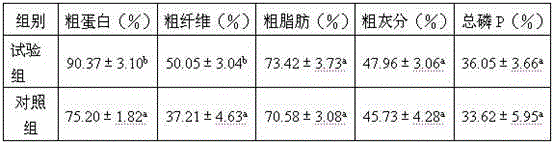
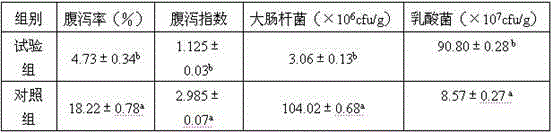
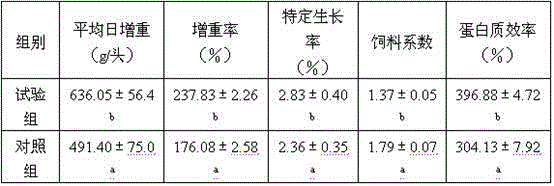
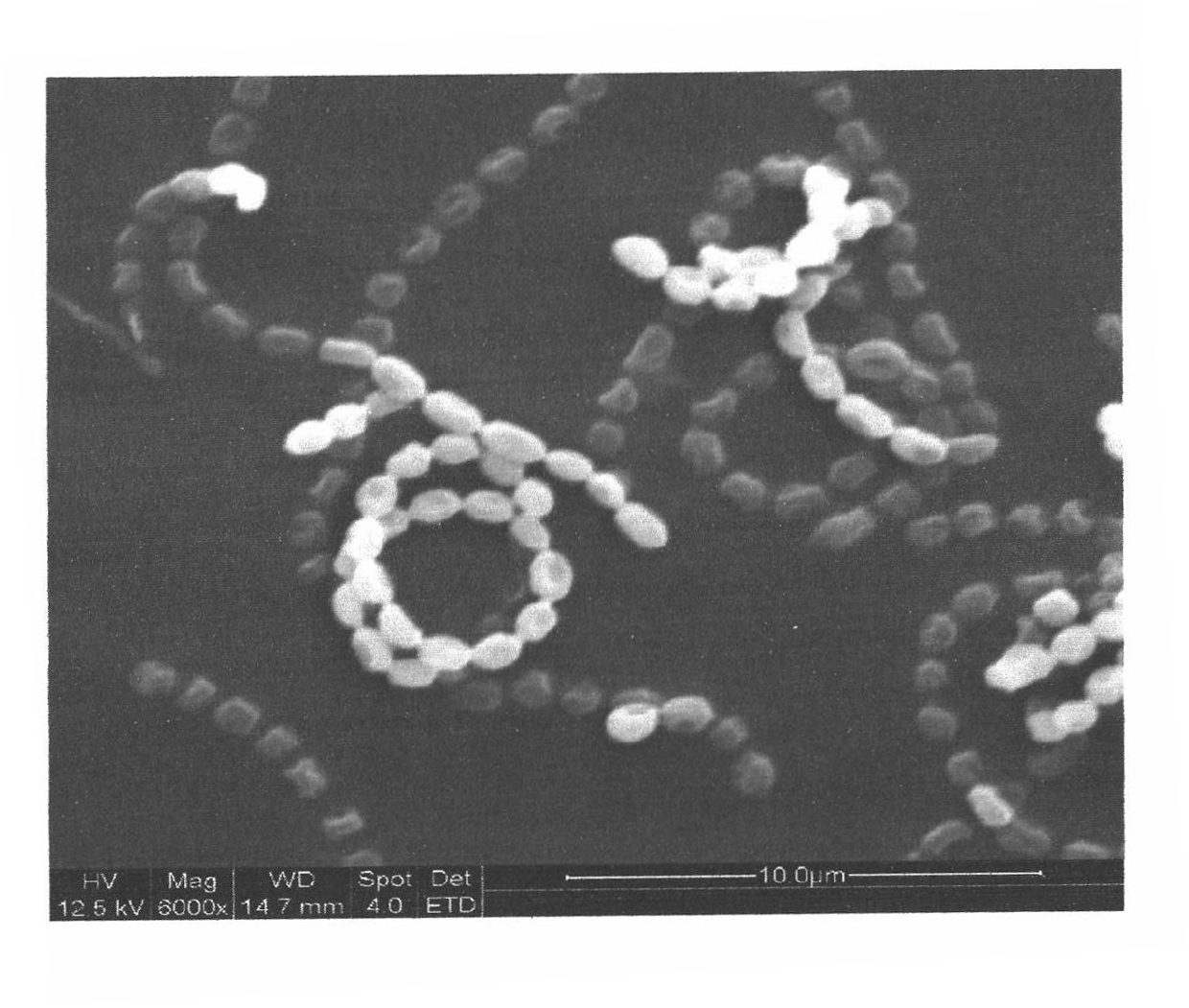
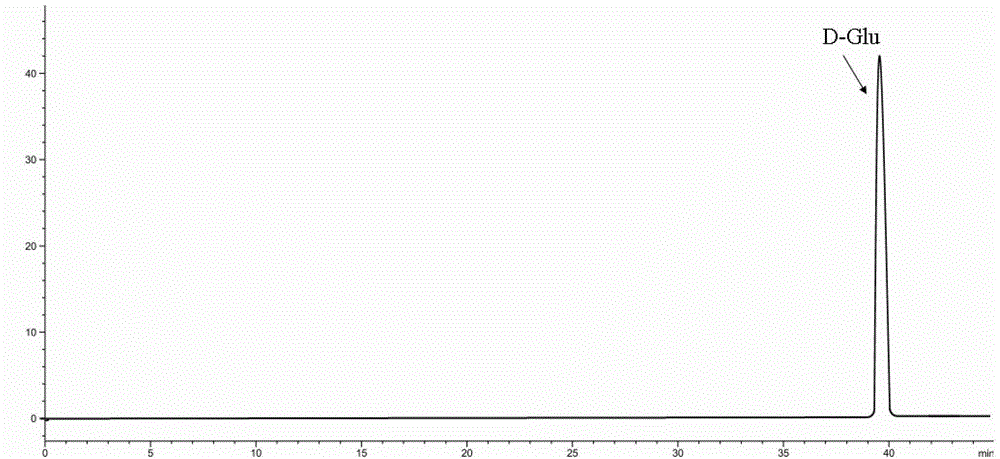
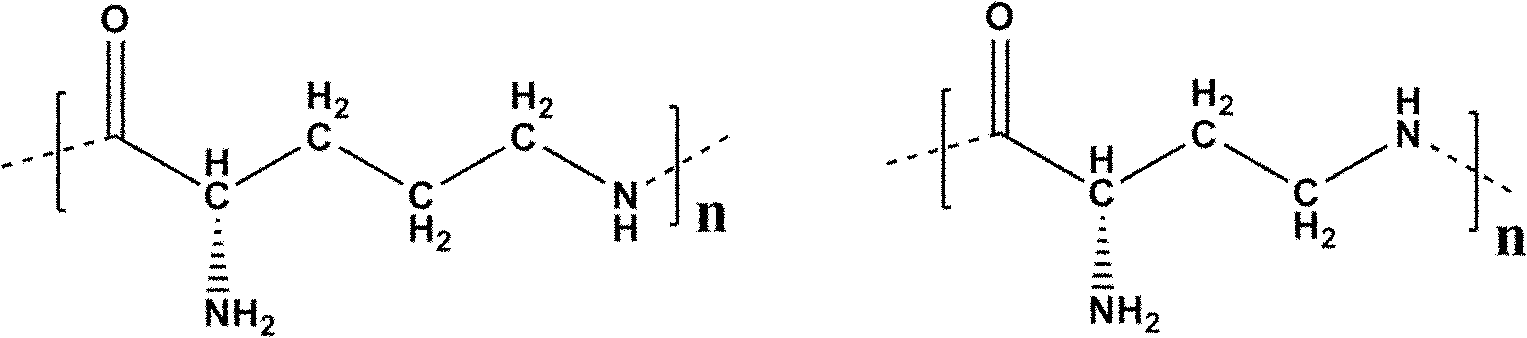Patents
Literature
46results about How to "Extensive culture conditions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bacillus and its use of preparation of gama-polycysteine
InactiveCN1644677AGood hygroscopicityGood moisturizing effectBacteriaFermentationOrganic solventNitrogen source
Production of gama-polyglutamic acid by fermentation is carried out by: culturing bacillus subtills zju-7 strain, i.e., CGMCC No. 1250, in medium with carbon and nitrogen sources, glutamic acid, MgSO4, NaCl and K2HPO4 to obtain ferment liquid, and making it to pass organic solvent settlement and dialysis. The process is easy, yields highly, and costs low with quality products.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Process of preparing propionic acid and coproducing vitamin B12 with Propionibacterium freudenreichii NX-4
InactiveCN101045910AEasy to operateExtensive culture conditionsBacteriaFermentationInorganic saltsPropanoic acid
The present invention discloses one kind of Propionibacterium freudenreichii NX-4 and the production process of propionic acid and vitamin B12 therewith. Propionibacterium freudenreichii NX-4 is preserved in the preservation number of CCTCC No. M 207015. Through inoculating Propionibacterium freudenreichii into culture medium containing carbon source, nitrogen source, inorganic salt and water, and static culturing, propionic acid or coproduced propionic acid and vitamin B12 may be prepared. The strain can utilize several kinds of carbon source and nitrogen source, and has extensive culture condition, simple operation, high propionic acid yield and low production cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Composite bacillus preparation containing three strains, preparation method of composite bacillus preparation and application of composite bacillus preparation to ecological breeding
