Method for improving parthenogenetic development potential of vitrified mature oocytes
A technology of vitrification and oocytes, which is applied in the field of improving the parthenogenetic development potential of vitrified mature oocytes, which can solve the problems of the influence of oocyte development potential and the lack of development ability, so as to achieve the reduction of ROS content and the development of oocytes. Potential enhancement and gene expression stabilization effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
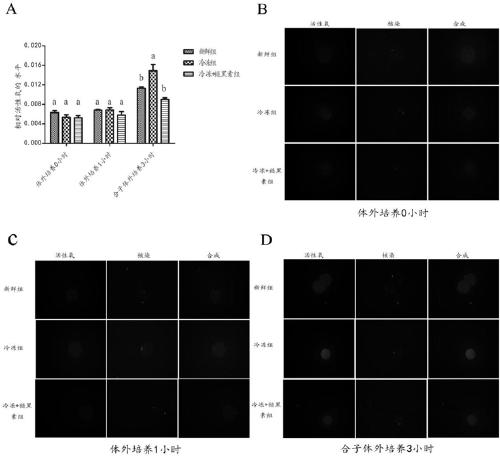
[0042] Example 1 Melatonin reduces the level of ROS in the G1 phase of the parthenogenetic mouse zygote
[0043] After the frozen oocytes were thawed, the oocytes of each group cultured in vitro for 0 hour and 1 hour were tested for ROS levels. Such as figure 1 As shown in A-1C, there was no significant difference in ROS levels between the groups at 0 hour and 1 hour (P>0.05). Three hours after the parthenogenetic activation of oocytes in each group, the zygote was in the late G1 stage, and the ROS level at this time was detected. Compared with the freezing + melatonin group, the ROS level in the freezing group was significantly increased (P0.05). Moreover, with the prolongation of the culture time, the ROS levels of each group had an upward trend.
Embodiment 2
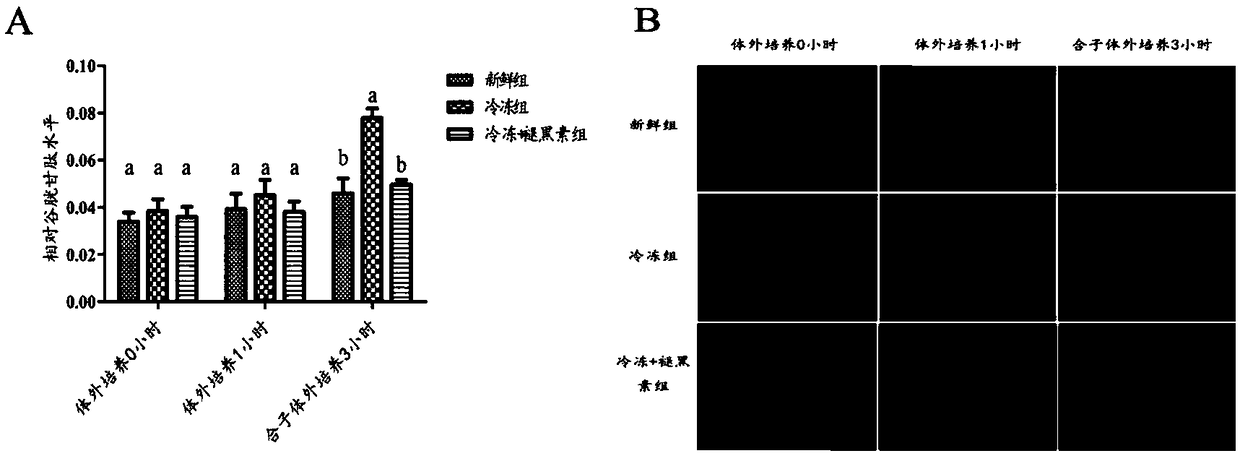
[0044] Example 2 Melatonin reduces the level of GSH in the G1 phase of parthenogenetic mice
[0045] GSH staining was performed on the oocytes of each group cultured in vitro for 0 hour and 1 hour and the combinatorial cells 3 hours after parthenogenetic activation. It was found by GSH staining analysis ( figure 2 ), there was no significant difference between the groups in GSH levels of 0 hour and 1 hour cultured in vitro (P>0.05). Three hours after the parthenogenetic activation of oocytes, the zygote was in the late G1 phase, and the GSH level in the freezing group was significantly higher than that in the freezing + melatonin group and the fresh group (P0.05).
