Nanoformulations for plants
A plant and nanoparticle technology, applied in the direction of chemicals for biological control, plant growth regulators, biocides, etc., can solve the problems of inability to reach plants, continuous and economic losses, losses, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0125] Example 1: XPclad Efficacy
[0126] The minimum effective dose (MED), optimal dosing regimen (ODS) and safety profile of XPclad nanoparticles were determined. Measuring the antifungal activity (IC 80 ), and to quantify changes in soybean growth caused by fungicide-containing XPclad nanoparticles compared to using other fungicide application methods.
[0127] Minimum effective dose (MED), optimal dosing regimen (ODS) and safety measures
[0128]Evaluation of the MED assay and optimal schedule in SBR fungi following inoculum preparation and inoculation after establishment of the inoculum in MED plates with 0.1 μg, 0.2 μg, 0.4 μg, 0.8 μg, 1.6 μg and 3.2 μg per day Triazole (trade name Tilt250EC / Bumper 25EC)- and methoxyacrylate (trade name Bankit) treated fungi alone, or similar amounts of triazole and methoxyacrylate in XPclad nanoparticles (per cm area), no treatment, or treatment with XPclad nanoparticles (triazole and methoxyacrylate free). For the optimal dosing...
Embodiment 2
[0137] Example 2: XPclad targeting and environmental stress