InactiveCN104480052APromote Microecological BalancePromote digestion and absorptionBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffEcological environmentBacillus megaterium
The invention provides a composite bacillus preparation containing three strains, a preparation method of the composite bacillus preparation and application of the composite bacillus preparation to ecological breeding, and belongs to the technical field of microorganism and feed additives. Bacillus coagulans, butyric acid clostridia and bacillus megaterium are used as fermentative strains respectively, and large-scale, low-cost and high-density fermentation production of spores is conducted through step-by-step magnification; three live bacterium preparations are prepared by mixing bacterial sludge with the spores and dry starch; the three live bacterium preparations are matched according to the equal weight ratio, the composite bacillus preparation is obtained, and the concentration of the spores reaches more than 1*108-109 cfu / g; the composite bacillus preparation serves as a microorganism and feed additive to be added to farmed animal feed according to the mass ratio ranging from 0.02% to 0.5%. The composite bacillus preparation is simple and stable in process, low in cost, high in spore content and environment tolerance, easy to store and high in survival rate; the purposes of composition and synergism are achieved through the collaborative supplementary effects of different bacilli in the aspect of micro-ecology adjustment, growth of farmed animals is promoted, the feed utilization rate and feed rewards are increased, diarrhea is prevented and reduced, and the breeding ecological environment is improved.
