Austenite low-temperature steel and preparation method thereof
A low-temperature steel and austenitic technology, which is applied in the field of low-temperature steel and its preparation, can solve the problems of complex preparation process and difficult implementation, and achieve the effects of cost reduction, excellent low-temperature impact toughness, and reduced use of Ni
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
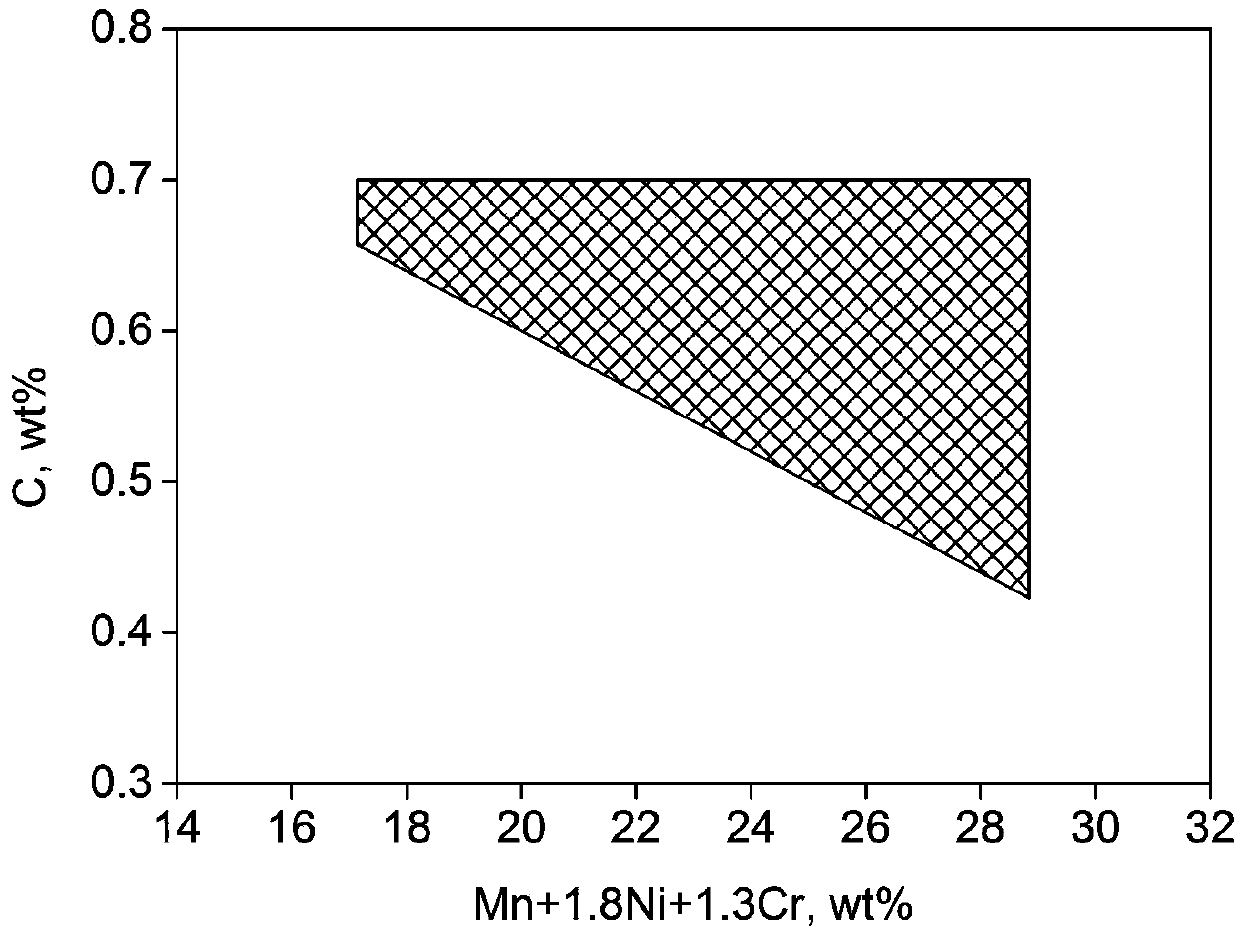
[0037] An austenitic low-temperature steel, its chemical composition and mass fraction are: 17.2% Mn, 1% Ni, 3.9% Cr, 0.57% C, 0.05% Nb, 0.21% Si, 0.1% Al, 0.05% N, the balance It is Fe and S and P impurity elements below 0.05%, 50C+Mn+1.8Ni+1.3Cr=52.57%.