[0138] In pot experiments, soybean seedlings were individually treated with coronatin-coated XPclad nanoparticles containing methoxyacrylate + triazole, uncoated XPclad nanoparticles, or methoxyacrylate alone + triazole. Plant growth parameters (stem weight, plant height, number of pods and seed weight / plant) were recorded within 3 months and after sowing with or without P. pachyrhizi challenge. Scanning electron microscopy and mass spectrometry (MS) were used to precisely quantify the (extracellular and intracellular) localization of XPclad nanoparticles in leaves and pods. Similarly, gas chromatography and mass spectrometry (GC-MS) was used to determine the residual fungicides present in potting soil.
[0139] Plant Material and Propagation
[0140] 5B066R2 and 5B024R2 soybean seeds (Mycogen Seed Company) were sown in 12 cm diameter pots (two plants per pot) in soilless mix (Sunshine Mix, LC1; Sun Gro Horticu...
Embodiment 3
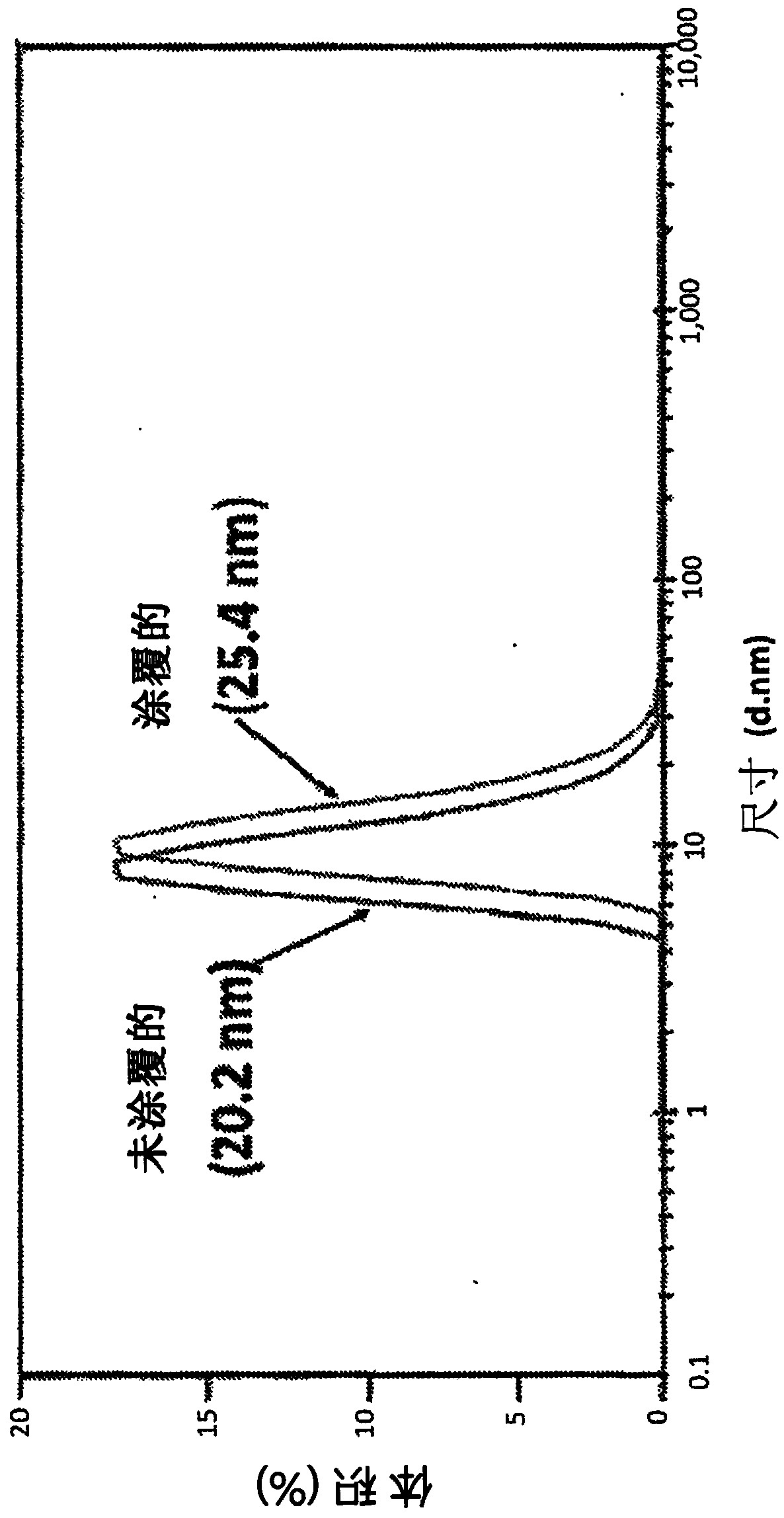
[0165] Embodiment 3: nanometer fertilizer
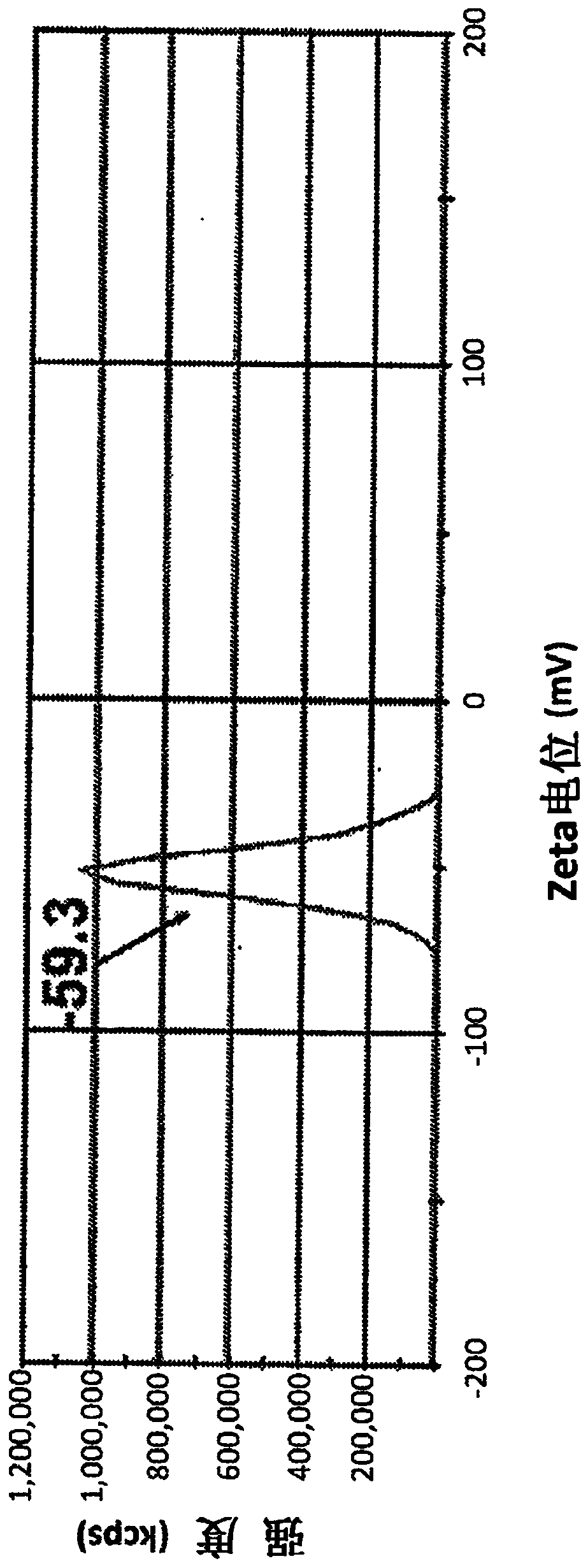
[0166] Preparation of nanofertilizer formulations containing macronutrients (N, P, K) or micronutrients (Zn, Mo, B). The size and zeta potential distributions of the nanofertilizers are shown in Figures 5A-5D . The Log P values of nanofertilizers are shown in Table 3.
[0167]
[0168] Further experiments will show that coated and uncoated nanofertilizer formulations have good delivery of macronutrients and micronutrients in a number of test settings. In some embodiments, the nanofertilizer comprises at least 15% (w / w) N-, P-, and K-containing compounds, and at least 8% (w / w) amino acids. In some embodiments, the nanofertilizer further comprises at least 10 per unit 12 beneficial bacteria.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com