Owner:江苏省苏微微生物研究有限公司 +3
Streptomyces albulus and application thereof in preparing polylysine and poly-diamino-butyric acid
ActiveCN102174448AEasy to operateExtensive culture conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesStreptomyces albulusMicrobiology
The invention discloses streptomyces albulus. The streptomyces albulus has a classification name of streptomyces albulus PD-1 and is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection with a registered number of CCTCC NO: M2011043 and a preservation date of 21st, February, 2011. The invention also discloses an application of the streptomyces albulus in preparing polylysine and poly-diamino-butyric acid. In the invention, the strain of the streptomyces albulus serves as the fermentation strain; primary and secondary seed amplification culture and fermentation production are carried out; and after extraction, the output of the polylysine can reach more than 30g / L, and the output of the poly-diamino-butyric acid can reach more than 12g / L. The strain features applications of carbon sources and hydrogen sources, extensive culture conditions, convenience and simpleness in operation, high output of polylysine and poly-diamino-butyric acid and low production cost.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Corynebacterium glutamicum and method for preparing L-ornithine and salts thereof by using same
ActiveCN101955901AThe fermentation process is simpleEasy to operateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-OrnithineCulture mediums
The invention belongs to the field of fermentation engineering and discloses corynebacterium glutamicum and a method for preparing L-ornithine and salts thereof by using the same. The corynebacterium glutamicum is corynebacterium glutamicum 1006 with the collection number of CGMCCNo.3663. The method comprises the following steps of: culturing the corynebacterium glutamicum in a culture medium containing carbon sources, nitrogen sources and inorganic salts at the temperature of between 28 and 30 DEG C to generate L-ornithine fermentation liquor; removing the thalli of the fermentation liquor by using ceramic membranes of 1 to 15 ten thousand Dalton; separating the fermentation liquor by using cation exchange resins to obtain L-ornithine solution; and decoloring and crystallizing the L-ornithine solution by a hydrochloric acid and ethanol method to obtain L-ornithine hydrochloride. The method has the advantages of simple thallus cultivation and contribution to industrialized mass production. The accumulation of the L-ornithine prepared from the corynebacterium glutamicum reaches 35 to 45g / L.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Epicoccum nigrum DB3 bacterial strain as well as preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN102329738AExtensive culture conditionsGood heat resistanceFungiMicroorganism based processesSea grassEpicoccum nigrum
The invention relates to an epicoccum nigrum DB3 bacterial strain as well as a preparation and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of: 1, placing rotten sea grass in an enrichment culture medium, standing and culturing at room temperature, then coating the enrichment culture medium in a separation culture medium, standing and culturing at a temperature of 30 DEG C for 1-4 days to obtain a wild type flax biological treatment bacterial strain; 2, inoculating the bacterial strain obtained from the step 1 into a flax lignin nutrition culture medium, culturing at a temperature of 28 DEG C for 72 hours; and 3, selecting the bacterial strain with the capacity of degrading the lignin from the flax lignin nutrition culture medium to obtain the epicoccum nigrum DB3 bacterial strain. The epicoccum nigrum DB3 bacterial strain can be applied to a process for preparing spinning flax, hemp, jute or red ramie fibers through peroxide degumming. The epicoccum nigrum DB3 bacterial strain has the characteristics of short growth period, low possibility of being polluted, low treatment cost, mild reaction conditions, strong pollution resistance capacity, good heat-resistant performance, no environment pollution and good quality of the treated fibers. The preparation method has a simple process and is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Bacillus subtilis for highly producing D-ribose and co-producing acetoin
