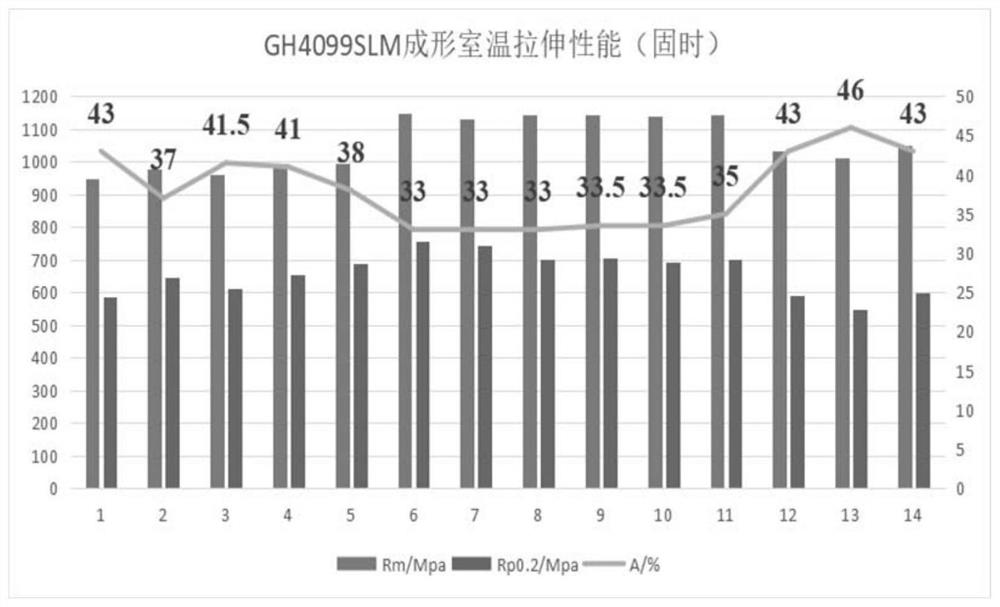
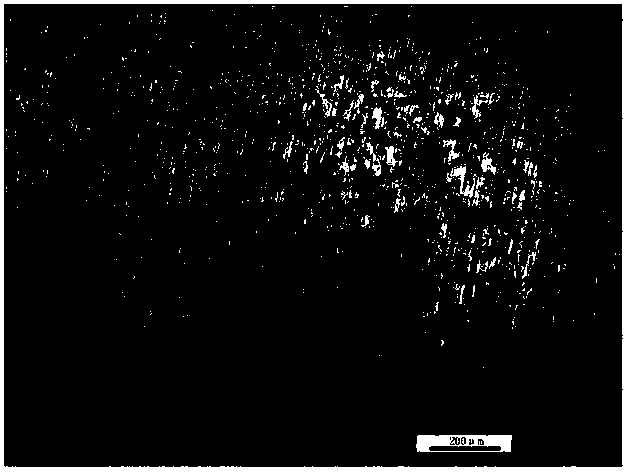
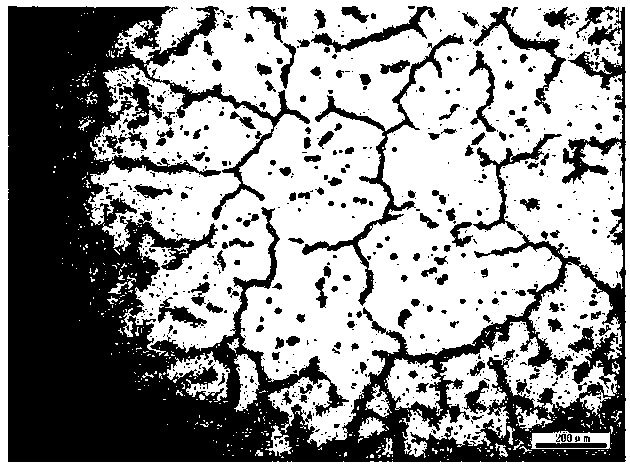
Selective laser melting forming process for GH4099 nickel-based alloy element
ActiveCN112589115AHigh precisionIncreased complexityAdditive manufacturing apparatusSelective laser meltingManufactured material
The invention belongs to the technical field of metal additive manufacturing and high-temperature alloys, and particularly relates to a selective laser melting forming process of a GH4099 nickel-basedalloy element. The preparation method includes the steps that GH4099 nickel-based alloy is prepared into alloy powder, drying treatment is conducted, and powder is obtained; the powder is subjected to selective laser melting forming, and an alloy element is obtained; and the alloy element is subjected to heat treatment, and the GH4099 nickel-based alloy element with the shape and the mechanical property meeting requirements is obtained. According to the selective laser melting forming process of the GH4099 nickel-based alloy element, the raw material powder is molten layer by layer through high-energy laser beams, so that element manufacturing with higher precision and higher complexity is achieved, and rapid manufacturing and direct manufacturing of precise elements are achieved. The forming quality of printed components can be guaranteed, a structure is uniform, and the defects of pores, cracks, unmelted particles and the like are avoided. The comprehensive mechanical property of the high-temperature alloy printed component reaches a forging level, so that the comprehensive mechanical property of the high-temperature alloy element is improved, and the application range is expanded.
Owner:BEIJING XINGHANG MECHANICAL ELECTRICAL EQUIP +1
Manufacturing technology for rare earth-magnesium alloy
The invention belongs to the fields of metal materials and metallurgy, aims to solve the problems that impurities of alloy are hard to separate, ingredients are nonuniform, the utilization rate of rare earth element is low, precipitated rare earth phases are nonuniform, the segregation is more, and effects for the quality is great by adopting the manner that alloying, rare earth process, and casting are conducted in a pot during a conventional manufacturing technology process, and provides a manufacturing technology for rare earth-magnesium alloy. According to the manufacturing technology, conducting adding, refining, and degassing with hexachloroethane degassing agent of alloy element in a melting pot; and pouring into a second pot after standing for 30 min, adding rare earth, and standing and casing. A manufactured bar material has uniform and stable metallographic structure and clear crystal boundary; the product is without pore, shrinkage cavity and cold shut, and the surface is smooth and without rugosity; the purity, ingredients, and equilibrium of physical properties of the product are guaranteed, the grain size of the alloy is refined, very stable dispersed phase is precipitated, and the rigidity and the decay resistance of texture are improved; therefore, product performances are allowed to be superior to an ordinary alloy standard.
