SNP molecular markers related to traits of grass carp and their application
A technology of molecular markers and grass carp, applied in the direction of recombinant DNA technology, microbial measurement/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problems of typing cost and high cost of measuring traits, so as to save breeding time, high accuracy, The effect of speeding up the breeding process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1 Obtaining of SNP markers
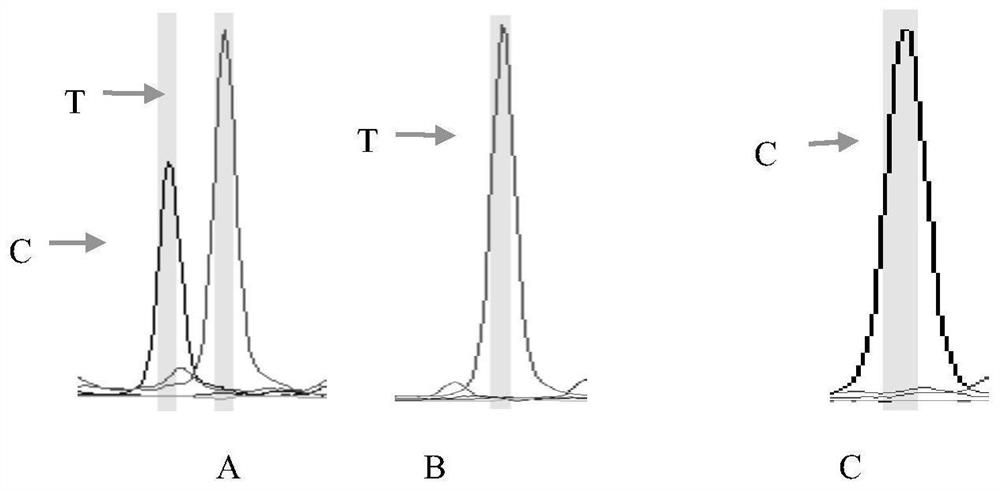
[0044]1. The grass carp gene sequence obtained by the sequencing of the present invention is as SEQ ID NO.1~SEQ ID NO.4, in the 159th base of SEQ ID NO.1, the 410th base of SEQ ID NO.1, the 410th base of SEQ ID NO.1 One SNP site was found at the 370th base and the 374th base of SEQ ID NO.1, the 159th base of SEQ ID NO.1, the 410th base of SEQ ID NO.1, and the 410th base of SEQ ID NO. 1 There are alleles C and T at the 370th base and the 374th base of SEQ ID NO.1, forming CC, TC, and TT genotypes.
[0045] The samples used in the analysis of growth traits (body weight) in the present invention are 25-month-old grass carp populations bred in the same batch and reared in the same pond. 298 grass carp were randomly selected for correlation analysis of growth traits (body weight), and 20 individuals with a very large body weight were selected. (average body weight is 2659±126.40g), and 20 extremely small individuals (average body weight ...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2 Screening of Growth Difference Markers
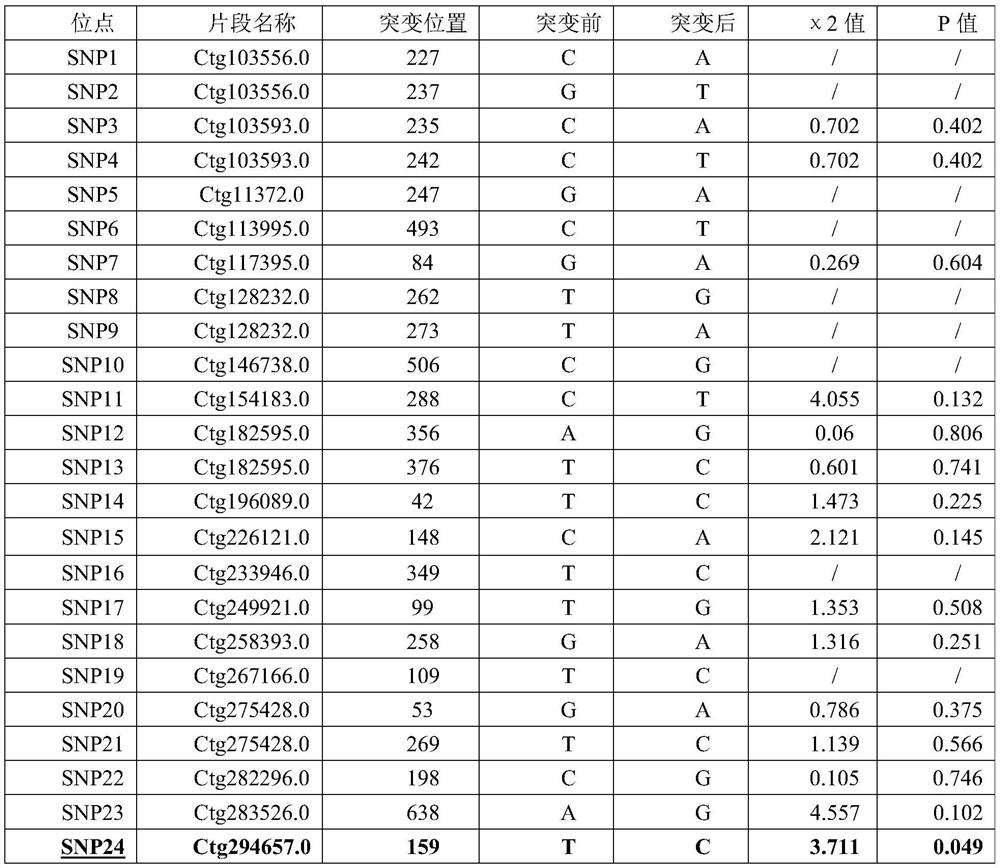