InactiveCN101974444AAvoid damageHigh mutation rateBacteriaMutant preparationBacterial strainButanediol
The invention discloses a bacillus subtilis for highly producing D-ribose and co-producing acetoin, which is preserved in a China general microbiological culture collection center with CGMCC No.3720 and the preservation data of April eighth, 2010. The invention also discloses a method for producing the D-ribose and co-producing the acetoin by fermenting the bacillus subtilis. The selected bacterial strains can produce produce the D-ribose and co-produce the acetoin by using the fermentation of a plurality of types of carbon and nitrogen sources, the operation is convenient and simple, the conditions of culture are extensive, and the industrialization is easy. In the invention, an organic acid is added to a fermentation medium, therefore, the yield of the D-ribose is improved by 64.5g / L compared with the original strains, and the acetoin is improved by 17.3g / L. The bacillus subtilis has higher capability for synthetizing the D-ribose and the acetoin, and the yield of reduced by-products of 2,3-butanediol of the acetoin is low.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Sphingomonas sp. and application in preparation of rhamsan gum
ActiveCN103013863AEasy to operateExtensive culture conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesInorganic saltsMicroorganism
The invention discloses sphingomonas sp. The sphingomonas sp. is named as sphingomonas sp. PG-8 and was collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), the registration number is CGMCC NO. 6833, and the collection data is November 15th, 2012. The invention also discloses application of the sphingomonas sp. in preparation of rhamsan gum. The strain is cultured in a culture medium containing carbon sources, nitrogen sources and inorganic salts, and 5 to 50g / L of rhamsan gum can be accumulated under optimized conditions. The strain can be cultured by using multiple carbon sources and nitrogen sources, the culture conditions are extensive, the operation is convenient and simple, the yield of the rhamsan gum is high, the production cost is low, and the rhamsan gum can be widely applied in the fields of food addition, petroleum drilling and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Streptomyces griseofuscus strain and method for preparing epsilon-polylysine and salt thereof by utilizing same
ActiveCN102086441ABroad-spectrum antibacterialNo toxicityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEpsilon-PolylysineFiltration
The invention discloses Streptomyces griseofuscus LS-H1, namely CCTCC M 209211, and a method for preparing epsilon-polylysine and salt thereof by utilizing the strain. The Streptomyces griseofuscus LS-H1 is the strain obtained through screening; and the epsilon-polylysine at the concentration of between 0.7 and 20g / L can be accumulated under optimum conditions by culturing the Streptomyces griseofuscus LS-H1 in a culture medium containing a carbon source and a nitrogen source. After thalluses are removed from a zymotic fluid through centrifugation or filtration, the epsilon-polylysine and the salt thereof are obtained through the separation by an ion exchange method. The method is simple in the culture of the thalluses, and is favorable for industrialized mass production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Arthrobacter mutant strain, method for producing lactase from mutant strain and method for preparing lactulose by using lactase
InactiveCN102168028ANot generatedHigh purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCatalytic methodLactase