Owner:孝义市东义镁业有限公司 +1
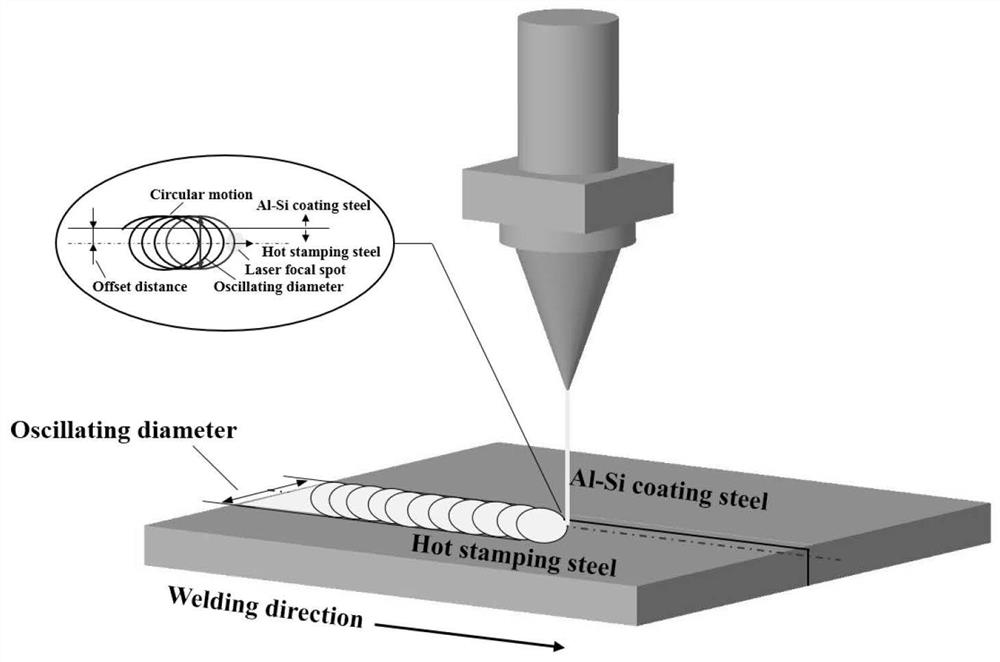
Manufacturing method of aluminum-silicon coated steel/high-strength hot-formed steel composite steel part
InactiveCN111843214AFirmly connectedImprove mechanical propertiesLaser beam welding apparatusLight spotGalvanometer
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of an aluminum-silicon coated steel / high-strength hot-formed steel composite steel part. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps of fixingan aluminum-silicon coated steel plate and a high-strength hot-formed steel plate on a workbench in a splicing manner, and enabling the two steel plates to be in close contact; under the protective atmosphere, carrying out laser galvanometer welding on the butt joint position of the two steel plates, melting and solidifying at a butt joint position, thereby forming a high-quality weld joint; carrying out hot stamping on the welded steel plate to obtain an aluminum-silicon coated steel / high-strength hot formed steel composite steel part, wherein the protective atmosphere contains 5-100 vol.% of oxidizing gas, and during galvanometer welding, a moving path of a light spot is controlled to deviate by 0-3 mm towards one side of the high-strength hot-formed steel plate. According to the laserwelding method of the aluminum-silicon coated steel / high-strength hot-formed steel, under the condition of not removing an Al-Si coating, good connection between the Al-Si coated steel and other high-strength hot-formed steel can be achieved, the mechanical property of a welding joint is improved, and formation of delta ferrite in a welding seam is reduced;
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for laser cladding Ni-based alloy+B4C wild phase on Q550 steel
InactiveCN103924238AImprove performanceIncrease productivityMetallic material coating processesSlagRoom temperature
The invention discloses a method for laser cladding Ni-based alloy+B4C wild phase on Q550 steel. The method comprises the following steps: grinding the surface of Q550 steel to remove greasy dirt and rust; cladding an enhancement layer on the surface of Q550 steel by using an optical fiber laser, wherein the technical parameters are as follows: the power is 2.0-4.0Kw, the cladding speed is 10-50cm / min, the laser heat source pattern can be circular spot with diameter being 5mm or rectangular spot with specification of 1.5mm*17mm; laser cladding the surface in forms of circular and rectangular spots, wherein the powder feeding rates are respectively 20-100g / min and 30-150g / min; and removing slag from the surface of the cladding layer, cooling to room temperature and processing chemically. The method disclosed by the invention realizes firm metallurgical combination of the Q550 steel and wild phase alloy powder, so that the method is high in production efficiency and convenient and agile to operate. The obtained cladding layer has fine texture, is free of cracks, pores and slag and also has excellent performance.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for performing surface modification on metal by ultrasonic nano-welding
ActiveCN102500912ATake full advantage of enhancementsGood interface wettabilityNon-electric welding apparatusMechanical bondMetal substrate
The invention relates to a method for performing surface modification on a metal by ultrasonic nano-welding and belongs to the technical field of nanomaterials. The method comprises the following steps: cleaning a to-be-treated region of the surface of the metal, coating a nanopowder material on the metal surface after cleaning, and performing ultrasonic nano-welding process on the nanopowder material on the metal surface to obtain a modified metal surface. The method is simple to operate and has controllable welding parameters. The nanomaterial and the welding region of the metal substrate form a local miscible body, leading to good interface infiltration, which enhances mechanical bonding effect and gives full play to reinforcement function of the nanomaterial. The nanomaterial is distributed densely and uniformly on the metal surface, and the surface is smooth and clean and has no cracks or air hole.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Detecting tools for combustion turbine transitory section renovation technique and renovation technique thereof
The invention provides detection equipment for gas turbine intermediate parts repair art which includes installation plate 1, straight pin 2, column 3, feeler gage main body 4, four feeler gage paws 5 and four bolts 6, one end of column 3 is fixed on the installation plate 1, and the other end is the positioning benchmark of feeler gage main body 4, the installation plate 1 is equipped with straight pin 2, four feeler gage paws 5 is fixed on the feeler gage main body 4 using hex bolts 6, its distribution angles is same and corresponding with the two distribution angles of intermediate part inlet gas end. The invention also provides repair art of intermediate parts, the process is: laser fusion casting: fusion pool diameter is 2~5mm, depth is 0.1~0.2mm, the heating time is 0.001 ~0.1 seconds, laser power is 500 ~ 2000W, laser scanning speed is 2~20mm / s; proofing shapes with jack; detecting with special equipment; spraying thermal barrier coatings on the inwall. The advantages of the process are: strong adaptability, simple operation, strong regulation, short repair cycle and less cost.
