High-concurrency service request processing method and device based on distributed ubiquitous computing
A service request and processing equipment technology, applied in the field of Internet of Things, can solve problems such as service search failure, network bandwidth occupation, network congestion, etc., and achieve the effect of shortening service response time and reducing data traffic
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
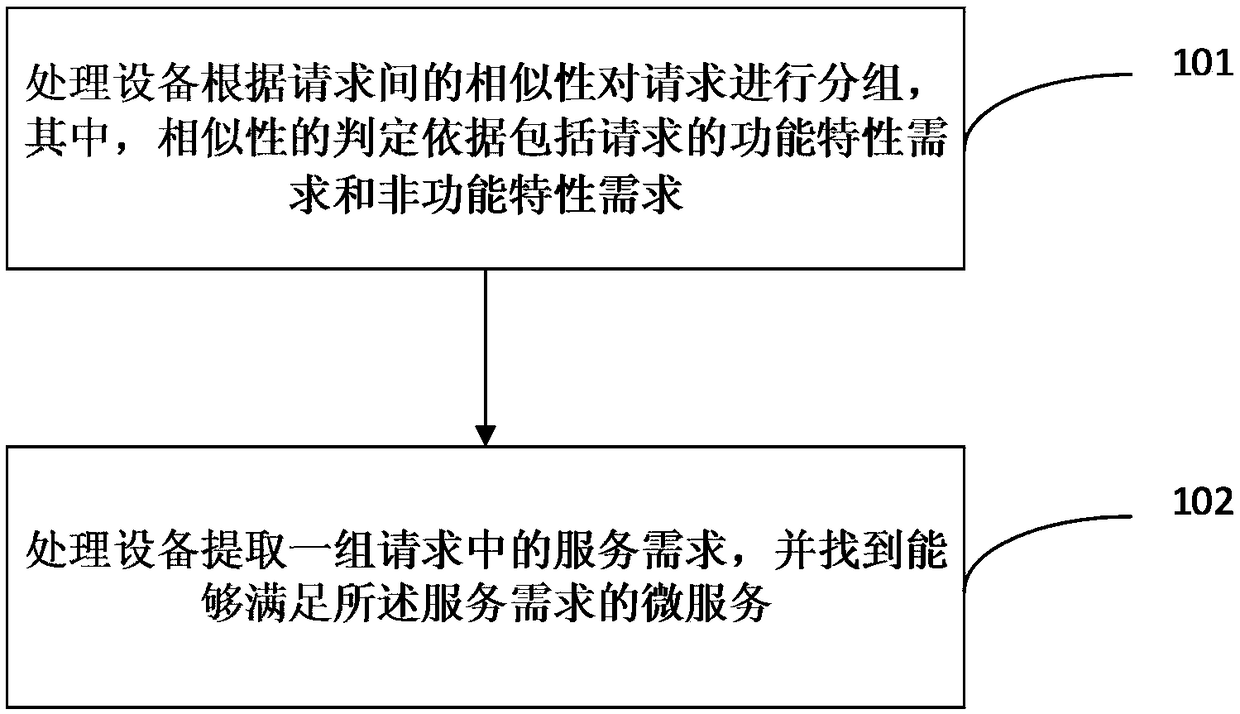
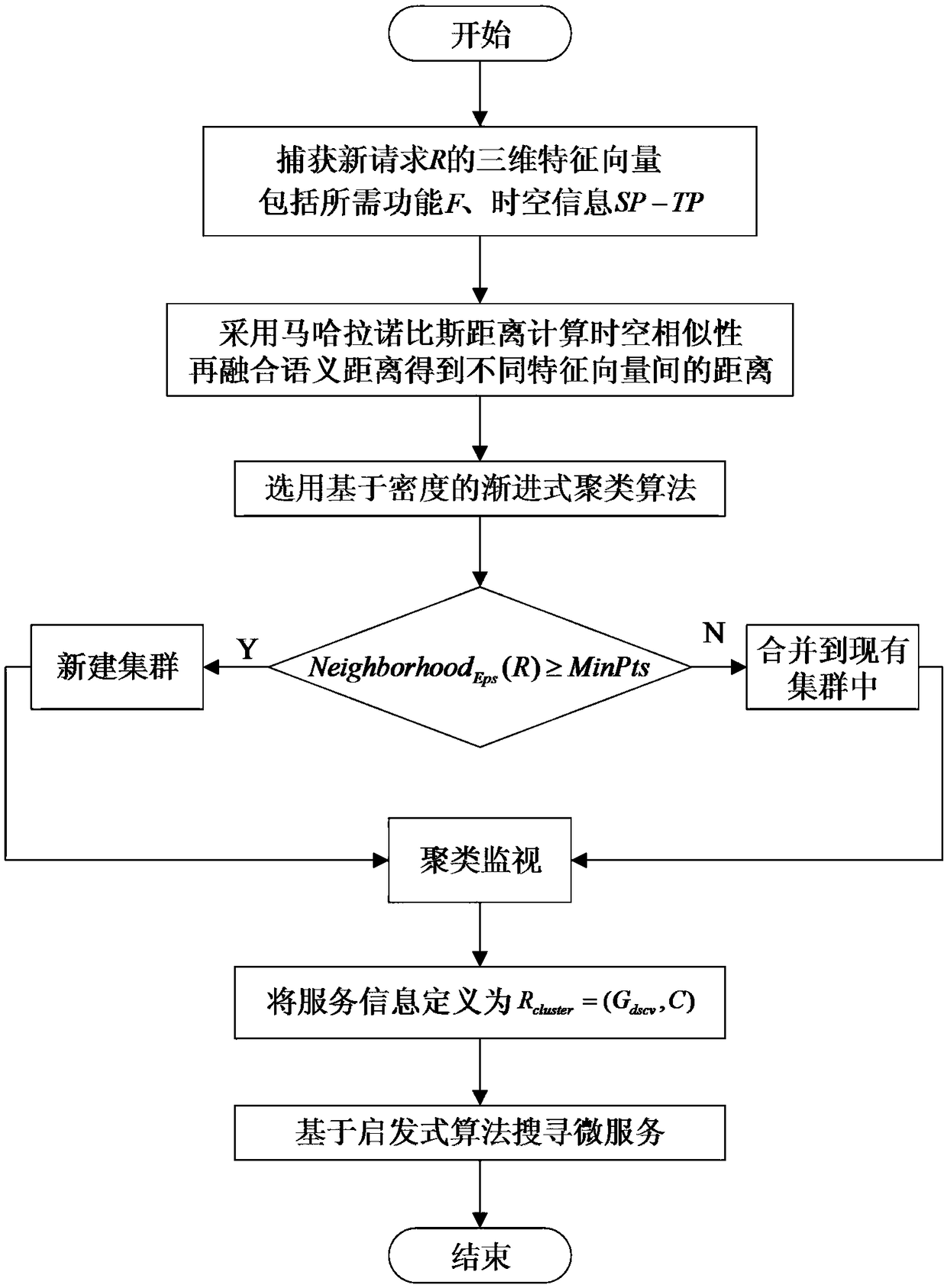
[0036] Embodiment 1: as figure 2 shown, including the following steps:
[0037] Step 1. The processing device groups the requests according to the similarity between the requests, wherein the basis for determining the similarity includes the functional characteristic requirements and non-functional characteristic requirements of the requests:
[0038] (1) In this example, the functional requirement is the semantic expression F of the function of the service request R, and the non-functional requirement is the sending time SP of the service request and the location TP of the sending device in the network topology;
[0039] Given the heterogeneity of the features in question, first consider a two-dimensional feature vector V i =(SP i ,TP i) indicates the sending time of the service request and the location of the sending device in the network topology, and the Mahalanobis distance (Mahalanobis distance) is used to calculate the similarity between request i and request j in t...