The invention belongs to the technical fields of food and biology, and discloses an Arthrobacter mutant strain (Arthrobacter sp.jnsb-2), a method for producing lactase by fermentation culturing of the mutant strain and a catalytic method for synthesizing lactulose from lactose and levulose by using the lactase as a catalyst. In the invention, the Arthrobacter mutant strain jnsb-2 is used as the strain of which the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M209210, and is subjected to fermentation culturing on a fermentation culture medium composed of a carbon source, a nitrogen source and inorganic salt, thus obtaining the lactase; and by using the lactase as a catalyst, lactose and levulose can be used as substrates and converted into the lactulose by an enzyme method. The lactase produced by the fermentation of the strain has the advantages of extensive culturing conditions, short enzyme production cycle and convenient operation process; and by using the enzyme method to convert the lactase into the lactulose, the defects that the product is easy to degrade and the colored byproduct is difficult to remove in the lactulose preparation process based on the chemical method are overcome, and a high product purity is achieved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Treatment method of slime water
InactiveCN104326625AExtensive culture conditionsPromote degradationWaste water treatment from quariesMultistage water/sewage treatmentMicroorganismFlocculation
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial application and relates to a method of floating and separating clay minerals and micro-fine pea coal in slime water which is flocculated by using a microbial flocculant. The main process of the method comprises preparation of the microbial flocculant, flocfloatation by microorganisms and flocculating settling by microorganisms. The method is characterized by specifically comprises the following steps: adding the microbial flocculant into 20-400g / L slime water; adjusting the pH of ore pulp and adding a flotation separation agent for floatation separation in a floatation separation column; further adding micro-fine pea coal microbial flocculant into the ore pulp subjected to flotation seperation to realize flocculating settling; and finally, respectively recovering a flotation froth product and combustible micro-fine pea coal, wherein the ash content of the forth product is over 80%, the flocculation rate of the combustible micro-fine pea coal is over 80% and the ash content is less than 10%. According to the method provided by the invention, combustibles in the slime water can be recycled with a good microbial flocculation effect. Moreover, the microbial flocculant is extensive in culture condition, strong in degradability, environment-friendly and free of secondary pollution.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
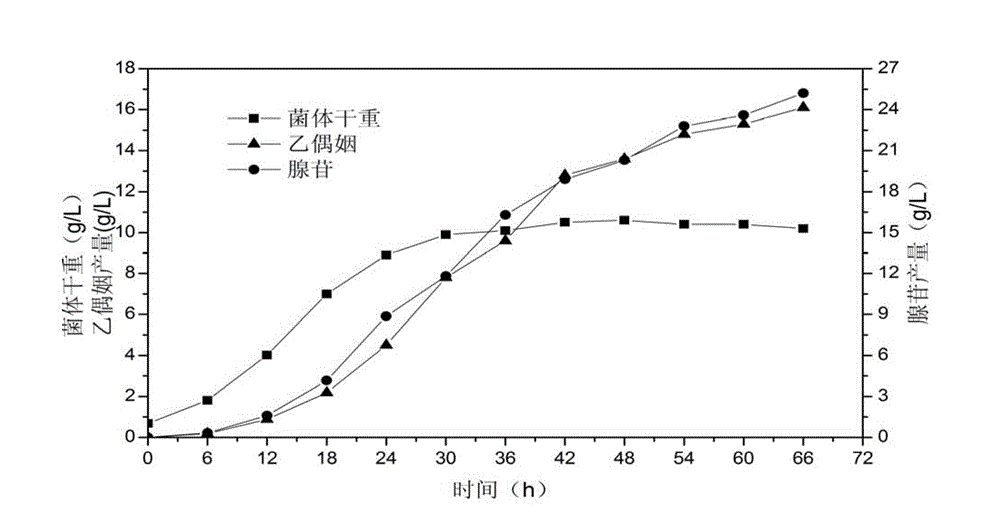
Application of Bacillus subtilis in high-yield adenosine and acetoin co-production
InactiveCN102876760AEasy to operateExtensive culture conditionsMicroorganism based processesFermentationAdenosineNitrogen source
The invention discloses application of Bacillus subtilis in high-yield adenosine and acetoin co-production. The Bacillus subtilis is CGMCC No. 4484. Screened strains can be fermented for adenosine production and acetoin co-production by multiple carbon sources and nitrogen sources. Yield of adenosine and acetoin can be evidently increased by adding sodium citrate into fermentation medium. Operation is convenient and simple, culture conditions are extensive, a higher level can be kept on a 5L fermentation tank, and potential of large-scale industrialization is provided.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH +1
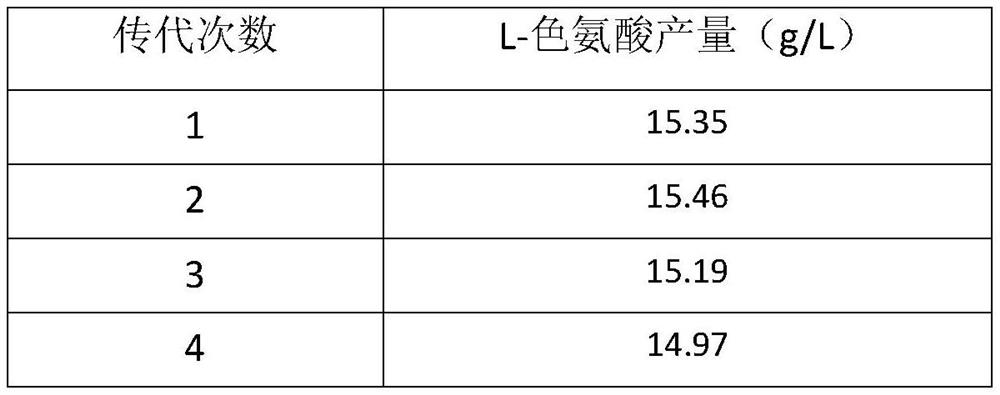
Escherichia coli and application thereof in fermentation production of L-tryptophan
PendingCN114480173AImproved strain stabilityIncreased acid production and conversionBacteriaMutant preparationLaboratory cultureTryptophan
The invention relates to Escherichia coli and an application thereof in fermentation production of L-tryptophan, the Escherichia coli is Escherichia coli ACTrp104, the Escherichia coli ACTrp104 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), the preservation date is December 3, 2018, and the preservation number of the strain is CGMCC No.16861. The invention further discloses an application of the Escherichia coli in fermentation production of L-tryptophan. The Escherichia coli AC-1042 is screened by combining an ARTP mutation breeding technology and a resistance directional screening technology, and the strain has unique physiological and biochemical characteristics and can be researched and applied in the fields of scientific research, industry and the like.