Owner:SHENYANG DALU LASER TECH
Solder for soldering different-component W-Cu alloy, preparing method and soldering method thereof
ActiveCN105171270AAccelerated corrosionEasy to processWelding/cutting media/materialsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesSolderingCopper
The invention discloses a solder for soldering a different-component W-Cu alloy, a preparing method and a soldering method thereof. The mass percents of the components of the solder are described as follows: 10.0-16.0% of Mn, 0.5-3.5% of Co, 1.0-5.0% of Ni, 1.0-4.0% of Ti, 0.2-0.6% of Si, 0.1-.03% of B, and the balance of Cu. The soldering temperature of the copper-based solder is 1000-1050 DEG C. Moderate fusing temperature of the solder and high fusion uniformity of the solder are realized. Through adding related beneficial elements, good wetability and high metallurgical miscibility of the solder to the W-Cu alloy are realized. An obtained solder joint has high strength and high corrosion resistance and can be totally applied in a complicated environment. The solder is an economical solder with high comprehensive performance. A prepared copper-based solder foil has functions of facilitating diffusion and interface reaction between alloy elements in a soldering connecting process, improving wetting and spreading capabilities of the solder on the surface of the W-Cu alloy, and facilitating forming of a compact solder joint.
Owner:无锡腾达海川新材料有限公司
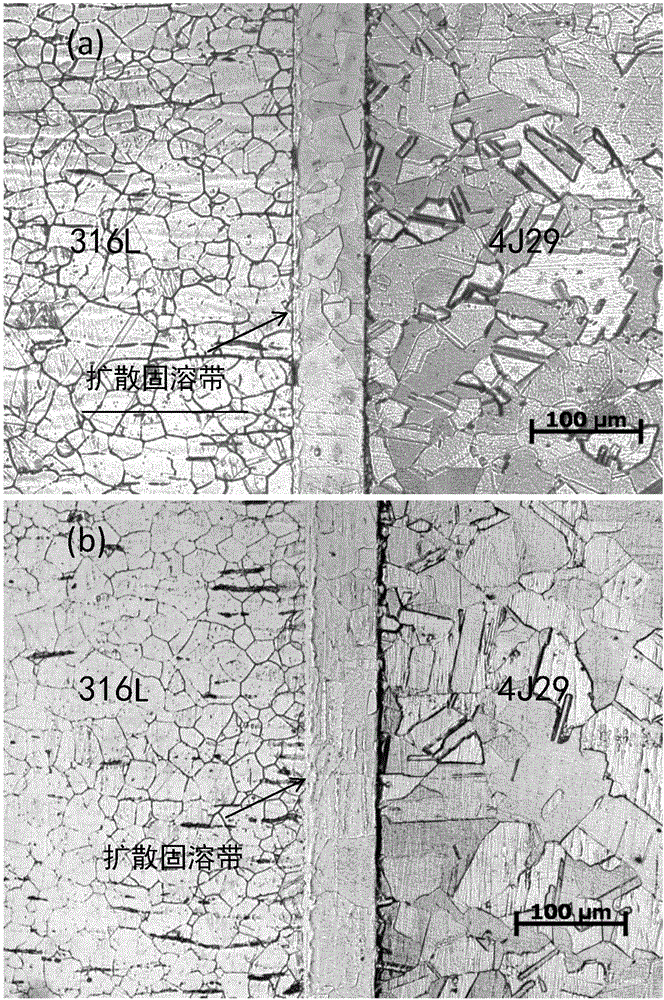
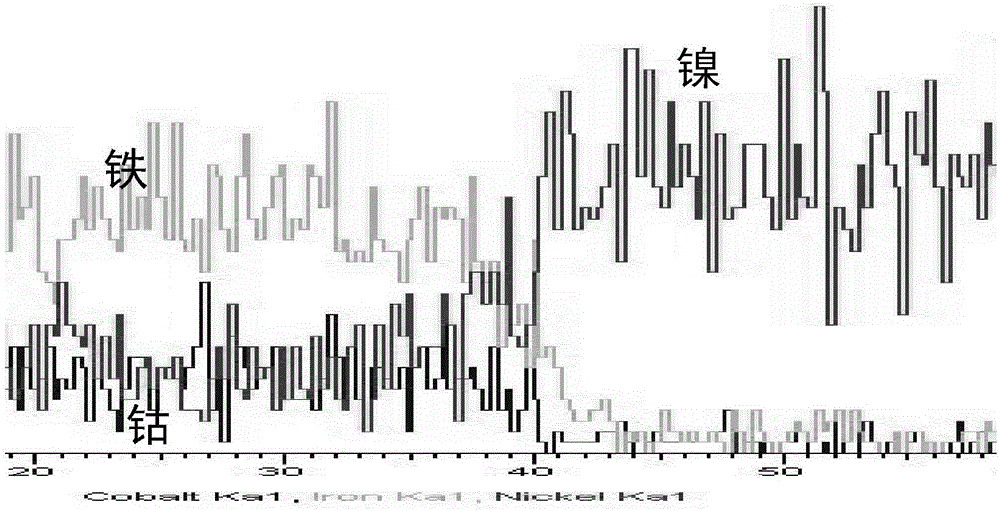
Diffusion welding method for stainless steel and Kovar alloy dissimilar metal
ActiveCN106271015AImprove tensile propertiesEasy transitionWelding/soldering/cutting articlesNon-electric welding apparatusSurface cleaningWeld seam
The invention discloses a diffusion welding method for stainless steel and Kovar alloy dissimilar metal and belongs to the field of dissimilar metal welding. The diffusion welding method comprises the following specific steps: (1) sample surface cleaning: grinding a surface to be welded and performing ultrasonic cleaning on acetone; after the completion of cleaning, wiping the surface to be welded with alcohol and blow-drying or airing to obtain cleaned stainless steel, Kovar alloy and a nickel foil; (2) sample stacking: alternately stacking the cleaned stainless steel, Kovar alloy and nickel foil obtained in the step (1); (3) welding: putting a stacked sample between an upper pressing head and a lower pressing head of a vacuum hot pressing furnace, maintaining the good axial centering property between the sample and the pressing heads and performing pressure relief, wherein the pre-pressure is 15-30 MPa; vacuumizing the vacuum hot pressing furnace to (2-5)*10<-1> Pa; raising the temperature at a speed of 5-20 DEG C / min, pressurizing after the temperature inside the furnace is raised to a certain temperature, preserving heat and pressure for a certain time and performing diffusion welding; after heat preservation, performing pressure relief, firstly slowly cooling and then cooling along with the furnace. A welding seam has the advantages of being high in compactness, good in plasticity, free from air hole and crack and the like.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for narrow-gap laser welding with filler wires for superconducting coil box
InactiveCN103252578ATo achieve weldingTo meet the welding requirementsLaser beam welding apparatusNuclear fusionSuperconducting Coils
The invention discloses a method for narrow-gap laser welding with filler wires for a superconducting coil box. The method is used for a superconducting coil box of a nuclear fusion reactor, and narrow-gap laser welding with filler wires is performed for a large superconducting coil shell by the aid of laser, so that the whole coil box is sealed. The method includes the steps: firstly, arranging a narrow-gap V-shaped groove on a part to be welded and cleaning weld joints and surfaces by the aid of acetone; secondly, fixedly placing the part to be welded on a bearing fixture and a profiling fixture and continuously welding truncated edges by tack welding and laser through a laser machining head driven by a robot; and finally, performing laser welding with multilayer hot filler wires for groove weld joints to integrally seal the coil box. Layers are welded in a symmetrical and alternant welding sequence. The method solves the sealing problem of a superconducting coil in a first international thermonuclear experimental reactor plan of China, and an effective method for welding an ultra-large structure is provided.
