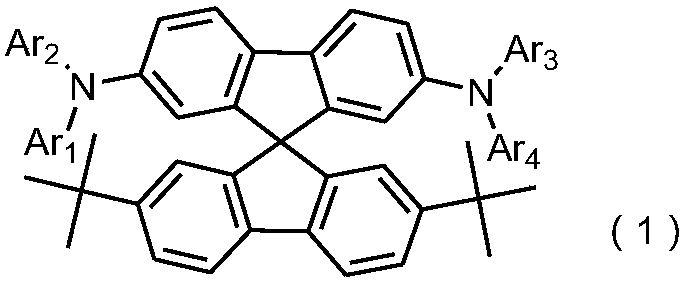
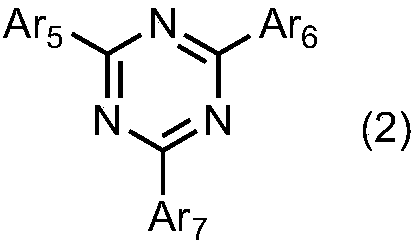
Organic light emitting device
A technology of organic light-emitting devices and light-emitting layers, which is applied in the manufacture of electric solid-state devices, semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state devices, etc., and can solve the problems of low luminous efficiency of light-emitting devices, low recombination efficiency of electrons and holes, and unbalanced carrier injection and other issues to achieve the effect of improving luminous efficiency and service life, avoiding heat accumulation, and avoiding imbalance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0096] Embodiment 1: the synthesis of compound 1
[0097]
[0098] Synthesis of compound 1
[0099] To compound a (107.3 g , 183 mmol) and diphenylamine (62.0 g, 367 mmol) in degassed toluene (1 L), and the mixture was heated at reflux for 2 hours. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, diluted with toluene and filtered through celite. The filtrate was diluted with water and extracted with toluene, and the combined organic phases were evaporated under vacuum. The residue was filtered through silica gel and recrystallized. Compound 1 (111.5 g, yield 80%) was obtained.
[0100] Mass Spectrum m / z: 762.43 (calculated: 762.40). Theoretical element content (%)C 57 h 50 N 2 : C, 89.72; H, 6.60; N, 3.67 The measured element content (%): C, 89.74; H, 6.61; N, 3.65. The above results confirmed that the obtained product was the target product.
Embodiment 2
[0101] Embodiment 2: the synthesis of compound 8
[0102]
[0103] Preparation of Intermediate C
[0104] To compound a (107.3 g , 183 mmol) and Intermediate A (57.2 g, 183 mmol) in degassed toluene (1 L), and the mixture was heated at reflux for 2 h. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, diluted with toluene and filtered through celite. The filtrate was diluted with water and extracted with toluene, and the combined organic phases were evaporated under vacuum. The residue was filtered through silica gel and recrystallized. Intermediate C (115.0 g, 80% yield) was obtained.
[0105] Mass Spectrum m / z: 786.90 (calculated: 786.92). Theoretical element content (%)C 53 h 56 BrN: C, 80.89; H, 7.17; Br, 10.15; N, 1.78 Measured element content (%): C, 80.88; H, 7.17; Br, 10.17; N, 1.78. The above results confirmed that the obtained product was the target product.
[0106] Preparation of compound 8
[0107] To intermediate C (143.8 g, 183 mmol) and intermed...
Embodiment 3
[0109] Embodiment 3: the synthesis of compound 13
[0110]
[0111] The intermediate A in Example 2 was replaced with an equimolar intermediate A-2, and the other steps were the same as in Example 2 to obtain the target compound 13. Mass Spectrum m / z: 1031.26 (calculated: 1031.37). Theoretical element content (%)C 78 h 66 N 2 : C, 90.83; H, 6.45; N, 2.72 Measured element content (%): C, 90.86; H, 6.44; N, 2.71. The above results confirmed that the obtained product was the target product.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com