Owner:江苏澳创生物科技有限公司
Fluorescent pseudomonad DA4 strain as well as acquisition method and application thereof
InactiveCN102002468BHigh enzyme productionEnzyme richBacteriaBiochemical fibre treatmentFlax fiberUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates to a fluorescent pseudomonad DA4 strain as well as an acquisition method and application thereof. The fluorescent pseudomonad DA4 strain has pectase and hemicellulase producing capacity and flax degumming activity. The fluorescent pseudomonad strain screened by the invention has fast propagation, high antipollution capacity and good heat and alkali resistance; since a composite degumming enzyme solution is used for flax degumming, the degumming period is shortened greatly, and the system and the culturing process is safe for operation without toxicity or environmental pollution; the invention can shorten the flax degumming period, enhance the flax yield and the strength of flax fibers, improve the quality of the flax fibers by adopting the composite degumming enzyme solution for flax microbial degumming, thereby being beneficial to popularization; in addition, the invention can not only be used for flax raw stem degumming, roving scouring and the biological pretreatment of flax fabrics, but also can be used for the degumming and the biological pretreatment of hemp bast fibers, i.e. ramie, jute, hemps, and the like.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Biological decalcification method in process for preparing chitin
This invention discloses a method for biologically removing Ca during preparation pf chitin. The method comprises: mixing Aspergillus niger with one of chitin-containing material, saccharide, starch or starch-containing carbohydrate, fermenting in a container equipped with stirrer at 28-40 deg.C, 0.1-0.3 MPa and pH value of 5-7, introducing asepsis wind with a flux of 400-700 m3 / h, stirring, terminating fermentation when the pH value is lower than 2.5 and the chitin content is lower than 10%, discharging, solid-liquid separating, washing the solid with water and drying to obtain chitin. The method has such advantages as no need for inorganic strong acid, no secondary pollution, low water and energy consumption, no waste liquid, little wastewater and little pollution. The obtained chitin has high quality. The method can effectively recover and utilize the byproducts, thus has a high profit.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Method for coagulation treatment of mining industry wastewater by means of microbial flocculant and surfactant
InactiveCN105712494AImprove flocculation efficiencyShorten flocculation timeWater treatment compoundsBiological water/sewage treatmentClay mineralsActive agent
The invention discloses a method for coagulation treatment of mining industry wastewater by means of a microbial flocculant and a surfactant and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The method comprises steps as follows: firstly, a silicate bacterium flocculant is prepared, the surfactant is added to the wastewater to be stirred, then the silicate bacterium flocculant is added to the wastewater, and pH is adjusted, so that fine solid particles in the wastewater are flocculated and settled. With the adoption of the method, suspended solids in the wastewater can be effectively deposited, the microbial flocculation efficiency is improved, the flocculation time of the microbial flocculant is shortened, the method has good treatment effects on slime water and coal-washing wastewater of coal preparation plants and suspensions containing clay minerals, silicate bacteria for producing the microbial flocculant are extensive in culture condition and environment-friendly, and the surfactant is high in degradability and free of secondary pollution.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing fibrilia by using alternaria tenuis DB3 strains
InactiveCN102409412AExtensive culture conditionsImprove heat resistanceFungiMicroorganism based processesFiberAlternaria
The invention relates to a method for preparing fibrilia by using epicoccum nigrum DB3 strains. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preserving the epicoccum nigrum DB3 strains in a potato dextrose agar medium for cultivation, and adding a freezing buffer solution; (2) inoculating bacteria the amount of which equals to the pick-up amount of an inoculating ring, obtained in the step (1) into the potato dextrose agar medium, and carrying out shaking culture; (3) inoculating the culture medium obtained in the step (2) into a flax lignin fermentation medium, and carrying out shaking culture to obtain a fermentation bacteria liquid; (4) mixing sterilized fiber raw material with the fermentation bacteria liquid obtain in the step (3), carrying out table shaking and removing fermentation liquid to obtain the fibrilia; and (5) mixing the fibrilia with degumming liquid, processing and then rinsing, oiling and drying to obtain the fibrilia. The method in the invention has simple technology, short degumming time and high degumming efficiency, thus being suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Method for microbial ash removal of coal
The invention discloses a method for microbial ash removal of coal, and belongs to the technical field of coal washing selection processing. The method comprises the following steps: crushing coal into granularities of less than 0.074 mm by virtue of a crusher, mixing a coal sample and a microbial liquid culture medium according to a certain proportion for sterilization treatment, inoculating a paenibacillus polymyxa strain into the sterilized culture medium, performing culturing in a constant temperature oscillation incubator, and finally performing filtration, washing and drying. According to the method, ash in difficult-to-float coal can be effectively removed, and the ash removal rate can maximally reach 70 percent. The method is easy to operate, mild in treatment condition and low in cost, and not only are active ingredients in the coal preserved, but also microbial culture cost is relatively lower.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for removing quartz from kaolin
