A method for detecting microorganisms in wood
A microbial and wood technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to purify strains, limit microbial research, and microbial identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Embodiment 1, a kind of method for detecting microorganisms in wood
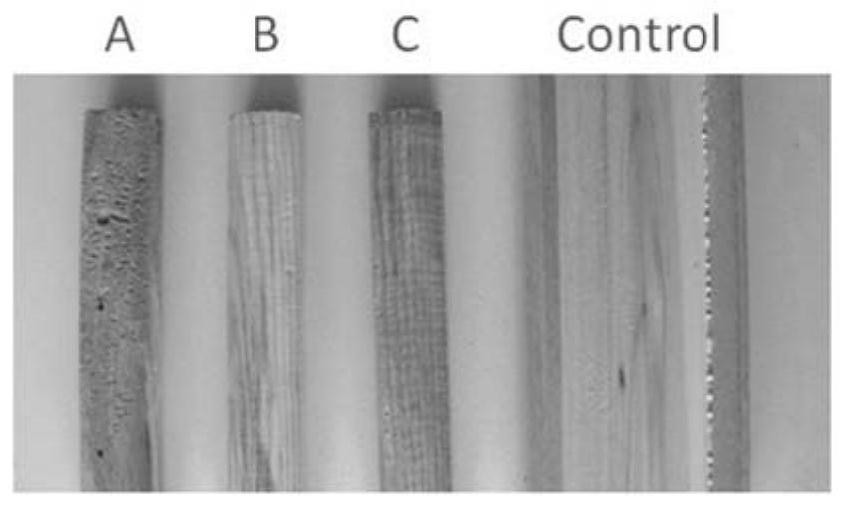
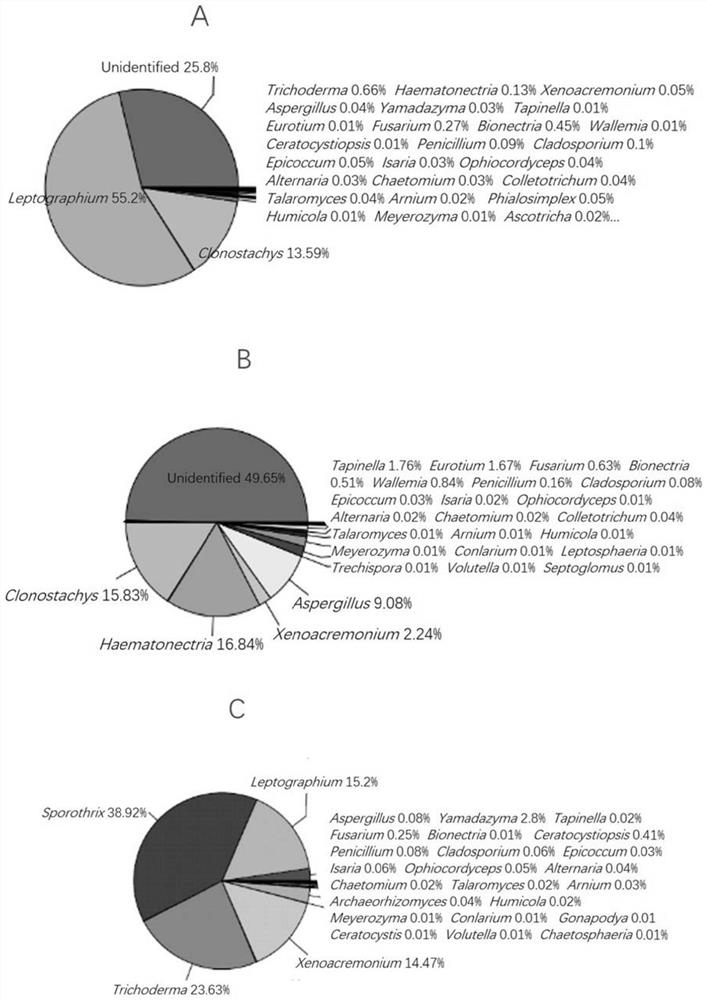
[0046] Three pieces of microbial spoilage and discoloration from different color changes (that is, wood decay and discoloration caused by microorganisms) are recorded as A, B and C ( figure 1 ) were treated according to the following methods, and these three woods all had typical biodegradation symptoms of discoloration:
[0047] 1. Collection of wood sawdust
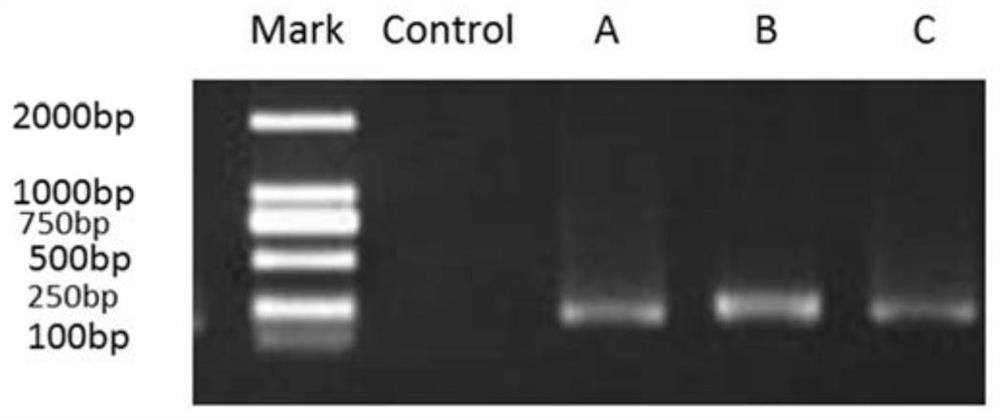
[0048] The wood is pretreated in a constant temperature and humidity box, and the moisture content of the wood is adjusted to about 20% to obtain the pretreated wood; the surface of the pretreated wood is sterilized with 75% ethanol aqueous solution to obtain the sterilized wood ;Select the position with typical biological deterioration symptoms in the sterilized wood, drill three positions with a hexagonal drill with a diameter of 5mm, collect the generated sawdust, and then collect each 0.1g sawdust as a portion and place it in a 1ml centrif...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com