Construction method of tree shrew model for evaluating pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of anti-influenza drugs
A technology of anti-influenza virus and pharmacokinetics, applied in the field of medicine
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1: Pharmacokinetics and antiviral efficacy of oseltamivir in tree shrews
[0023] 1. Pharmacokinetic study of oseltamivir
[0024] After 40 adult healthy Chinese Burmese tree shrews (male and female) fasted for 12 hours (free drinking water), 4 tree shrews in each group were given oseltamivir 10mg / kg by oral gavage, and recorded to At the time of drug administration, 0.5ml of blood was collected through the tail vein or femoral vein at 0.25, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 12 hours after administration, and the collected blood was placed in a centrifuge tube containing heparin. Centrifuge at 1500g at 4°C for 10 minutes, then transfer the plasma to an EP tube and store it in a deep-low temperature freezer at -80°C.
[0025]Accurately weigh an appropriate amount of oseltamivir phosphate, oseltamivir carboxylate and internal standard peramivir, and use 90% v / v methanol aqueous solution to make a stock solution of about 1 mg / mL, in which oseltamivir phosphate needs to...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Example 2: Pharmacokinetics and antiviral pharmacodynamics results of oseltamivir in tree shrews
[0031] 1. Comparison of pharmacokinetic parameters between tree shrews and several other animal models of influenza
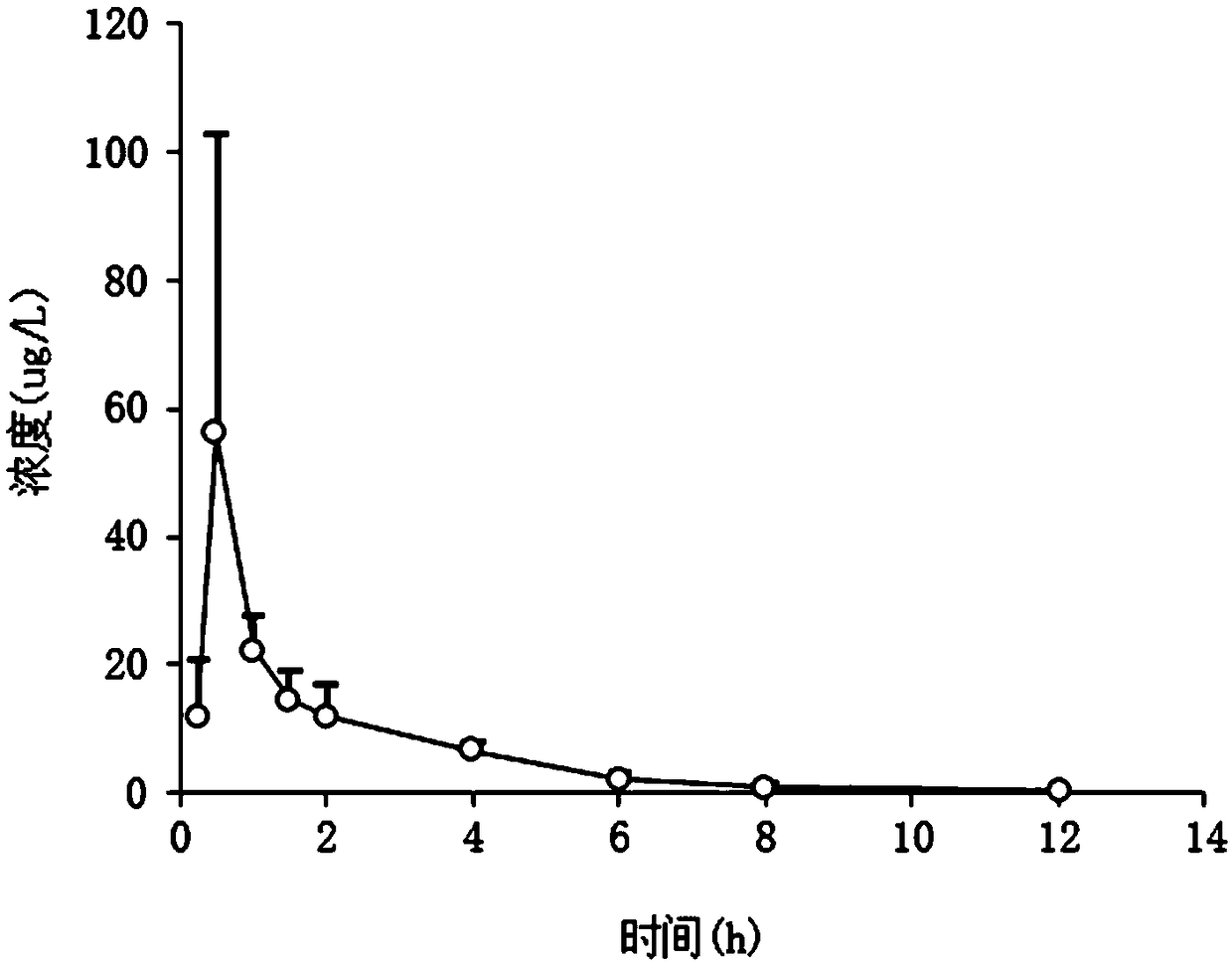
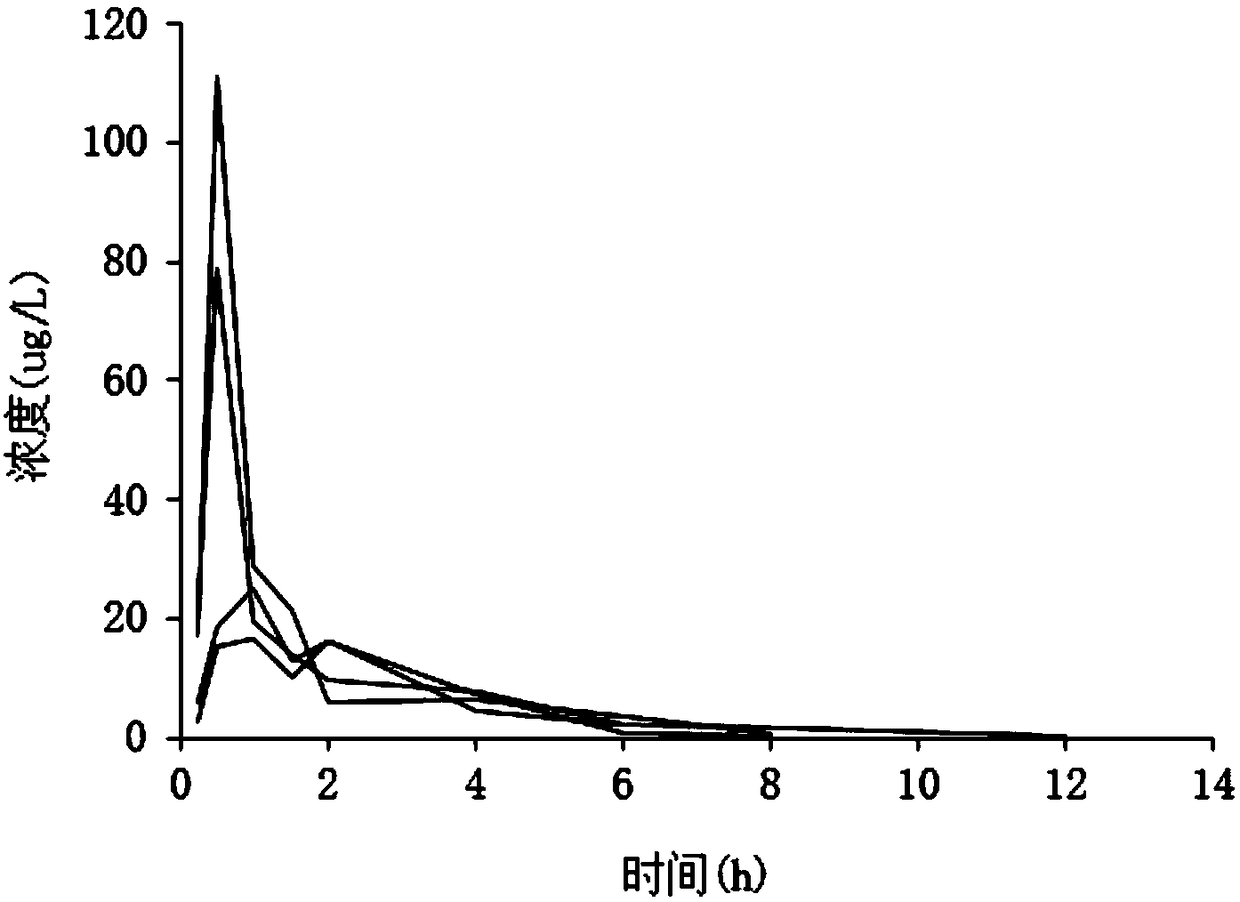
[0032] Tree shrews were orally administered oseltamivir phosphate 10mg / kg / d, and the drug-time curve after administration was as follows figure 1 and figure 2 (The four different curves in the figure represent the respective C-t drug-time curves of the four tree shrews) As shown: the main pharmacokinetic parameters in the tree shrews were calculated by detecting the blood drug concentration of oseltamivir after oral administration, and the peak blood drug Concentration (C max ) is 1.34μg / ml, peak time (T max ) is 0.75h, serum clearance half-life (T 1 / 2 ) is 2.03h, the area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC 0-12 ) is 1.76mg*h / liter.
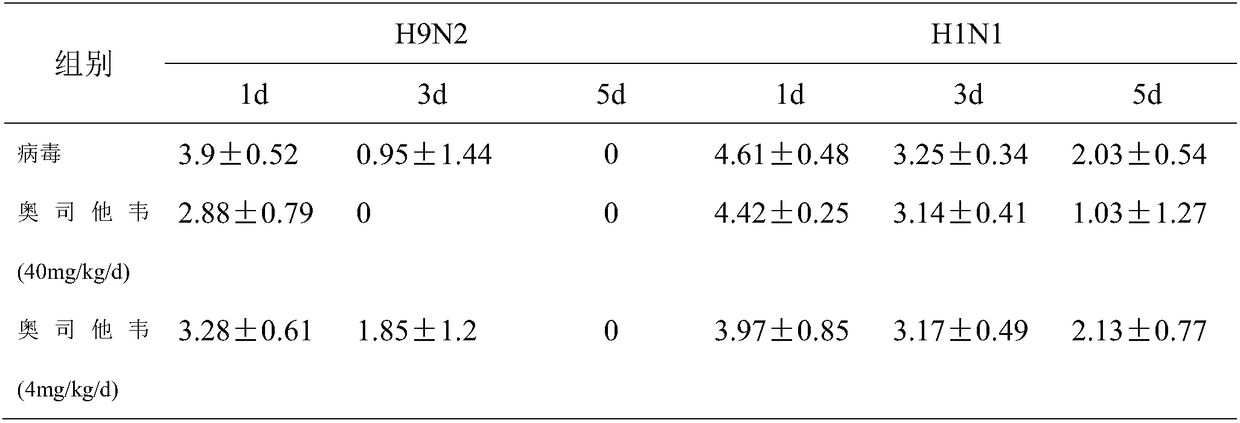
[0033] 2. Pharmacodynamic study of oseltamivir on tree shrews infected with H9N2 and H1N1 influenza virus...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com