Protein fiber low temperature neutral reduction bleaching method
A protein fiber, low temperature technology, applied in the field of dyeing and finishing, can solve the problems of high energy consumption, long process time and high production cost, and achieve the effect of avoiding cost increase and good water solubility.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
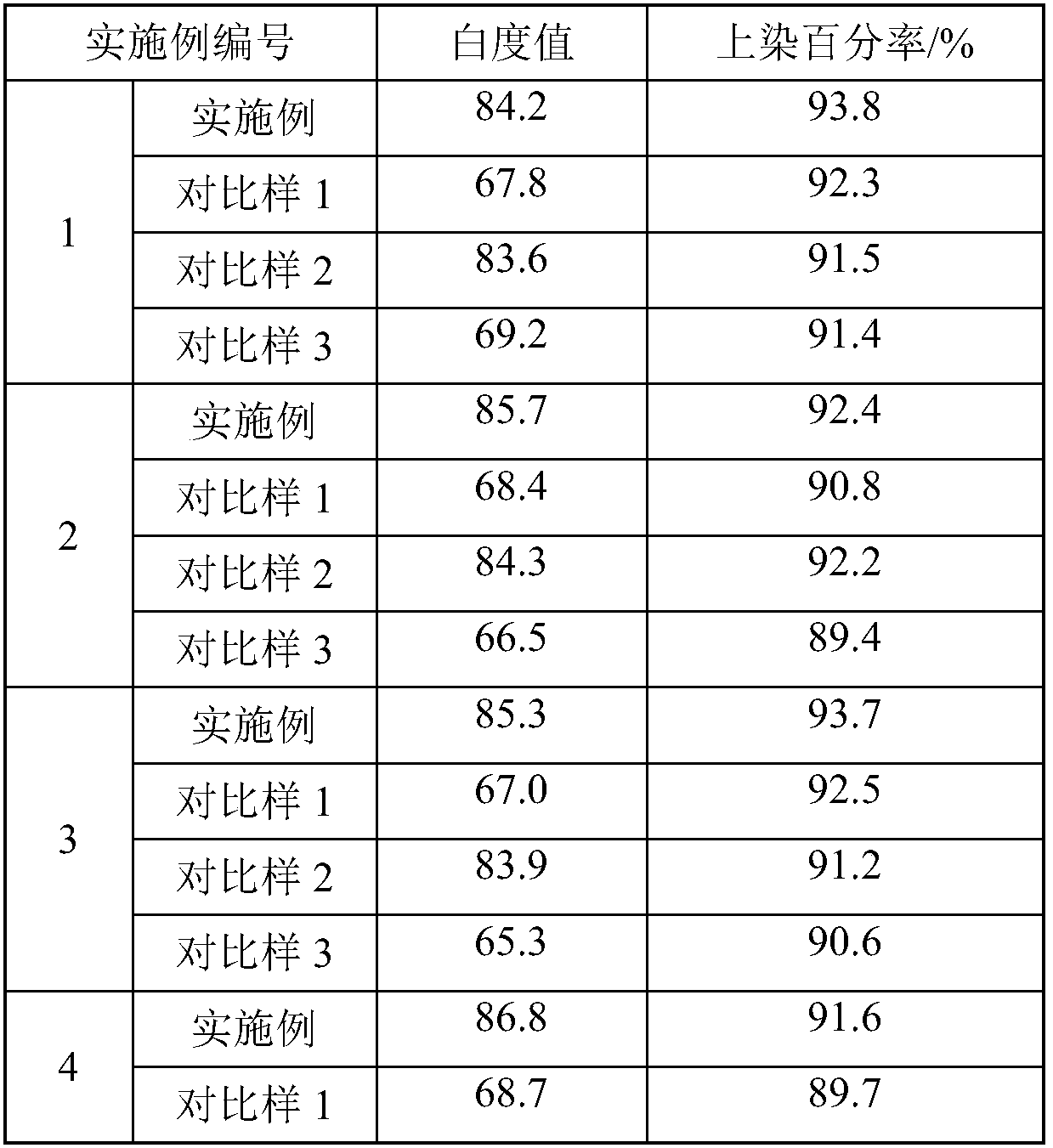
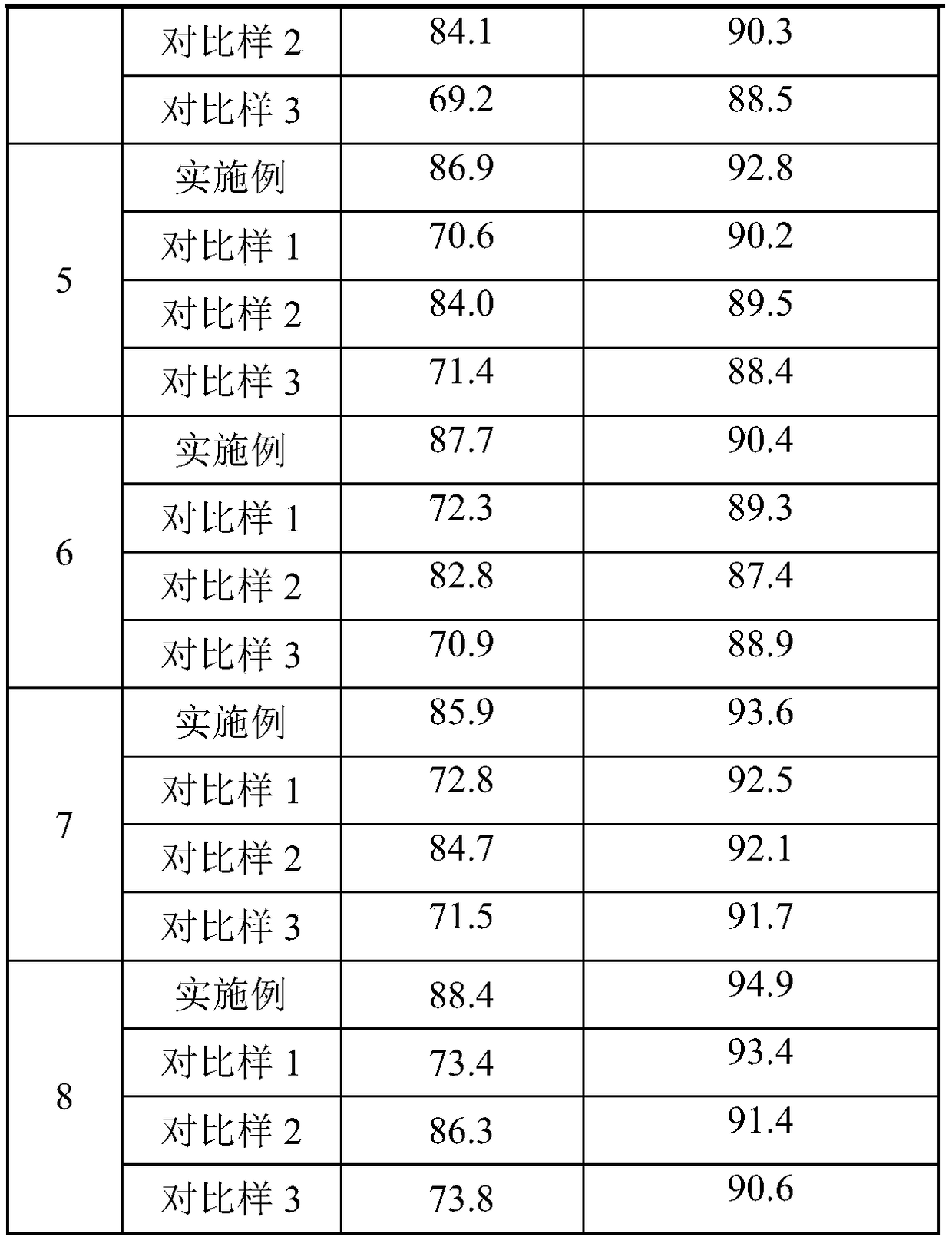
Embodiment 1
[0025] A method for neutral reduction bleaching of protein fibers at low temperature, the steps are as follows:
[0026] (1) Preparation of low-temperature bleaching catalyst: weigh the rare earth chloride and the colorless aromatic compound with relatively simple structure according to the molar ratio of 1:1, put the weighed cerium chloride and o-hydroxybenzoic acid into the Put an appropriate amount of distilled water in an Erlenmeyer flask, heat it to 40°C under ultrasonic conditions, stir it ultrasonically to dissolve it completely, then slowly pour the aqueous solution of cerium chloride into the aqueous solution of o-hydroxybenzoic acid under the condition of ultrasonic 40°C, and ultrasonically After stirring for 10 minutes, add concentrated ammonia water dropwise to adjust the pH of the solution to 10, then continue the ultrasonic stirring reaction for 60 minutes, and let the reacted aqueous solution stand at room temperature for 48 hours, and obtain a solid powder after...
Embodiment 2
[0029] A method for neutral reduction bleaching of protein fibers at low temperature, the steps are as follows:
