Mismatched fluorescence tolerance real-time quantitative PCR method for detecting multiple pathogens
A real-time quantification of pathogens, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of primer and template mismatch, increase the difficulty of detection, error detection results, etc., to achieve maximum convenience and detection results Accurate and reliable, easy and fast detection operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
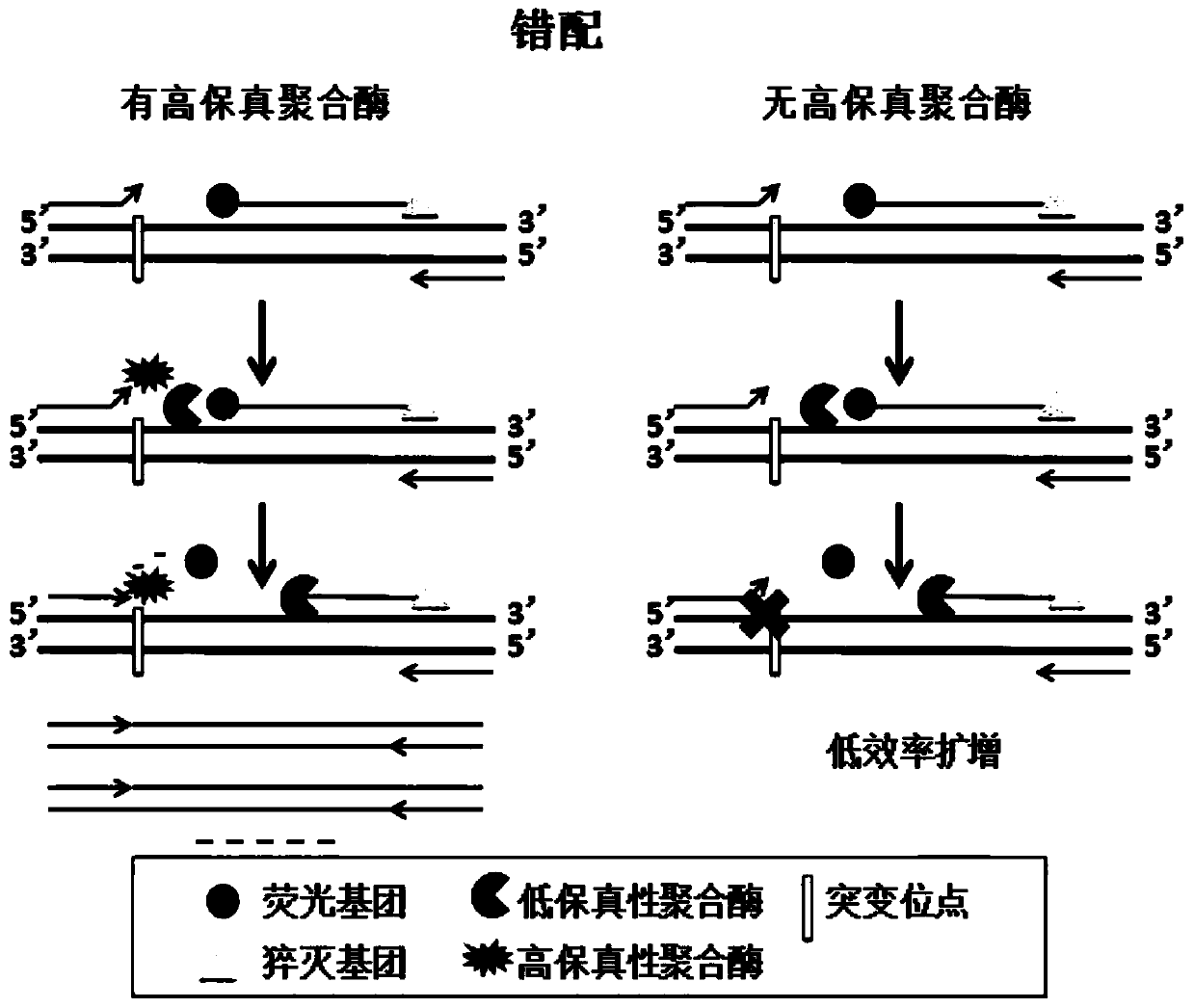
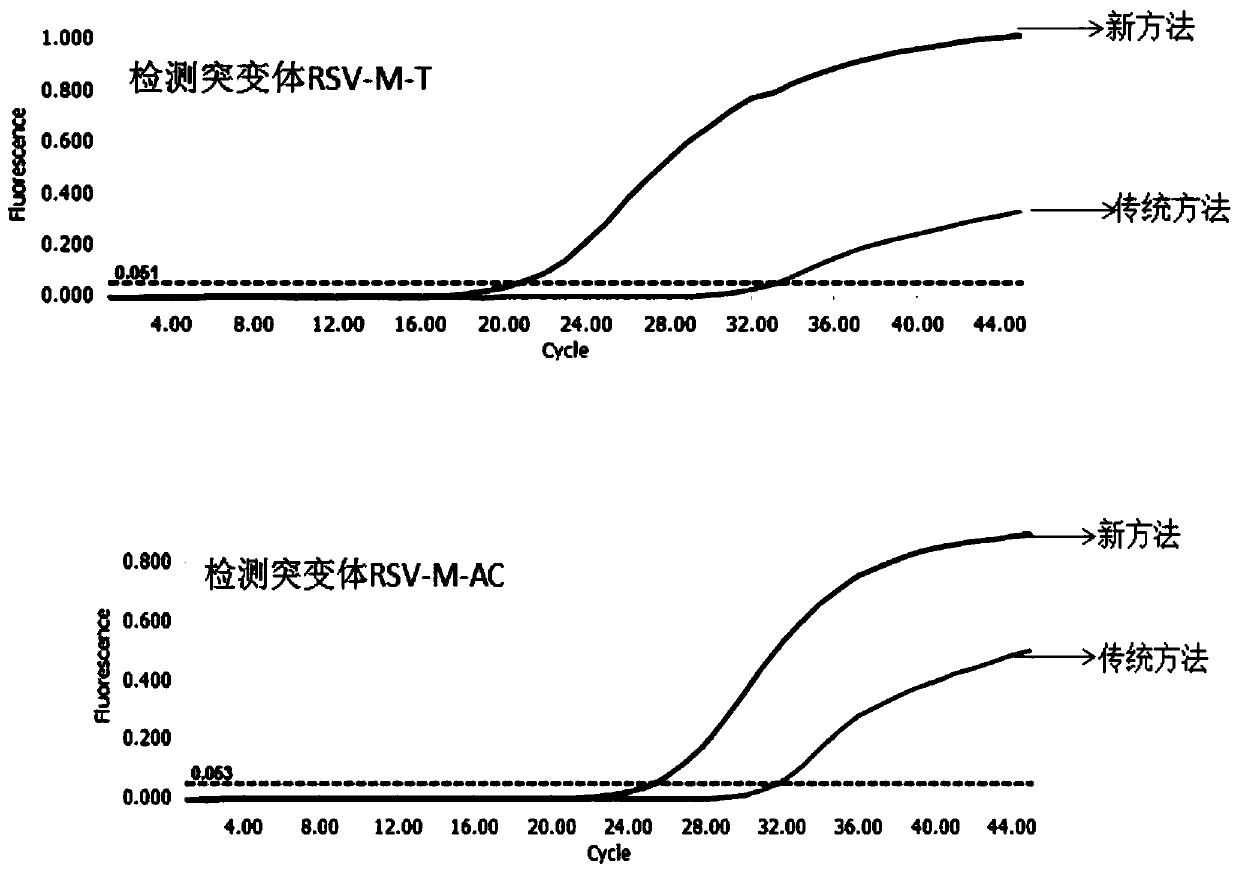
[0048] Example 1. Detection of RSV wild-type templates and mutant templates based on common primer pairs, a small amount of high-fidelity DNA polymerase and non-high-fidelity DNA polymerase.