Owner:SHENYANG SIASUN ROBOT & AUTOMATION
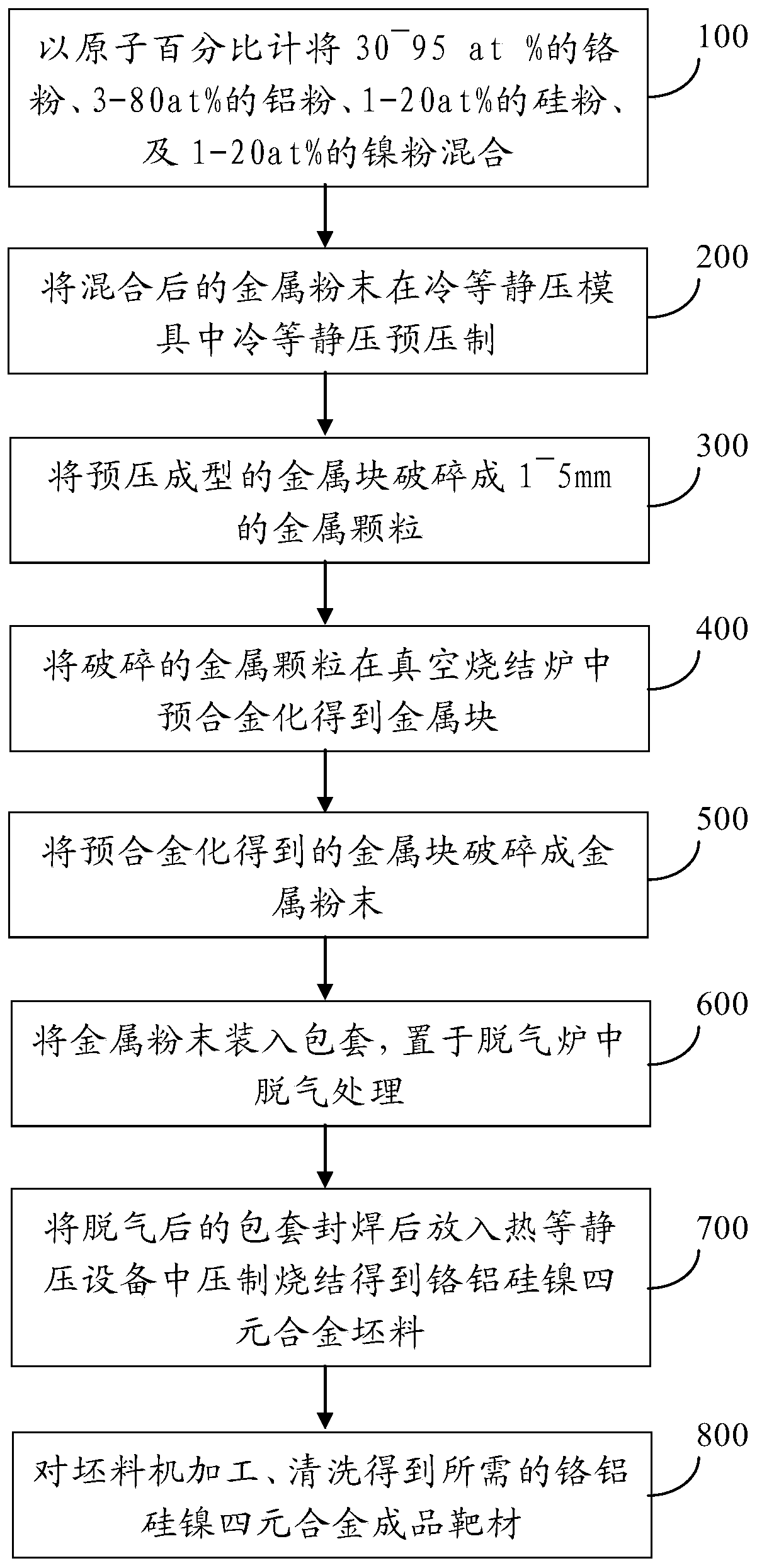
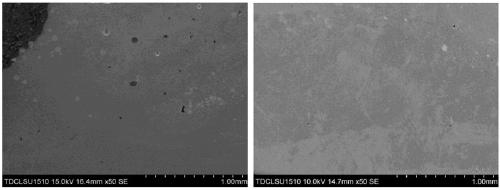
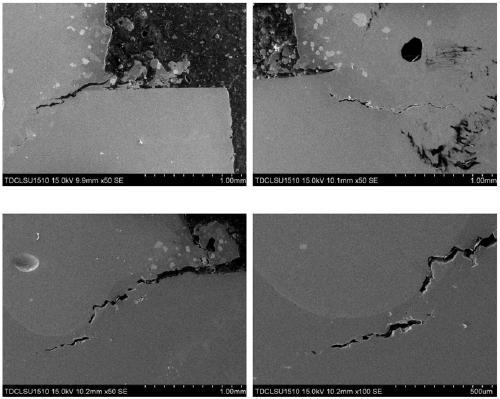
Chromium, aluminum, silicon and nickel quarternary alloy target material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110257781AHigh densityNo stomataVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSilica fumeHot isostatic pressing
The invention provides a chromium, aluminum, silicon and nickel quarternary alloy target material which is prepared from the following components in percent by atom: 30-95at% of chromium, 3-80at% of aluminum, 1-20at% of silicon and 1+20at% of nickel. A preparation method of the chromium, aluminum, silicon and nickel quarternary alloy target material provided by the invention comprises the following steps: first uniformly mixing chromium powder, aluminum powder, silicon powder and nickel powder in proportion; pre-pressing the mixture by isostatic cool pressing; then crushing a press cake and pre-alloying the press cake in a vacuum state; carrying out encapsulating, degassing and hot isostatic pressure sintering; and finally, machining the prepared blank to obtain the chromium, aluminum, silicon and nickel quarternary alloy target material. The chromium, aluminum, silicon and nickel quarternary alloy target material provided by the invention has the advantages of being high in compactness, free of pores, looseness and segregation, small in grain size, uniform in tissue and the like, and can be suitable for sputtering hard coatings needed by various tools and molds.
