Method for positioning single-phase grounding fault sections of feeders of low-current grounding systems
A single-phase grounding fault, low-current grounding technology, applied in the fault location, measuring current/voltage, detecting faults by conductor type, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of easy promotion and use, easy operation and convenient realization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
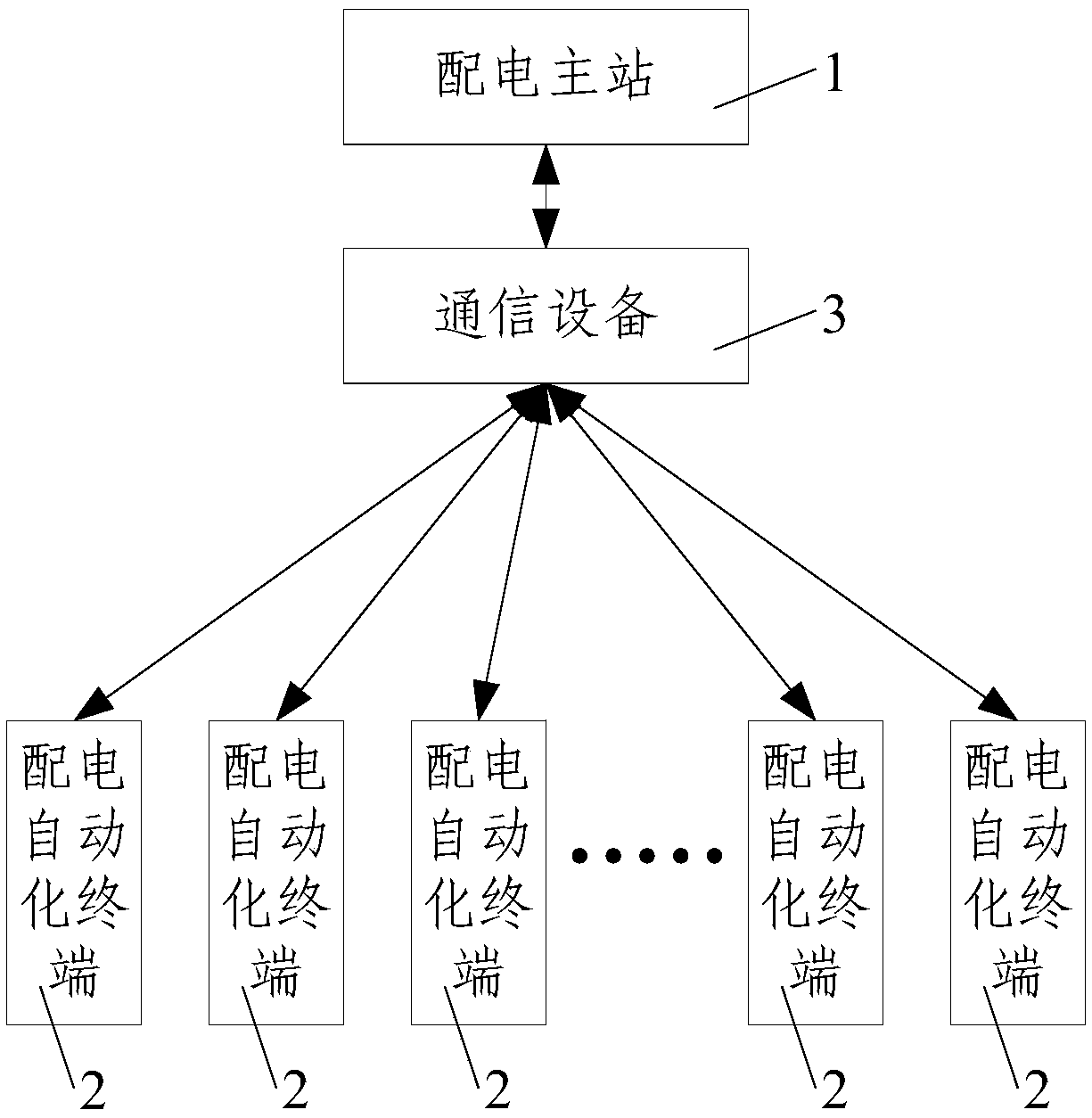
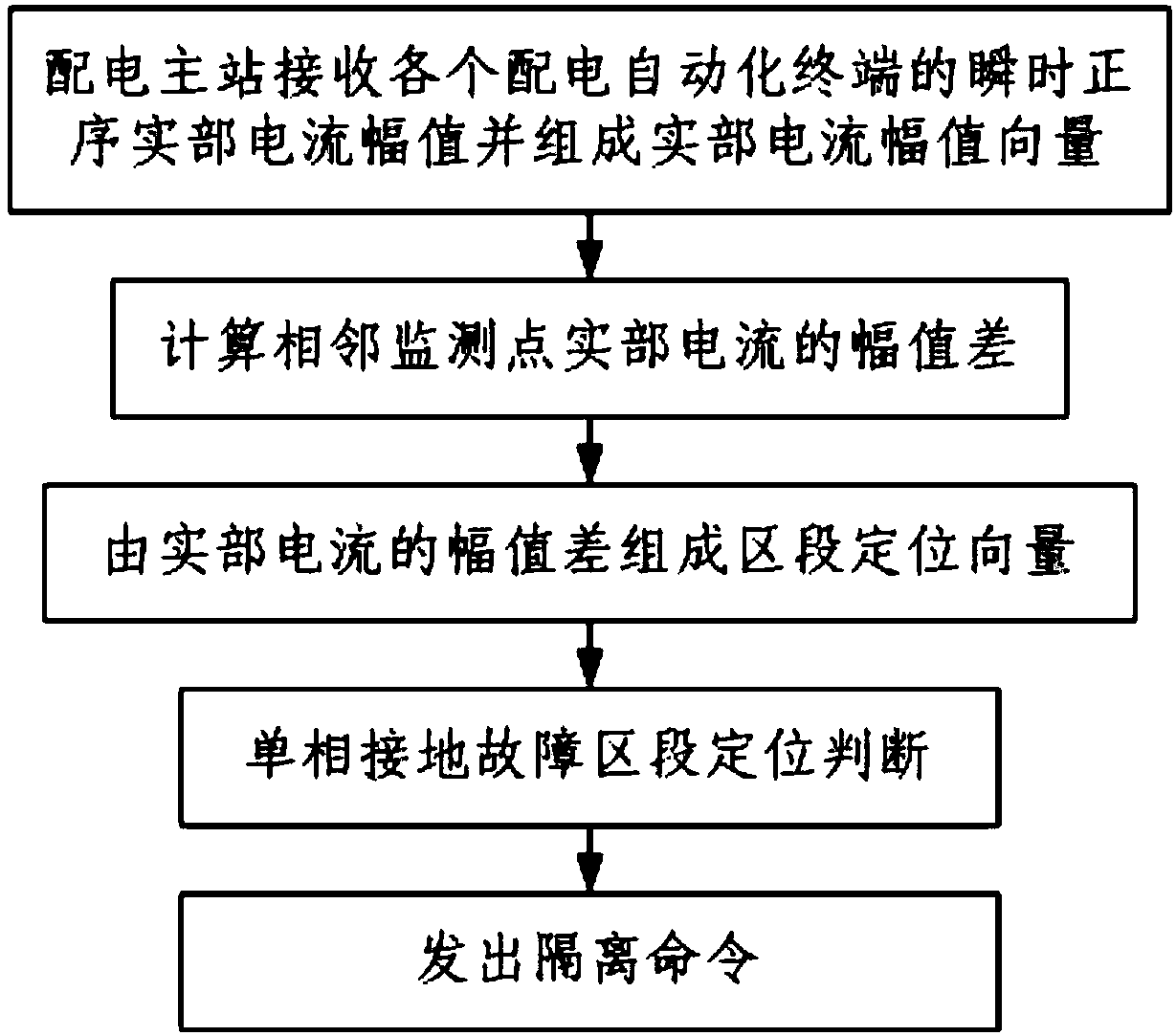
[0072] Such as image 3 As shown, when the present invention is used, the small current grounding system is a 10kV resonant grounding system, and there are three outgoing lines on the bus, and the circuit 1 3 is the fault line, line l 1 The length is 12km, the line l 2 The length is 18km, the fault line l 3 The length of each section is 2km, and the line parameters are LGJ-240 type wires; the arc suppressing coil adopts the overcompensation method, and the compensation degree is 10%; In the phase-to-ground fault section, in this embodiment, 6 distribution automation terminals 2 are used to respectively collect the current i of each monitoring point of the feeder ka i kb and i kc ,k=1,2,...,6, 6 distribution automation terminals 2 simultaneously calculate the three-phase additional state current Δi of the feeder monitoring point ka , Δi kb and Δi kc , and then calculate the fault instantaneous positive sequence current at the feeder monitoring point real part of Get...
Embodiment 2
[0077] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that for a small current grounding system with an initial voltage phase angle of 90°, the grounding resistance is transformed to calculate the single-phase grounding fault section; in the simulation environment of MALAB, two adjacent monitoring points are The amplitude difference of the internal current is shown in Table 2.
[0078] Table 2
[0079]
[0080]
[0081] In the experiment, the main power distribution station 1 judges the single-phase ground fault section of the feeder through the difference of the magnitude of the fault instantaneous positive sequence current real part power frequency component of two adjacent monitoring points on the feeder, which is still the third monitoring point and the first The amplitude difference of the real part power frequency component of the fault instantaneous positive sequence current at the four monitoring points is the largest. Therefore, the feeder section be...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com