Non-metallic heating device for cooking
A heating device, non-metallic technology, applied in heating devices, applications, kitchen utensils, etc., can solve the problem of low cost, achieve good compactness, good chemical stability, and good acid and alkali resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0098] 1. Preparation of glass powder: the proportion of glass powder is SiO 2 29%, Al 2 o 3 14%, B 2 o 3 7%, CaO 45%, TiO 2 3%, ZrO 2 2%, the above components were melted at 1450 ° C, quenched in water, dried, and crushed to obtain D 50 = 2.5 μm powder, that is, to obtain glass powder;
[0099] 2. Preparation of the first glass powder coating: 38% of organic components and 62% of glass powder. The above components are fully stirred and dispersed evenly by a three-roller machine to obtain a coating with a viscosity of 1 to 2 pa.s;
[0100] 3. Clean the surface of the heating plate of the heating base, and apply the first glass powder coating evenly on the surface of the heating plate by spraying or printing;
[0101] 4. Dry the heating plate coated with the first glass powder coating at 150°C, and then sinter at 850°C for 10 minutes to obtain a translucent coating with a thickness of about 20-40 μm;
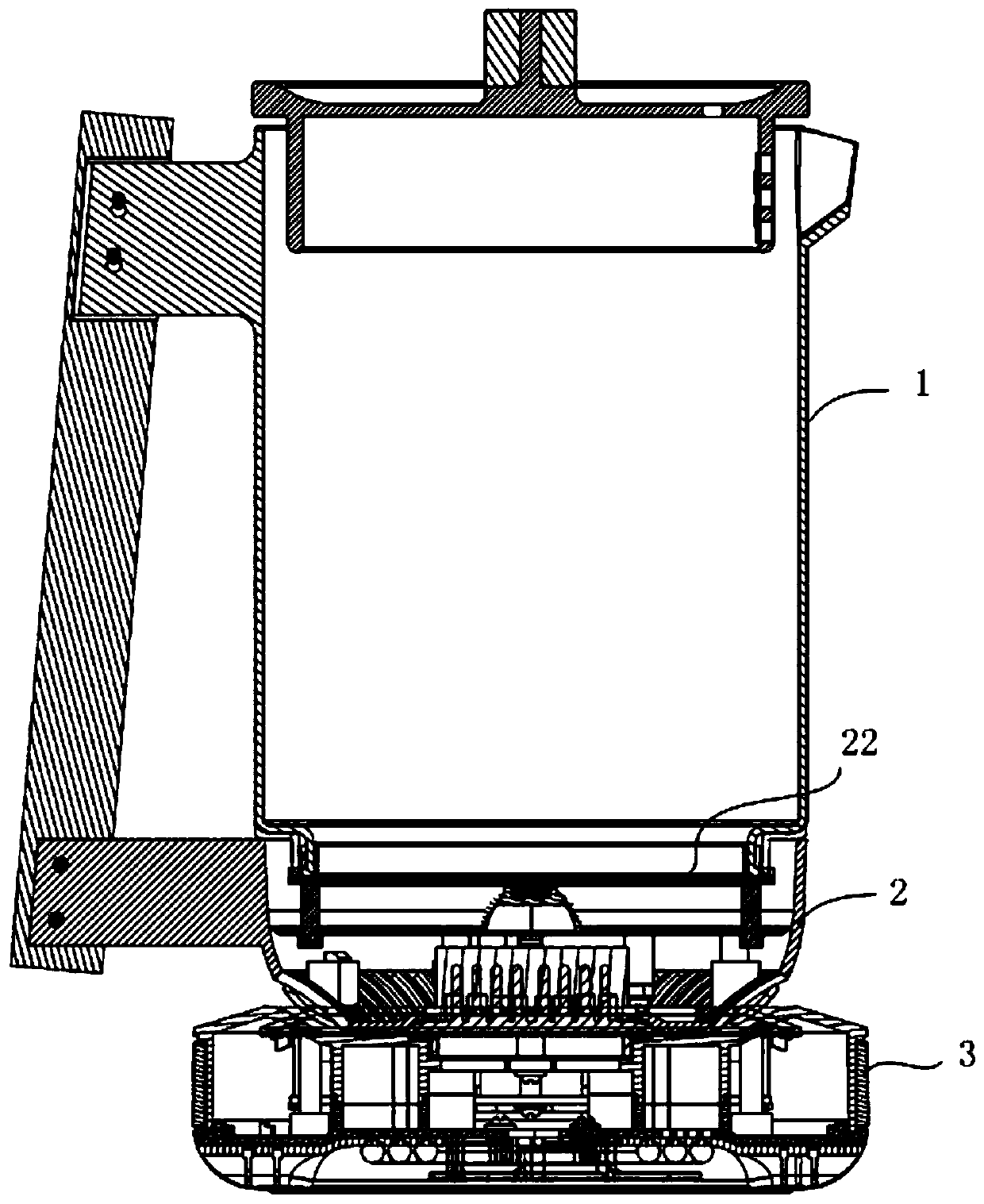
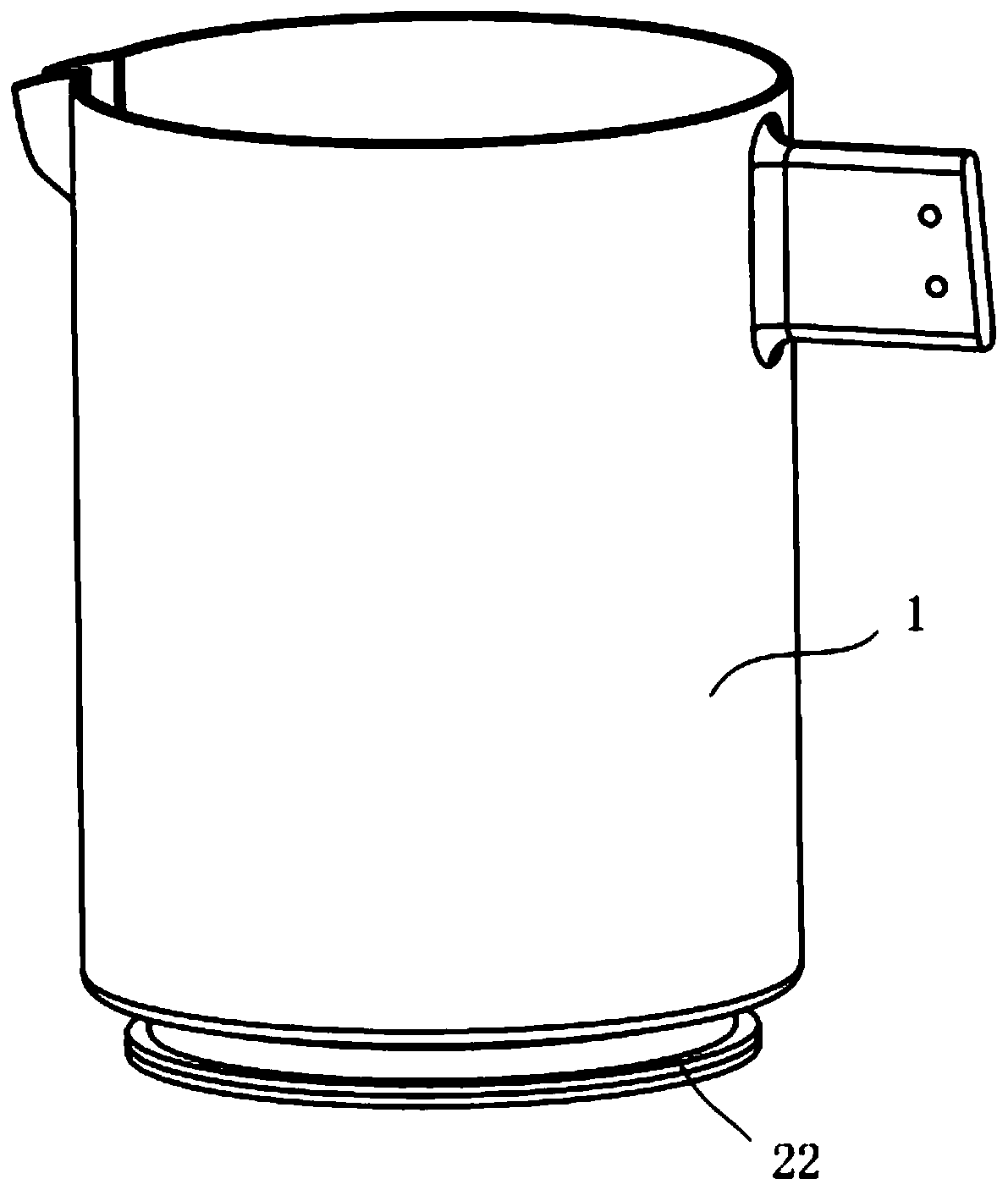
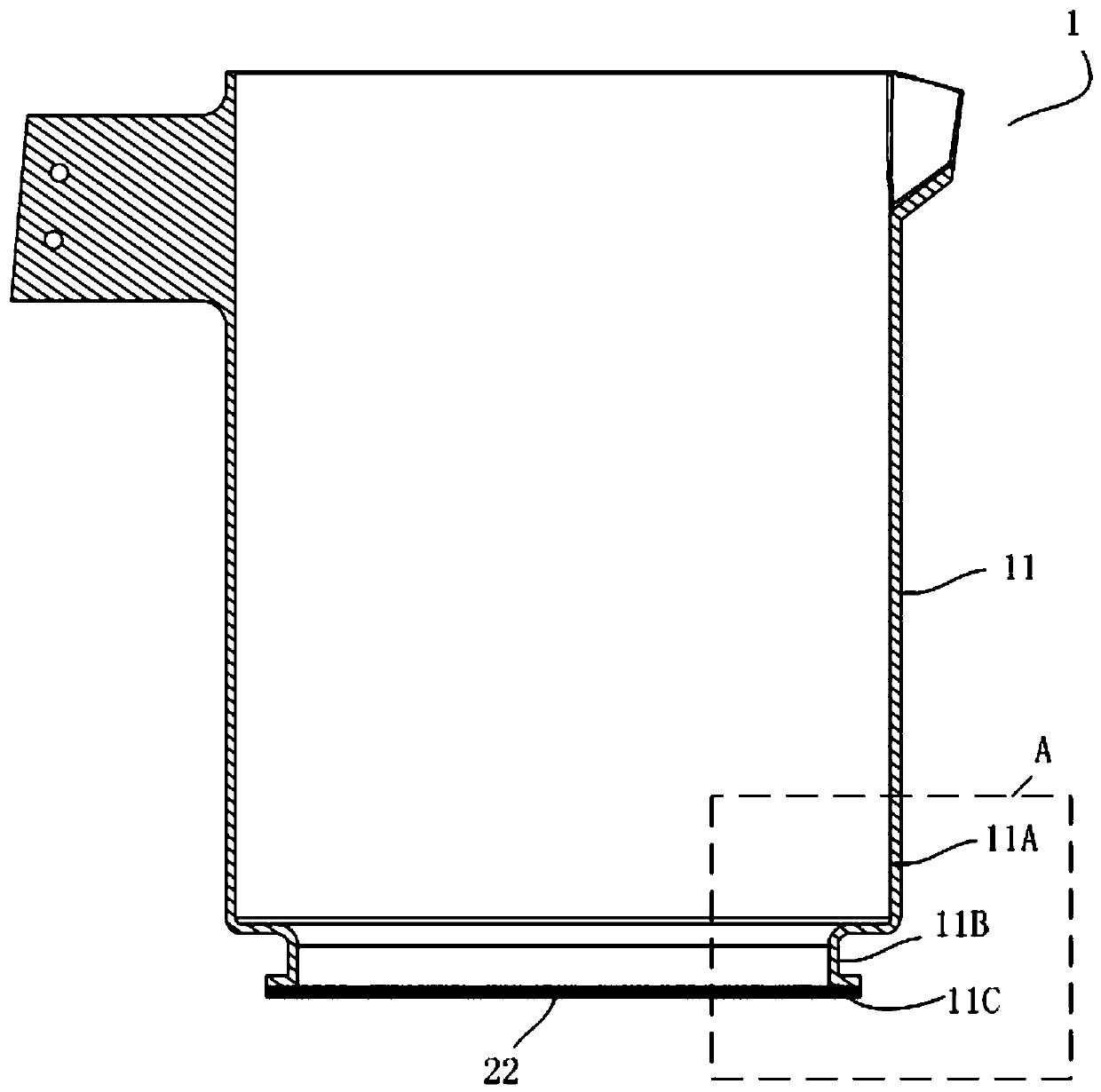
[0102] 5. Connect the non-metallic pot body and the heating base ...
Embodiment 2
[0104] 1. Preparation of glass powder: the proportion of glass powder is SiO 2 32%, Al 2 o 3 12%, B 2 o 3 7%, CaO 45%, TiO 2 2%, ZrO 2 2%, the above components were melted at 1450 ° C, quenched in water, dried, and crushed to obtain D 50 = 2.5 μm powder, that is, to obtain glass powder;
[0105] 2. The proportion of functional mixture: tungsten carbide 60%, iron oxide 25%, zinc oxide 15%;
[0106] 3. Preparation of the first glass powder coating: 40% of organic components, 50% of glass powder, and 10% of functional mixture, fully stir the above components, and disperse evenly through a three-roller machine to obtain a coating with a viscosity of 1-2pa.s;
[0107] 4. Clean the surface of the heating plate of the heating base, and apply the first glass powder coating evenly on the surface of the heating plate by spraying or printing;
[0108] 5. Dry the heating plate coated with the first glass powder coating at 150°C, and then sinter at 850°C for 10 minutes to obtain...
Embodiment 3
[0111] 1. Preparation of glass powder: the proportion of glass powder is SiO 2 5%, Al 2 o 3 30%, B 2 o 3 8%, CaO 50%, TiO 2 3%, ZrO 2 3%, K 2 O1%, the above components were melted at 1250 ° C, quenched in water, dried, and crushed to obtain D 50 = 2.5 μm powder, that is, to obtain glass powder;
[0112] 2. Preparation of the first glass powder coating: 25% of organic components and 75% of glass powder, fully stir the above components, and disperse evenly through a three-roller machine to obtain a coating with a viscosity of 20-30pa.s;
[0113] 3. Clean the surface of the heating plate of the heating base, and apply the first glass powder coating evenly on the surface of the heating plate by screen printing;
[0114] 4. Dry the heating plate coated with the first glass powder coating at 150°C, and then sinter at 650°C for 10 minutes to obtain a translucent coating with a thickness of about 20-40 μm;
[0115] 5. Connect the non-metallic pot body and the heating base ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com