Novel method for extracting phage genome DNA
An extraction method and phage technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of phage reduction, large differences in biological characteristics, degradation, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing experimental costs, shortening extraction time, and wide application range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
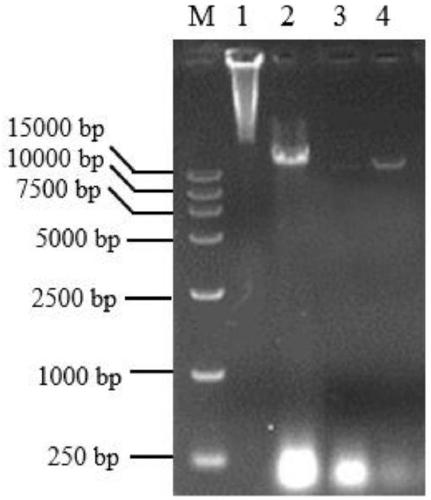
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] According to the above embodiment, the genomic DNA of the chloroform-sensitive phage is extracted, wherein the name of the phage is ΦH2, and the classification name is Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14Phage. The host bacterium lysed by phage ΦH2 is named: Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14, and the taxonomic name is Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
[0047] ①Take the same preparation method of phage lysate
[0048] ②The effect of chloroform extraction on the titer of phage ΦH2
[0049] During the extraction of the phage genome, after resuspension in TM buffer, chloroform was added to extract to remove residual PEG6000. The titer of phage after extraction with chloroform was determined by double-layer plate method.
[0050] Chloroform pumped ahead of time, ΦH2 titer was 6×10 11 pfu / ml, after chloroform extraction, the titer is 3.6×10 10 pfu / ml, the loss reached 94%, seriously affecting the concentration of the extracted phage genomic DNA.
[0051] ③The effect of chloroform extraction on ...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Extraction of Genomic DNA of Staphylococcus aureus Phage Z-1
[0056] (1) Cultivate the host bacteria overnight at 37°C, inoculate 2% (V / V) in 100mL fresh LB medium, add phage according to the optimal MOI, culture at 30°C, 220r / m shaking for 8h
[0057] (2) Add NaCl to a final concentration of 0.1M, mix and dissolve, then ice-bath for 1h, centrifuge at 10000r / / m for 20min
[0058] (3) Add DNase I and RNase A to the lysate to a final concentration of 5 μg / mL, mix well, and let stand at 37°C for 1 hour
[0059] (4) After centrifugation, transfer the supernatant to another centrifuge tube, add PEG6000 to a final concentration of 10%, fully shake and dissolve, and place at 4°C overnight
[0060] (5) Centrifuge the overnight treatment solution at 10000r / m for 20min, discard the supernatant
[0061] (6) Resuspend the pellet with 1 / 50 volume of TM buffer, add DNase I and RNase A to a final concentration of 10 μg / mL, and let stand at 37°C for 1 hour
[0062] (7) Add EDTA (pH...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com