Owner:河北宏靶科技有限公司
In-situ preparation method for manufacturing high-entropy alloy by gradient powder feeding laser additive material
ActiveCN109079137AImprove molding efficiencyReduce manufacturing costAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyMaterials preparationMetallurgy
The invention discloses an in-situ preparation method for manufacturing high-entropy alloy by gradient powder feeding laser additive materials. The in-situ preparation method comprises the following steps of raw material preparation and gradient powder feeding laser additive material preparation. The material forming efficiency prepared by the in-situ preparation method is high, and a part model is not subjected to technological constraints, so the in-situ preparation method can be used to prepare parts with complex shapes, and the near-net forming of the materials can be realized, the production cost of the parts is greatly reduced. Samples have good forming effect, no air holes and macroscopic cracks, no micro-air holes and micro-cracks, good density, uniform organization and coexistenceof three phase structures. Composition detecting is carried out by using an energy disperse spectroscopy, and the definition of high-entropy alloy is met from the composition. The boundary between aprinting layer and two sides of base is fuzzy, the combination is better, and the crack tendency is low. It can be concluded that the gradient powder feeding mode greatly reduces the crack tendency atthe joint.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Low-speed laminar-flow high-pressure die-casting process
The invention relates to a low-speed laminar-flow high-pressure die-casting process. The low flow gate filling speed of 0.1-6 m / s is adopted, molten metal rises horizontally at a constant speed in a flow gate and a cavity to be filled into the cavity, when the molten metal flows from the flow gate to the cavity, the flowing speed of the molten metal, close to the peripheral side of the cavity, onthe surface of a die is low, the flowing speed of the molten metal close to the middle of the cavity is high, and a streamline flowing mode that the speed is increased layer by layer from the outer layer to the inner layer is formed; and the phenomena of spraying and rolling do not occur, alloy liquid flows in the cavity and is in a laminar flow state that the whole wall thickness is evenly increased, laminar flow filling achieves the effect of avoiding gas wrapping, gas in the cavity can be sequentially exhausted from an overflow groove and an exhaust groove in the upper portion, air holes formed by flowing and gas wrapping of the alloy liquid do not exist in a casting, and the performance of the casting can be improved through high-temperature solid solution heat treatment.
Owner:SUZHOU UNION PRECISION METAL PROD CO LTD
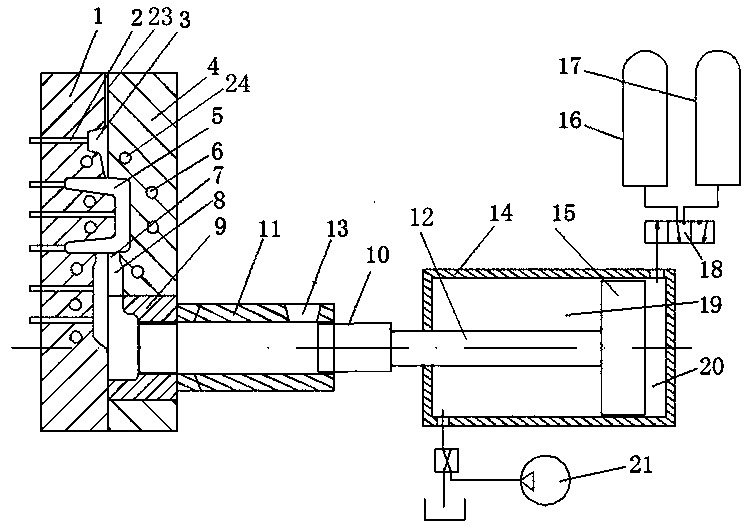
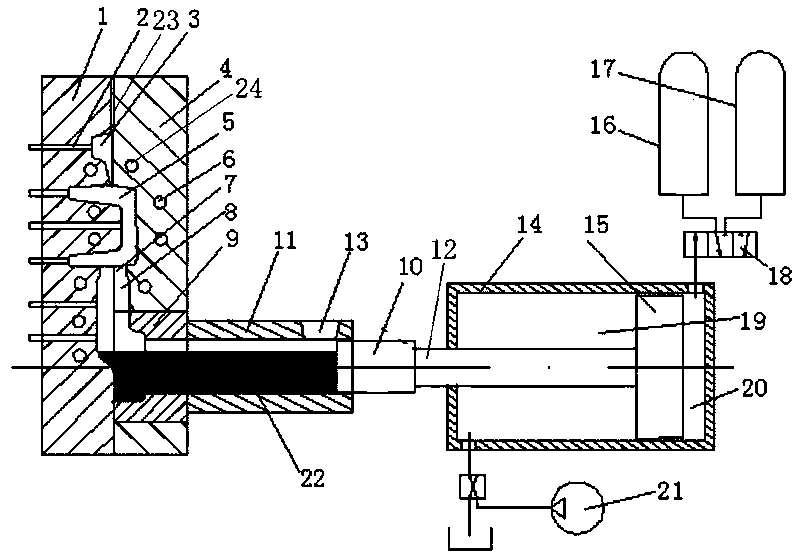
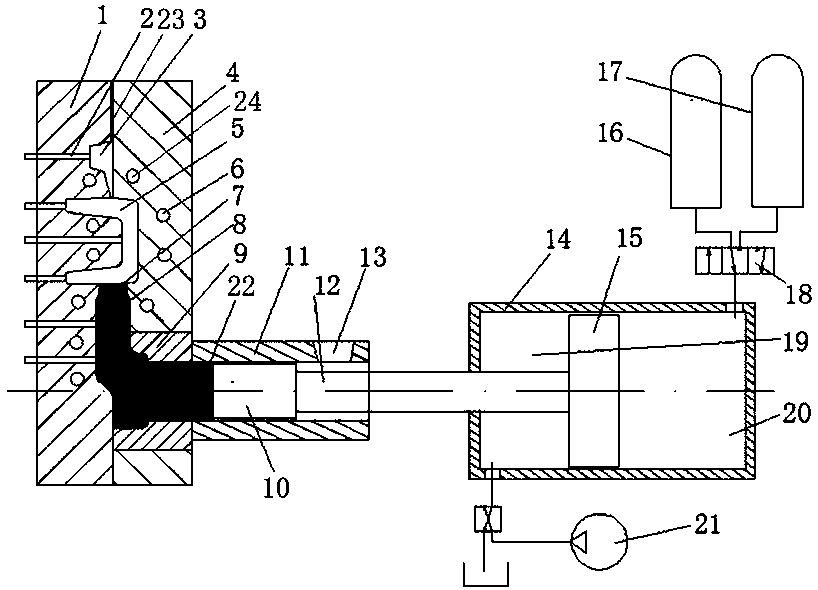
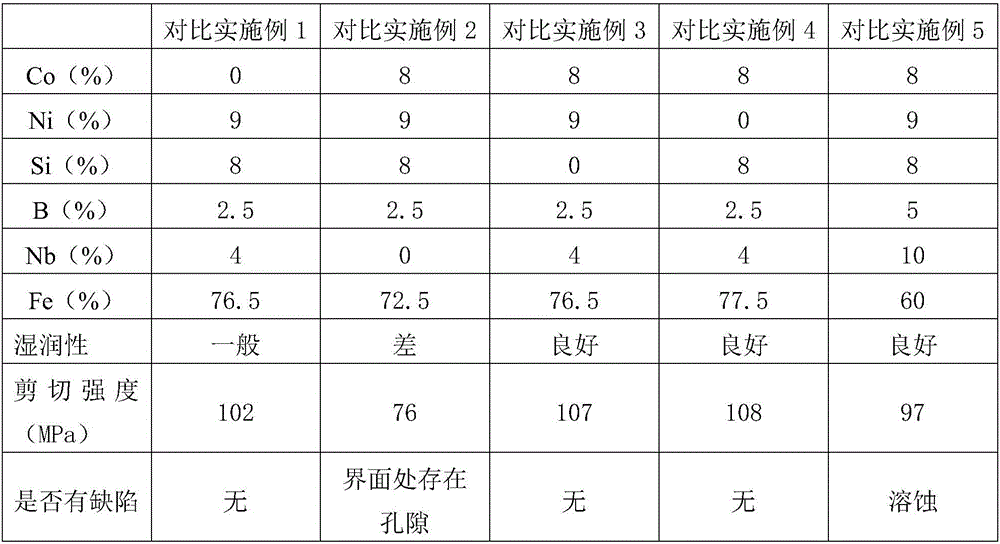
High temperature Fe-based solder for brazing 50Mo-50Re alloy and preparation method thereof, and brazing process
ActiveCN106271209AHigh melting pointHigh melting temperatureWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaMo elementSolid solution
