Liquid curing agent for phosphate bonding agent and application thereof
A binder and phosphate technology, which is applied to casting molding equipment, molds, cores, etc., can solve problems such as poor stability, dust-prone sand mold (core) demoulding time, low strength, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] 1) Weigh 100g of tap water and 40g of citric acid for later use;
[0023] 2) Add 40g of citric acid and 100g of water in 1) into the reactor, start the agitator, and discharge after stirring evenly to obtain a colorless and transparent citric acid aqueous solution;
[0024] 3) Take 6g of silane coupling agent for subsequent use;
[0025] 4) Take by weighing 1000g of former sand, 25g of phosphate binder, 7g of citric acid aqueous solution for subsequent use;
[0026] 5) Mix the weighed citric acid aqueous solution and the phosphate binder evenly for subsequent use;
[0027] 6) Stir and mix the silane coupling agent and the raw sand in the sand mixer until uniform, then continue to add the mixed solution of the phosphate binder and citric acid aqueous solution obtained in step 5) and mix the sand until uniform and then produce sand (adding without stopping during the process).
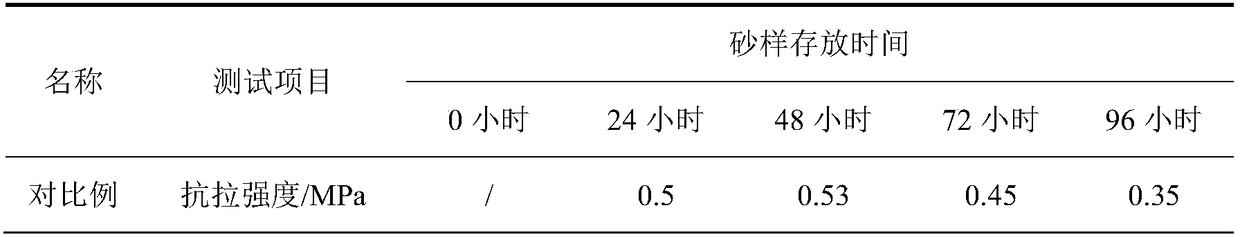
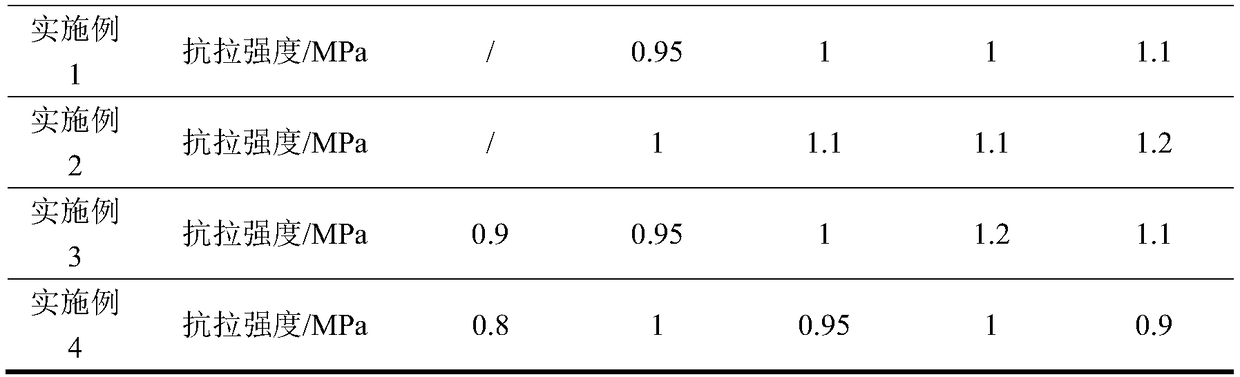
[0028] 7) Fill sand into the "8" sample mold, blow in compressed air for 3 minutes, take th...
Embodiment 2
[0030] 1) Weigh 100g of tap water and 62.5g of citric acid for later use;
[0031] 2) 62.5g of citric acid and 100g of water in 1) are added in the reaction kettle, start the agitator, and discharge after stirring evenly to obtain a colorless and transparent citric acid aqueous solution;
[0032] 3) Take 8g of silane coupling agent for subsequent use;
[0033] 4) Take by weighing 1000g of former sand, 25g of phosphate binder, 6.5g of citric acid aqueous solution for subsequent use;
[0034] 5) Mix the weighed citric acid aqueous solution and the phosphate binder evenly for subsequent use;
[0035] 6) Stir and mix the silane coupling agent and the raw sand in the sand mixer until uniform, then continue to add the mixed solution of the phosphate binder and citric acid aqueous solution obtained in step 5) and mix the sand until uniform and then produce sand (adding non-stop during the process);
[0036] 7) Fill sand into the "8" sample mold, blow in compressed air for 2 minute...
Embodiment 3
[0038] 1) Weigh 100g of tap water and 21.43g of citric acid for later use;
[0039] 2) Add 21.43g of citric acid and 100g of water in 1) into the reaction kettle, start the stirrer, and discharge after stirring;
[0040] 3) Take 7g of silane coupling agent for subsequent use;
[0041] 4) Take by weighing 1000g of former sand, 25g of phosphate binder, 8.5g of citric acid aqueous solution for subsequent use;
[0042] 5) Mix the weighed citric acid aqueous solution and the binder evenly for subsequent use;
[0043] 6) Stir and mix the silane coupling agent and the raw sand in the sand mixer until uniform, then continue to add the mixed solution of phosphate binder and citric acid aqueous solution to mix the sand until uniform, and then produce sand (do not stop during the feeding process) );
[0044] 7) Fill sand into the "8" sample mold, blow in compressed air for 7 minutes, and take the mold.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com