[0038] A steel billet with a thickness of 150mm is heated to 1120°C and held for 180min; after heating, it is rolled, the final rolling temperature is 980°C, the deformation of each pass is 20%, the total deformation is 85%, and the thickness of the steel plate is 22.5mm; immediately after rolling, it is water-cooled to room temperature , The cooling rate is 23°C / s in the range of 400-850°C.
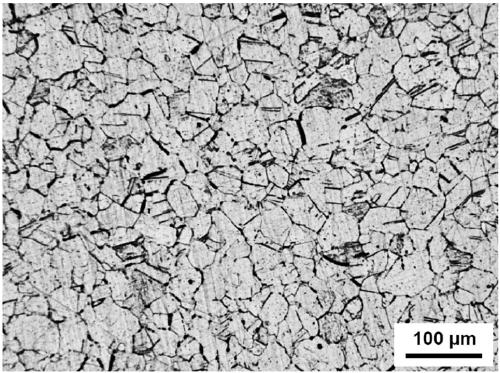
[0039] figure 2 Shown is the optical microstructure of low temperature steel, the structure is austenitic. The volume fraction of austenite is 99.4%, the average grain diameter is 63μm, almost no carbide, and the impact energy of Charpy impact test at -196℃ is 164J.
Embodiment 2
[0041] 19.8% Mn, 1.3% Ni, 4.9% Cr, 0.43% C, 0.1% Nb, 0.1% Si, 0.02% Al, 0.12% N, and the balance Fe and S, P impurity elements below 0.05%; 50C+Mn +1.8Ni+1.3Cr=50.01%
[0042] A steel billet with a thickness of 220mm is heated to 1050°C and held for 300min; after heating, it is rolled, the final rolling temperature is 960°C, the deformation of each pass is 15%, the total deformation is 75%, and the thickness of the steel plate is 55mm; immediately after rolling, it is water-cooled to room temperature, 400 The cooling rate in the range of ~850°C is 60°C / s.
[0043] The volume fraction of austenite is 99.6%, the average grain diameter is 75μm; there is almost no carbide, and the impact energy of Charpy impact test at -196℃ is 203J.
[0044] In this example, the contents of Mn, Ni, and Cr are close to the upper limit of the range, and the content of C is relatively low, but the total alloy content is 50C+Mn+1.8Ni+1.3Cr=50%, and a stable austenite structure can also be obtained. ...
Embodiment 3
[0046] 20% Mn, 1.25% Ni, 5% Cr, 0.7% C, 0.02% Nb, 0.6% Si, 0.3% Al, 0.015% N, and the balance of Fe and S, P impurity elements below 0.05%; 50C+Mn +1.8Ni+1.3Cr=63.75%.
[0047] A billet with a thickness of 80mm is heated to 1180°C and held for 65min; after heating, it is rolled, the final rolling temperature is 1020°C, the deformation of each pass is 22%, the total deformation is 90%, and the thickness of the steel plate is 8mm; immediately after rolling, it is water-cooled to room temperature, 400 The cooling rate in the range of ~850°C is 10°C / s.
[0048] The volume fraction of austenite is 98.5%, the average grain diameter is 71μm; there are very few carbides at the grain boundary, and the impact energy of Charpy impact test at -196℃ is 94J.
[0049] In this embodiment, the contents of Mn, Ni, and Cr are close to the upper limit of the range, and the content of C is also close to the upper limit of the range. Although the higher content of C and Cr increases the carbide i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com