The invention discloses a high temperature Fe-based solder for brazing 50Mo-50Re alloy and preparation method thereof, and brazing process. The solder includes the components with following weight ratios: Co 4wt%-9wt%, Ni 3wt%-12wt%, Si 3wt%-8wt%, B 0wt%-3wt%, Nb 3wt%-5wt%, and the balance Fe. The preparation method for the high temperature Fe-based solder comprises the following steps: mixing Fe particles, Si particles, B particles, Co particles, Ni particles and Nb particles evenly in proportion, making the solder into foil strip shape with a thickness ranging from 20-50Mum by using vacuum induction melting furnace and high vacuum spinning machine. The temperature for brazing the solder ranges from 1060-1160 DEG C, and the melting temperature of the solder keeps extremely high to ensure the high temperature performance of a weld. The solder is molten uniformly. The use of solder foil is conducive to promoting the diffusion of alloy elements in soldered connection process, and the solder foil is conducive to promoting element diffusion in soldered connection process. Solid solution can be generated by Fe element and Mo element; Co element and Nb element can promote the diffusion of Mo element and Re element in a brazing seam, so as to form a wide diffusion layer. The performance of the brazing seam is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TEHCHNOLOGIES CO LTD
Alkaline cyanide-free electro-deposition zinc-nickel alloy additive and application thereof
The invention discloses an alkaline cyanide-free electro-deposition zinc-nickel alloy additive and an application thereof. The alkaline cyanide-free electro-deposition zinc-nickel alloy additive is prepared from an additive and ultrapure water. The additive is an organic additive or a mixture of the organic additive and an inorganic additive and can be applied to an alkaline cyanide-free electro-deposition zinc-nickel alloy plating solution to replace a traditional cadmium coating and cyanide electro-deposition zinc-nickel alloy process. According to the alkaline cyanide-free electro-deposition zinc-nickel alloy additive and the application thereof, through additive screening and adding, an electroplating process for electro-deposition zinc-nickel alloy is optimized, and a zinc-nickel alloy coating which is bright in appearance, high in hardness and excellent in corrosion resistance is finally obtained; the obtained plating solution is good in stability, dispersity and covering capacity, and the problems that a conventional alkaline zinc-nickel alloy plating solution is poor in stability and low in current efficiency, and an obtained coating is poor in quality are solved fundamentally; and the industrialized application feasibility of the alkaline cyanide-free electro-deposition zinc-nickel alloy additive is improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Special alloy powder for continuous wave fiber laser cladding
ActiveCN103602857AHigh hardnessImprove toughnessMetallic material coating processesIridiumHigh energy
The invention discloses a special alloy powder for continuous wave fiber laser cladding. The special alloy powder contains the following components in percentage by weight: 11-13% of titanium carbide, 2-5% of lanthanum oxide, 5-7% of aluminum oxide, 8-10% of chromium, 2-4% of iridium, 0.1-0.2% of carbon, 1-1.2% of manganese and the balance of nickel. The alloy powder is specially used for the cladding process of a high-energy continuous fiber laser, the absorption and utilization ratios of laser are remarkably increased, and the formed cladding layer has high hardness, high toughness and high corrosion resistance. The cladding layer is compact in tissue and free of defects such as pores, cracks, shrinkage holes and the like; when the alloy powder is used for laser cladding, the process is simple and convenient, and heat treatment before and after cladding is not needed.