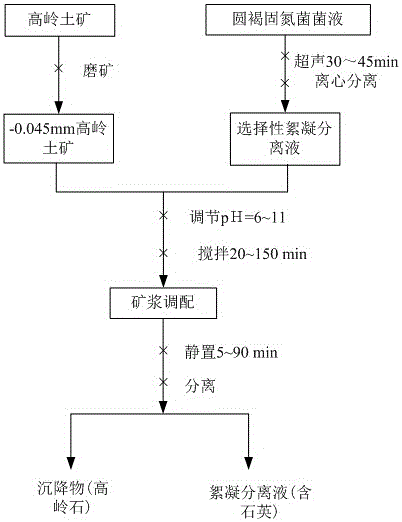
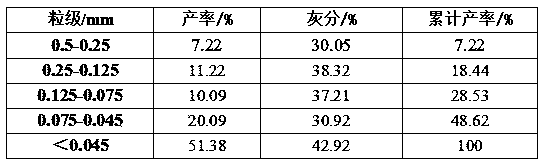
InactiveCN105855064AEfficient removalEasy to removeDifferential sedimentationFlotationFlocculationKaolinite
The invention discloses a method for removing quartz from kaolin. The method for removing the quarts from the kaolin belongs to the technical field of non-metallic mine kaolin upgrading, and comprises the steps of firstly finely grinding the kaolin ore by using an ore mill to enable the particle size of the finely ground kaolin core to be 0.045 mm or below; then blending the finely ground kaolin ore and microorganism selective flocculation separation liquid to prepare an ore pulp and adjusting a pH value of the ore pulp; and standing after stirring for a while, enabling kaolin particles to be precipitated and quartz particles to be suspended in the selective flocculation separation liquid, and separating precipitates from the selective flocculation separation liquid so as to realize the separation of the kaolin from the quartz. The selective flocculation separation liquid provided by the invention has both functions of flocculating the kaolin and dispersing the quartz, so that the micro-fine quartz can be effectively removed from the kaolin ore, and the technological process is simple.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
A method for coagulation treatment of mining wastewater with microbial flocculant and surfactant
InactiveCN105712494BImprove flocculation efficiencyShorten flocculation timeWater treatment compoundsBiological water/sewage treatmentFlocculationClay minerals
The invention discloses a method for coagulation treatment of mining industry wastewater by means of a microbial flocculant and a surfactant and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The method comprises steps as follows: firstly, a silicate bacterium flocculant is prepared, the surfactant is added to the wastewater to be stirred, then the silicate bacterium flocculant is added to the wastewater, and pH is adjusted, so that fine solid particles in the wastewater are flocculated and settled. With the adoption of the method, suspended solids in the wastewater can be effectively deposited, the microbial flocculation efficiency is improved, the flocculation time of the microbial flocculant is shortened, the method has good treatment effects on slime water and coal-washing wastewater of coal preparation plants and suspensions containing clay minerals, silicate bacteria for producing the microbial flocculant are extensive in culture condition and environment-friendly, and the surfactant is high in degradability and free of secondary pollution.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Escherichia coli ACThr1032 and application thereof in fermentation production of L-threonine
ActiveCN109266578AUnique physiologyUnique characteristicsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliL-threonine
The invention relates to a strain of Escherichia coli ACThr1032 and application thereof in fermentation production of L-threonine, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The strain of Escherichiacoli ACThr1032 has a classification name of namedEscherichia coli, a deposit number of CGMCC No.16144, and a preservation date of July 23, 2018. The Escherichia coli ACThr1032 is cultured, fermented,purified and fermented to prepare L-threonine. The strain stability of Escherichia coli ACThr1032 in the invention is greatly improved, and the strain is used for fermentation production of L-threonine, acid production and conversion have been significantly improved, and breakthroughs have been made in technology, with significant progress. Moreover, the culture condition of the strain is extensive, which greatly reduces the energy consumption and has a good prospect of industrial application.
Owner:江苏澳创生物科技有限公司
Recombinant bacillus subtilis of exocytosis PNAG polysaccharide and application of recombinant bacillus subtilis
ActiveCN110184231AExtensive culture conditionsClear genetic backgroundBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMetabolic engineeringProbiotic
The invention discloses recombinant bacillus subtilis of exocytosis PNAG polysaccharide. A PNAG polysaccharide synthetase coding gene and expression plasmid are connected, recombinant expression plasmid is constructed, then the recombinant expression plasmid is transferred into bacillus subtilis, and the recombinant bacillus subtilis is obtained. The invention further discloses a construction method of the recombinant bacillus subtilis. A new metabolism synthetase gene is guided into bacillus subtilis, the recombinant bacillus subtilis is successfully constructed, PNAG polysaccharide can be produced through fermentation, the produced exocytosis PNAG polysaccharide can reach 136mg / L, and a base is established for further reforming the bacillus subtilis for producing the PNAG polysaccharidethrough metabolic engineering. The invention further discloses an application of the recombinant bacillus subtilis to preparation of products containing the PNAG polysaccharide through fermentation indifferent fields of foods, medicines and chemical industry. The PNAG polysaccharide produced from recombinant strains can promote growth of probiotics and restrain harmful bacteria, and has good application prospects in many fields.
