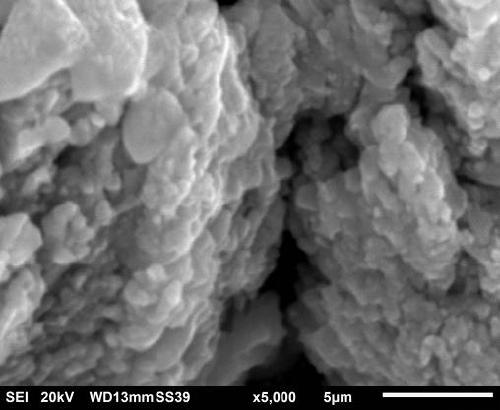
A soil solidification method for a sandy ground site
A soil solidification and foundation technology, which is applied in the field of soil solidification on sandy ground sites, can solve problems such as low solidification strength, low quality and effect, and insufficient strength of cement piles, so as to improve the solidification effect and the coating effect Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
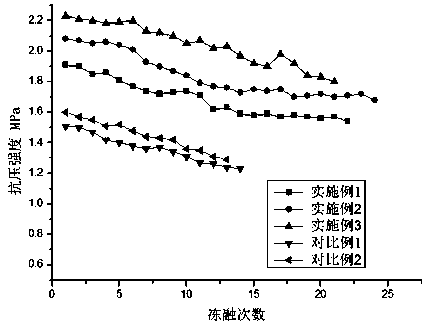
Embodiment 1
[0027] Preparation of temperature-changing polymer materials: According to parts by weight, 12 parts of N, N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate, 0.35 parts of 4-vinylpyridine, and 0.10 parts of crosslinking agent N, N-methylenebisacrylamide Parts, 0.12 parts of initiator azobisisobutyronitrile mixed, dissolved in 15 parts of dimethyl sulfoxide, heated to 65 ° C for 30 hours of reaction, after the reaction, the gel was taken out and soaked in deionized water to remove unreacted Complete monomers and impurities are obtained to obtain temperature-changing polymer materials.
[0028] Preparation of curing agent: The curing agent is made of the following components by weight percentage: 15% cement, 27% fly ash, 24% desulfurized gypsum, 12% quicklime, 10% aluminum sulfate, 6% polyacrylamide, high temperature change Molecular Materials 6%.
Embodiment 2
[0030] Preparation of temperature-changing polymer materials: According to parts by weight, 8 parts of N, N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate, 0.3 parts of 4-vinylpyridine, and 0.05 parts of crosslinking agent N, N-methylenebisacrylamide Parts, 0.1 parts of initiator azobisisobutyronitrile mixed, dissolved in 12 parts of dimethyl sulfoxide, heated to 50 ° C for 20 hours of reaction, after the reaction, the gel was taken out and soaked in deionized water to remove unreacted Complete monomers and impurities are obtained to obtain temperature-changing polymer materials.
[0031] For the preparation of the curing agent, prepare the raw materials according to the following percentages by weight: 20% of cement, 26% of fly ash, 24% of desulfurized gypsum, 12% of quicklime, 7% of aluminum sulfate, 5% of polyacrylamide, 6% of temperature-changing polymer material %.
Embodiment 3
[0033] Preparation of temperature-changing polymer materials: According to parts by weight, 10 parts of N, N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate, 0.32 parts of 4-vinylpyridine, and 0.06 parts of crosslinking agent N, N-methylenebisacrylamide Parts, 0.11 parts of initiator azobisisobutyronitrile mixed, dissolved in 13 parts of dimethyl sulfoxide, heated to 55 ° C for 25 hours of reaction, after the reaction, the gel was taken out and soaked in deionized water to remove unreacted Complete monomers and impurities are obtained to obtain temperature-changing polymer materials.
[0034] The preparation of the curing agent, the curing agent is made of the following components by weight percentage: 19% cement, 29% fly ash, 23% desulfurized gypsum, 9% quicklime, 9% aluminum sulfate, 6% polyacrylamide, high temperature Molecular Materials 5%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| water content | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com