[0030] (1) Preparation of low-temperature bleaching catalyst: weigh rare earth chlorides and colorless aromatic compounds with relatively simple structures in a molar ratio of 1:2, and weigh ytterbium chloride and lutetium chloride (molar ratio 1:1) ) and m-hydroxybenzoic acid, 1-hydroxyl-2-naphthoic acid (molar ratio 1:1) were respectively placed in conical flasks equipped with appropriate amount of distilled water, heated to 50 °C under ultrasonic conditions, and ultrasonically stirred to make it completely dissolved , and then slowly pour the aqueous solution of ytterbium chloride and lutetium chloride into the aqueous solution of m-hydroxybenzoic acid and 1-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid under the condition of ultrasonic 60°C, and after ultrasonic stirring for 10 minutes, add concentrated ammonia water dropwise to adjust the solution pH to 12, and then continue the u...
Embodiment 3
[0033] A method for neutral reduction bleaching of protein fibers at low temperature, the steps are as follows:
[0034] (1) Preparation of low-temperature bleaching catalyst: weigh the rare earth chloride and the relatively simple colorless aromatic compound according to the molar ratio of 1:3, and weigh the yttrium chloride, praseodymium chloride, neodymium chloride (mol Ratio 1:1:1) and 3,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid, 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid, 2,6-dihydroxybenzoic acid (molar ratio 1:1:1) were placed in a suitable amount of distilled water In a Erlenmeyer flask, heated to 50°C under ultrasonic conditions, ultrasonically stirred to dissolve it completely, and then slowly poured the aqueous solution of yttrium chloride, praseodymium chloride, and neodymium chloride into 3, In the aqueous solution of 5-dihydroxybenzoic acid, 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid, and 2,6-dihydroxybenzoic acid, after ultrasonic stirring for 10 minutes, concentrated ammonia water was added dropwise to adjust th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com