Embodiment 3
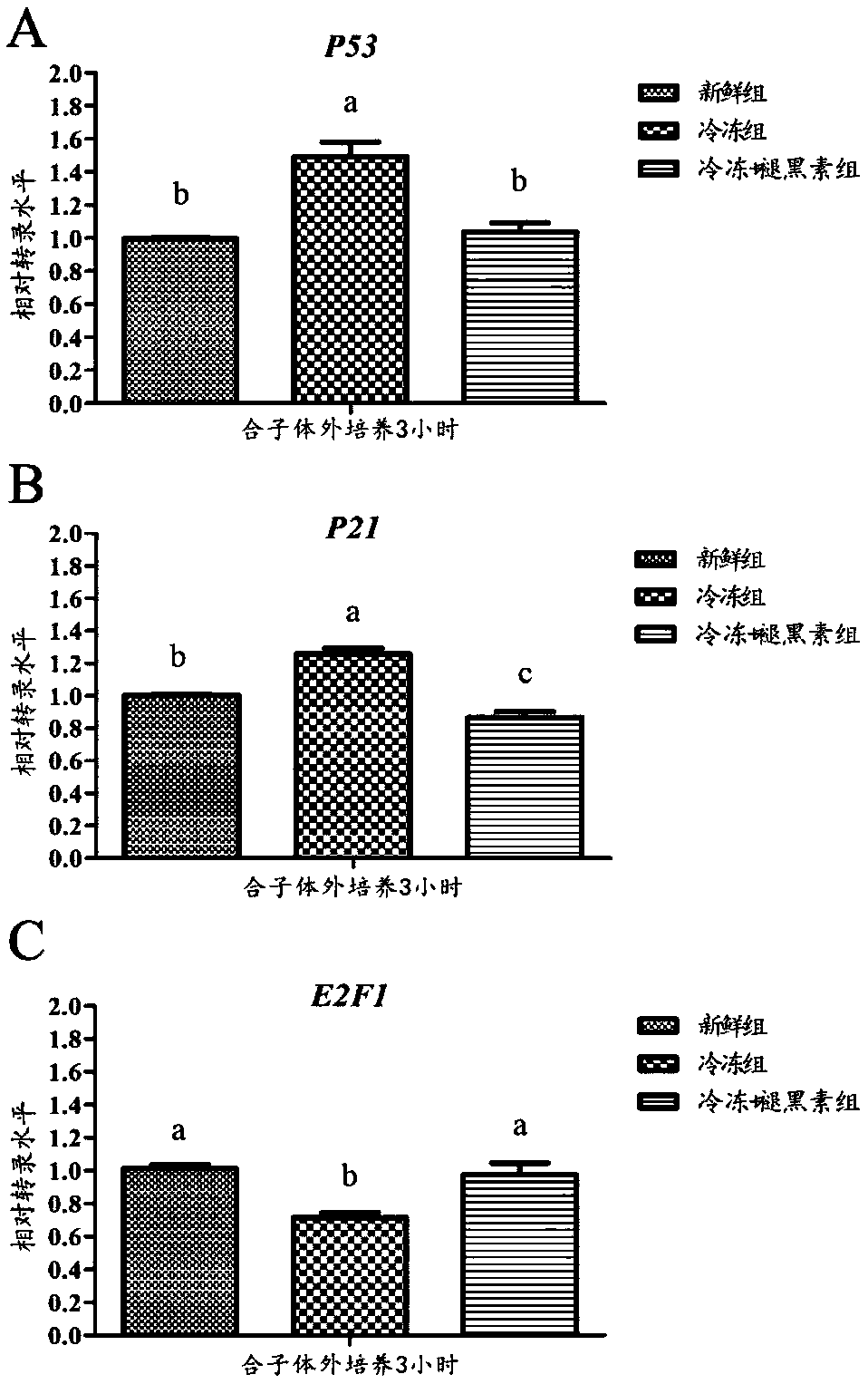
[0046] Example 3 Melatonin changes the mRNA expression of G1 cycle-related genes in parthenozygous mice
[0047] Three hours after parthenogenetic activation of oocytes in each group, the zygote was in the late G1 phase. At this time, the relative mRNA expression levels of key genes regulated in cell cycle checkpoints P53, P21 and E2F1 were detected. Such as image 3 As shown in A, the mRNA expression of P53 in the frozen group was significantly higher than that in the fresh group and the frozen + melatonin group (P0.05). exist image 3 In B, the result is similar to that in Figure A, the mRNA expression level of gene P21 in the frozen group was significantly higher than that in the frozen + melatonin group and the fresh group (P image 3 As shown in C, the expression level of the frozen group was significantly lower than that of the fresh group and the frozen + melatonin group (P0.05).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com