Owner:CHANGZHOU TIANZHENG IND DEV CO LTD
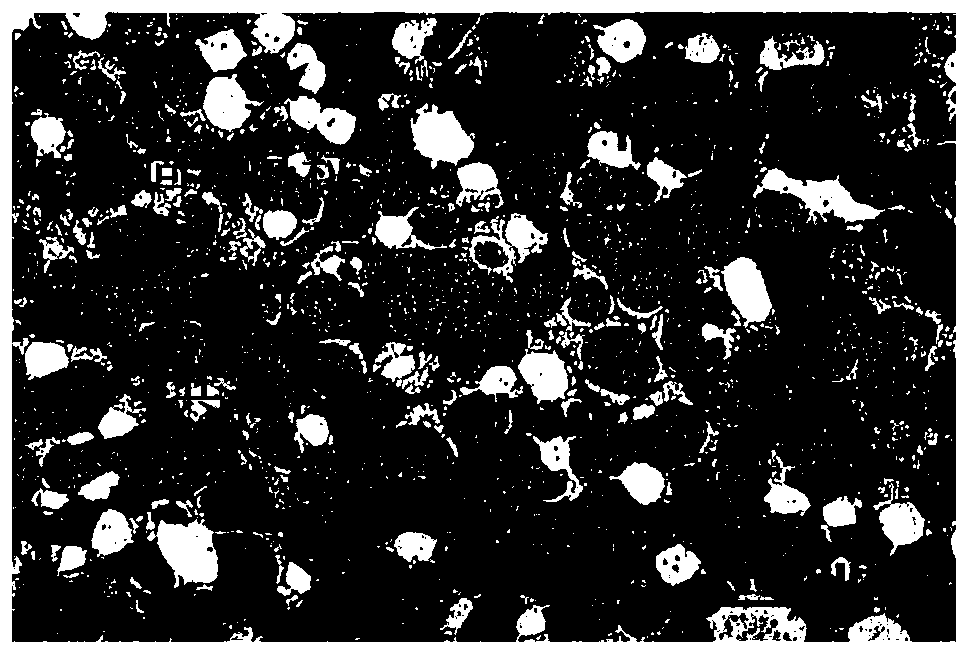
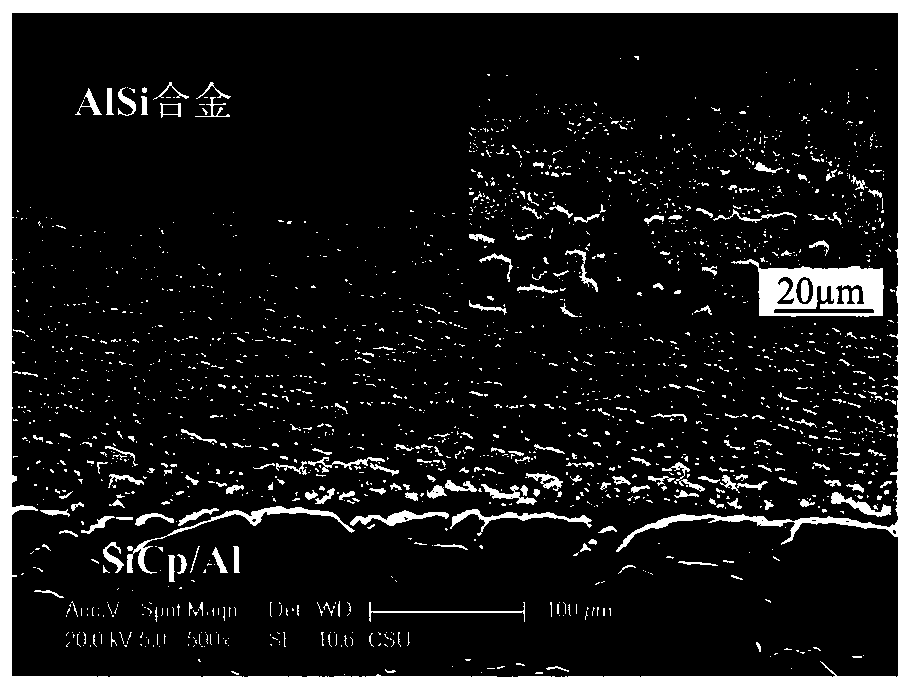
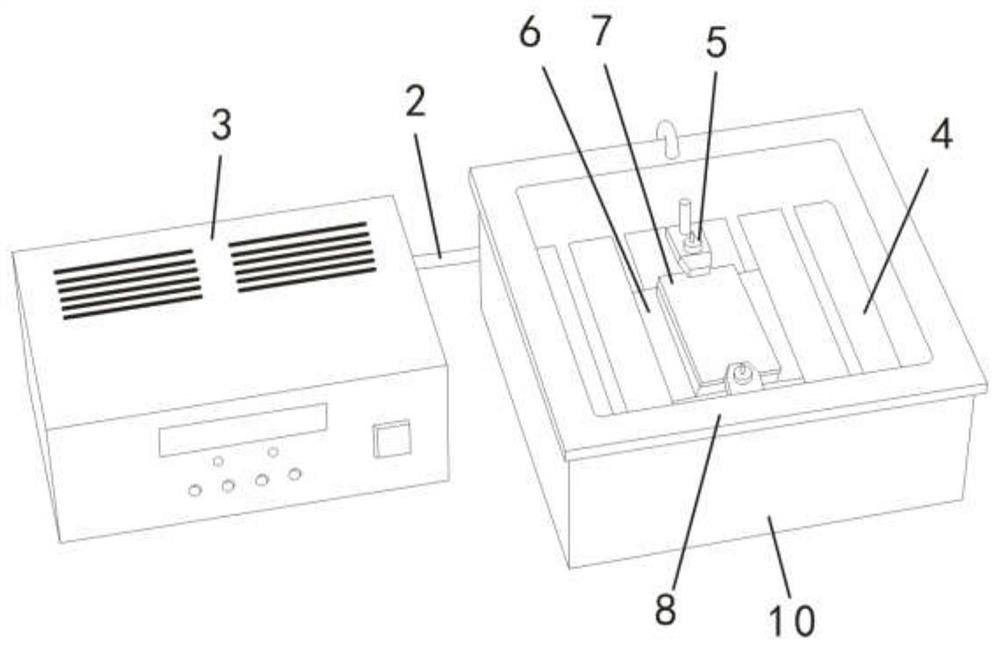
Brazing method of high-volume-fraction silicon carbide particle reinforced aluminum matrix composite material and aluminum-silicon alloy
ActiveCN110576232AReduce residual stressHigh strengthSoldering apparatusAfter treatmentSilicon alloy
The invention discloses a brazing method of a high-volume-fraction silicon carbide particle reinforced aluminum matrix composite material and an aluminum-silicon alloy. The brazing method includes thefollowing steps that S1, the to-be-welded surfaces of the silicon carbide particle reinforced aluminum matrix composite material and the aluminum-silicon alloy are subjected to surface clearing; S2,ceramic powder is prearranged on the to-be-welded surface of the aluminum-silicon alloy after treatment in the S1; S3, a brazing filler metal is placed between the to-be-welded surfaces of the aluminum-silicon alloy and the silicon carbide particle reinforced aluminum matrix composite material to form a to-be-welded part; and S4, under the protective atmosphere, the to-be-welded part is heated up,kept warm and pressurized to 5-20 MPa, and continuous heat preservation and pressure maintaining are conducted, and then the to-be-welded part is furnace-cooled to the room temperature. According tothe brazing method, oxide films on the surfaces of the silicon carbide particle reinforced aluminum matrix composite material and the aluminum-silicon alloy are broken by using the hard ceramic powderto assist the metal brazing filler metal, the brazing filler metal is fully wetted and spreads on the surfaces of the silicon carbide particle reinforced aluminum matrix composite material and the aluminum-silicon alloy, and metallurgical bonding of the connection surface of the silicon carbide particle reinforced aluminum matrix composite material and the aluminum-silicon alloy is induced.
Owner:HUNAN HARVEST TECH DEV
Method for laser cladding of copper alloy powder on surface of copper substrate
ActiveCN112430811AQuality improvementHigh hardnessAdditive manufacturing apparatusMetallic material coating processesSurface cleaningSurface oxidation
A method for laser cladding of copper alloy powder on the surface of a copper base comprises the following steps: (1) , using a polishing tool for polishing the surface of a copper base workpiece to remove a surface oxide layer; cleaning the surface of the copper-based workpiece by using a detergent to obtain a copper-based surface with a clean surface; (2), fixing the copper-based workpiece on aworking platform; and (3), carrying out high-speed laser cladding on the copper-based workpiece by using laser cladding powder through a high-speed laser cladding optical fiber laser device. The lasercladding powder comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.01%-0.25% of C, 0.5%-3% of B, 1%-4% of Si, 012% of Cr, 0.5%-14% of Fe, 10%-50% of Cu, 30%-80% of Ni, wherein a powder particle size interval is 25-150 microns and a sphericity degree is more than or equal to 80%. The method has the advantages that for specific laser cladding powder, a transition layer, a pre-coating layer and the like do not need to be added before cladding, a desired cladding layer is directly obtained through single-layer cladding in the mode that powder is fed from the center and the working included angle of the cladding head is controlled, and the process is simplified.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Automobile die surface film repair technology
