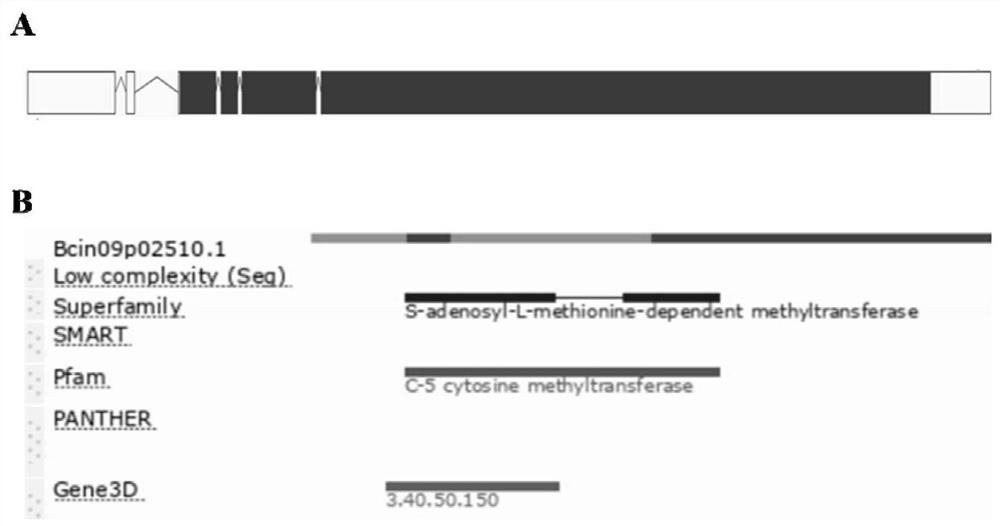
Application of bcdmt2 protein and its coding gene in regulating pathogenicity and conidia production of Botrytis cinerea
A technology of conidia and coding genes, which is applied in the fields of plant pathology and microbial genetic engineering, can solve the problems of reduced drug efficacy and achieve broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Example 1, Construction and Phenotype Analysis of Bcdmt2 Knockout Mutants
[0049] 1. Construction of Bcdmt2 knockout mutant strain
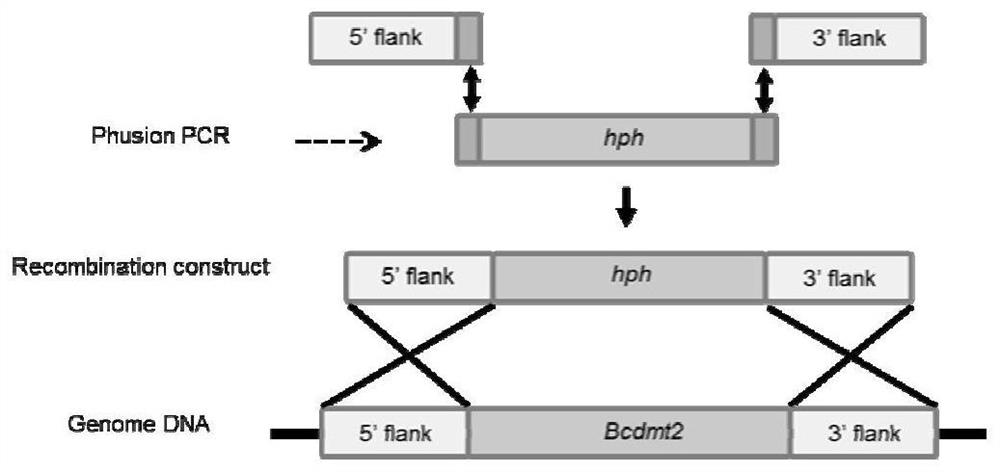
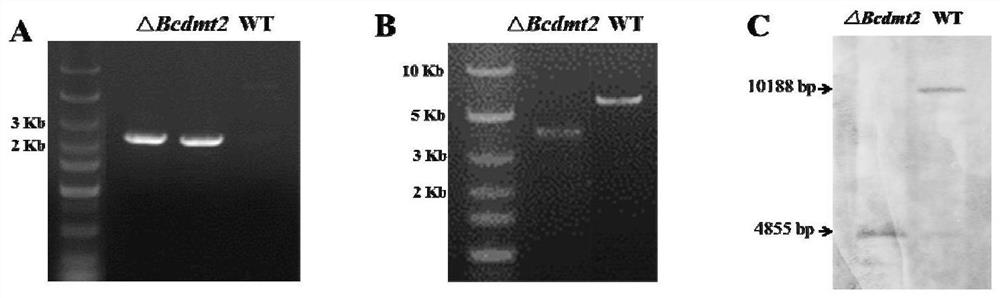
[0050] Using the principle of homologous recombination of gene flanking sequences, the Bcdmt2 gene on the Botrytis cinerea genome was replaced with the hygromycin B resistance gene, so as to achieve the purpose of knocking out the Bcdmt2 target gene. The knockout strategy is as follows: figure 2 shown. Specific steps are as follows:
[0051] 1. Construction of knockout vector
[0052] Use the upstream and downstream sequences of the Bcdmt2 target gene as a template to design primers to amplify the upstream and downstream recombination arms (500-1000bp is appropriate), use the pLOB7 vector as a template to amplify a hygromycin-resistant fragment, and use fusion PCR to amplify the upstream and downstream recombination arms. The recombination arms are connected to both ends of the hygromycin-resistant fragment. Specific steps are as fol...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com