Embodiment 2
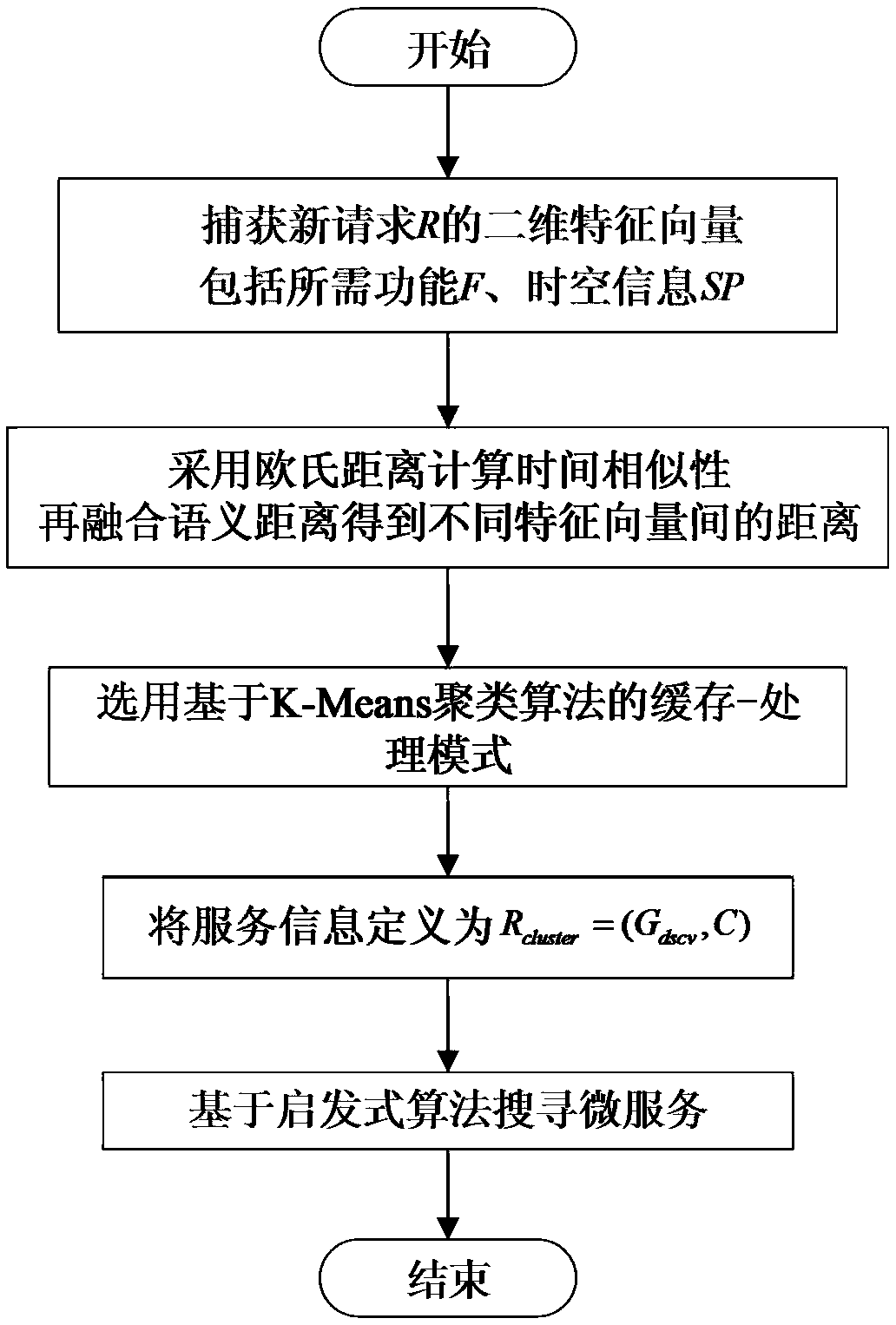
[0063] Embodiment 2: as image 3 shown, including the following steps:
[0064] Step 1. The processing device groups the requests according to the similarity between the requests, wherein the basis for judging the similarity includes the functional characteristic requirements and non-functional characteristic requirements of the requests:
[0065] (1) In this example, the functional requirement is the semantic expression F of the function of the service request R, and the non-functional requirement is the sending time SP of the service request;
[0066] Firstly, Euclidean distance is used to calculate the similarity between request i and request j in the time SP dimension:
[0067] dist sp (i,j)=|SP i -SP j |
[0068] Semantic distances are then utilized to indicate functional similarity, requesting a semantic representation F of an R function as a workflow consisting of a set of subtasks. The similarity calculation is defined as:
[0069] dist sem (i,j)=sim(F i , F ...
Embodiment 3
[0091]Another embodiment of the present invention relates to a high-concurrency service request processing device based on distributed ubiquitous computing. The device may be an edge device such as a small base station, a vehicle terminal, or a fog computing device; a mobile phone, a car, and a household appliance and other terminal devices are connected to the nearest device through a wired or wireless connection. The device structure is as Figure 4 As shown, it mainly includes a request grouping module 310 and a service management module 320 . The request grouping module 310 is used for receiving requests from multiple terminal devices, and grouping requests according to the correlation between functional and non-functional features. The basis for grouping requests is that there may be a large number of requests in a short period similarity, for example, live video service requests from terminal devices during the World Cup, real-time traffic service requests from vehicle ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com