[0056] The 84 differential SNPs markers screened out were preliminarily verified by constructing 20 samples of extremely large individuals and 20 samples of extremely small individuals. Among the 84 selected SNPs loci, no SNP mutations were detected in 40 of them, and SNP mutations were detected in 44. The approach analysis of the difference between the 44 SNPs that detected the mutant type in the extremely large individual group and the extremely small individual group showed that there was a significant difference between SNP24 and SNP36 (P<0.05), and a very significant difference between SNP37 and SNP38 (P<0.01) (see Table 2).
[0057] Table 2 Markers in extreme group typing
[0058]
[0059]
[0060]
[0061] Note: "_" means P<0.05 for this site.
Embodiment 3
[0062] Example 3 Verification of SNP markers associated with body weight in grass carp and body weight
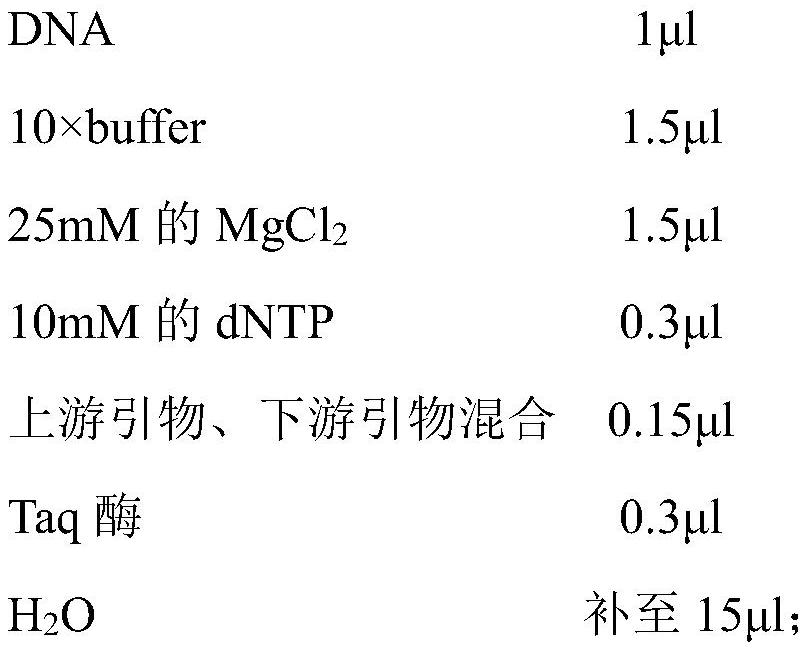
[0063] 1. Sample DNA Extraction
[0064] (1) Take 100ul of blood from the fish to be tested or 3mg of shredded fin ray tissue, add 0.5mL of lysate (10mmol / LTris-HCl; 0.1mol / L EDTA; 0.5% SDS; 30mg / L RNase; 100mg / L Proteinase K, pH 8.0), digested at 55°C for 1 hour with gentle shaking from time to time.
[0065] (2) Add an equal volume of phenol / chloroform / isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1), mix upside down, let stand at room temperature for 5 minutes, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 10 minutes, take the supernatant, and then wash with chloroform Extract once, let stand at room temperature for 5 minutes, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 10 minutes, and take the supernatant.
[0066] (3) Add 2 times the volume of absolute ethanol, let stand at room temperature for 10 minutes to precipitate DNA, and centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 10 minutes.
[0067] (4) Wash once with 70% ethanol, centrifuge...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com