[0049] This embodiment has obtained RSV virus wild-type template (RSV-W, SEQ ID NO.1), made 2 templates (RSV-M-T, SEQ ID NO.2) and (RSV-M- AC, SEQ ID NO.3), the mutation sites are the template positions corresponding to the 3' end of the upstream primer, and one common upstream primer (RSV-F, SEQ ID NO.5) and one common downstream primer (RSV-F, SEQ ID NO.5) were designed ( RSV-R, SEQ ID NO.6) and probe (RSV-P, SEQ ID NO.7), the 5' end of the probe is labeled with VIC fluorescent group, and the 3' end is labeled with MGB quenching group. Common upstream primers, downstream primers, and probes are perfectly complementary to wild-type templates.
[0050] Use non-high-fidelity DNA polymerase (Taq) and high-fidelity DNA polymerase (Q5) to apply to the amplification reaction. The reaction sy...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Example 2. Based on two common primers and one probe, a large amount of non-high-fidelity DNA polymerase and a small amount of high-fidelity DNA polymerase are used to detect Boca virus.
[0059] In this example, a recombinant plasmid inserted into a partial fragment of Boca virus was obtained as a wild-type template (BOV-W, SEQID NO.4), and two upstream primers (bov-F-M1, bov-F-M1, bov -F-M2, SEQ ID NO.8, SEQ ID NO.9), 1 common upstream primer (bov-F, SEQ ID NO.10) and 1 common downstream primer (bov-R, SEQ ID NO.11), The first T at the 3' end of one of the upstream primers was mutated to A (bov-F-M1), and the first and second T at the 3' end of the other upstream primer were both mutated to A (bov-F-M2). The 5' end of the needle is labeled with the FAM fluorophore, and the 3' end is labeled with the BHQ1 quencher. The common upstream primer, downstream primer and probe (bov-P, SEQ ID NO.12) are fully complementary to the wild-type template (BOV-W).
[0060] Use non-...
Embodiment 3
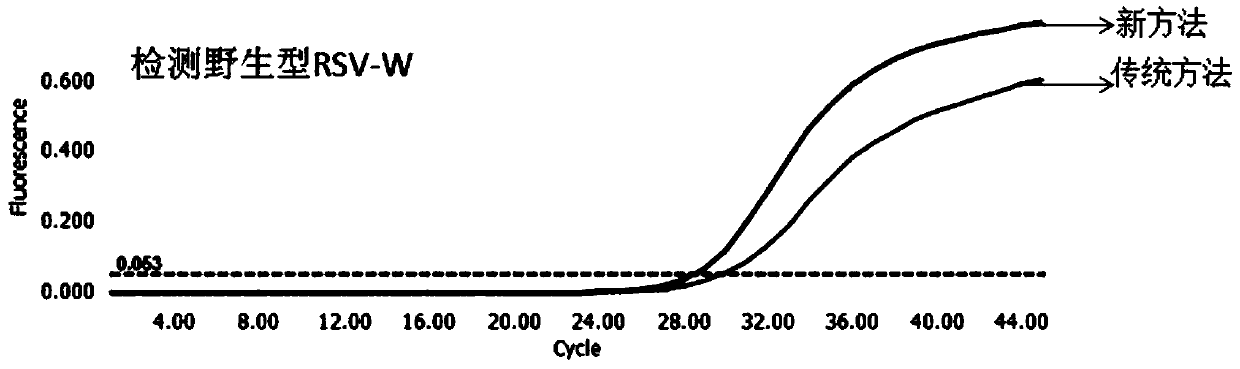
[0068] Example 3. Using the new method and the traditional Taqman method to simultaneously detect 10 RSV positive clinical samples.
[0069] The present embodiment has obtained 20 parts to determine the nucleic acid of the clinical sample of positive RSV, with the designed RSV upstream primer (RSV-F, SEQ ID NO.5), downstream primer (RSV-R, SEQ ID NO.6) and The probe (RSV-P, SEQ ID NO.7) was detected by qRT-PCR on 10 samples using the new method and the traditional Taqman method.
[0070] The new method uses non-high-fidelity DNA polymerase (Taq) and high-fidelity DNA polymerase (Q5) for amplification reactions. The reaction system and procedures are as follows:
[0071]
[0072] The reaction conditions are as follows:
[0073]
[0074] The traditional Taqman method does not add Q5, and the remaining components and reaction conditions of the system are the same as the new method.
[0075] According to the above reaction system and reaction conditions in ROCHE The reac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com