InactiveCN107805809AEffective recoveryAvoid damageMetallic material coating processesSand blastingThin layer
The invention discloses an automobile die surface film repair technology. The technology comprises the following steps that 1, sand blasting treatment is carried out; 2, coating repair pretreatment iscarried out; 3, coating repair is carried out, wherein a laser cladding method is adopted for carrying out coating repair on a die; 4, oiling protection is carried out, wherein after a laser claddinglayer is cooled at a normal temperature to a room temperature, a thin layer of silicon oil is smeared on the repaired surface; and 5 detecting is carried out. The technology is easy to operate, usedmaterials are low in price and easy to obtain, and the damaged automobile die surface film can be effectively repaired; as local repair is adopted, in comparison with complete integral spraying in theprior art, damage to a die base body is reduced as much as possible, and the repair quality is ensured; and the laser cladding method is adopted for repairing the repair portion, and the film which is flat and smooth in surface, free of air holes and cracks, high in hardness and good in wear resistance and corrosion resistance can be formed. The technology can be applied to and popularized in dies used in fields of other types of aircraft engine turbines and the like and has a wider use range.
Owner:JIANGSU YUYAN MOLD IND
High-performance aluminum alloy added with rare earth element and preparation method of high-performance aluminum alloy
The invention discloses a high-performance aluminum alloy added with a rare earth element. The high-performance aluminum alloy is characterized by being prepared from, by mass percent, 6.5%-7% of silicon, 0.2%-0.25% of magnesium, 0.25%-0.3% of iron, 0.01%-0.012% of boron, 0.3%-0.4% of cerium, 0.1%-0.2% of zinc, 45%-50% of waste aluminum intermediate alloy powder and the balance aluminum. Alloy compositions are optimized, the rare earth element cerium is added, and therefore the tensile strength of the alloy can be improved; and a scientific and reasonable heat treatment technology is adopted, and therefore the mechanical property, especially the high-temperature mechanical property, of the alloy can be improved. The stability of a strengthening phase can be improved, precipitation and growth of the strengthening phase can be stopped, grains can be refined, cracks can be avoided, no air hole exists inside, and the product formability and the rate of finished products are improved. The prepared aluminum alloy has the beneficial effects of being high in performance, good in weldability and formability and the like, and can be used for manufacturing an engine air cylinder cover.
Owner:ANHUI QIANTONG EDUCATION MFG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com