Owner:杭州丰海生物科技有限公司
Streptomyces roseospora and method for producing daptomycin using combined precursors
ActiveCN102796680BExtensive culture conditionsCan implement industrial productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSnow moldMicroorganism
The invention discloses a streptomycete and a method for producing daptomycin by using the streptomycete. The strain is preserved in the General Microorganism Center of China Microbial Strain Preservation Management Committee, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.5956. In the present invention, Streptomyces CGMCC No.5956 is cultivated under suitable fermentation conditions by adding capric acid and capric aldehyde composition as a precursor Fermentative production of daptomycin. By adopting the method for producing daptomycin by Streptomyces described in the present invention, the titer of the target product daptomycin is high, the resource utilization rate is high, and the production cost is low, which is beneficial to industrial scale production.
Owner:鲁南新时代生物技术有限公司
Bacillus and its use of preparation of gama-polycysteine
InactiveCN1269951CEfficient fermentation productionExtensive culture conditionsBacteriaFermentationOrganic solventNitrogen source
Production of gama-polyglutamic acid by fermentation is carried out by: culturing bacillus subtills zju-7 strain, i.e., CGMCC No. 1250, in medium with carbon and nitrogen sources, glutamic acid, MgSO4, NaCl and K2HPO4 to obtain ferment liquid, and making it to pass organic solvent settlement and dialysis. The process is easy, yields highly, and costs low with quality products.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Bacillus alcaligenes and its application in preparing Weilan gum
InactiveCN100529055CEasy to operateExtensive culture conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyInorganic salts
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Bacillus subtilis and application thereof in adenosine production by fermentation
ActiveCN110791462AImprove stabilityHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a Bacillus subtilis and an application thereof in adenosine production by fermentation. The Bacillus subtilis is Bacillus subtilis ACA301, the Bacillus subtilis ACA301 is deposited in the China General Microbial Species Preservation and Management Center, and the strain preservation number is CGMCC No.16753. According to the Bacillus subtilis ACA301 in the invention, the stability of the strain is greatly improved, the breakthrough progress is made in the technology, the strain is used to produce adenosine by fermentation, the yield and conversion rate have relatively high level, and the advancement is significant. Moreover, the fermentation raw materials are easy to obtain, the culture conditions are extensive, and the control process is simple. The Bacillus subtilis is suitable for industrial production, and has relatively good industrial application prospect.
Owner:江苏澳创生物科技有限公司
Application of Bacillus subtilis in high-yield adenosine and acetoin co-production
InactiveCN102876760BEasy to operateExtensive culture conditionsMicroorganism based processesFermentationAdenosineNitrogen source
The invention discloses the application of Bacillus subtilis in high-production of adenosine and co-production of acetoin. The Bacillus subtilis (Bacillus subtilis) is CGMCC No. 4484. The strains screened in the present invention can utilize a variety of carbon sources and nitrogen sources to ferment to produce adenosine and co-produce acetoin. By adding sodium citrate to the fermentation medium, the production of adenosine and acetoin can be significantly increased, and the operation is easy. It is simple, has extensive culture conditions, can maintain a high level in a 5L fermentation tank, and has the potential for large-scale industrialization.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV +1
Bacillus subtilis and application thereof in preparation of gamma-D-polyglutamic acid
ActiveCN102965311BEasy to operateExtensive culture conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFood additiveMicrobiological culture
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis. According to the bacillus subtilis, the category name is bacillus subtilis PG-8, the bacillus subtilis is collected at China general microbiological culture collection center (CGMCC), the registered number is CGMCC NO. 6324, and the collection data is 10, July, 2012. The invention further discloses application of the bacillus subtilis in preparation of gamma-D-polyglutamic acid. The bacillus subtilis is cultured in a culture medium containing L-glutamic acid only, and then, the gamma-D-polyglutamic acid of 30-60 g / L can be accumulated under optimized conditions. According to the bacillus subtilis, a variety of carbon and nitrogen sources can be utilized, culture conditions are extensive, the operation is convenient and simple, the yield of the gamma-D-polyglutamic acid is high, and the production cost is low, so that the bacillus subtilis can be widely applied to the fields of plant water conservation, food additives and the like.
Owner:NANJING SHINEKING BIOTECH CO LTD
Cellulomonas fimi DA 8 bacterial strain as well as acquiring method and application thereof
InactiveCN102010836BIncrease the lengthGrain reductionBacteriaBiochemical fibre treatmentBiotechnologyPectinase
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
A strain of Bacillus subtilis and its application in fermentative production of adenosine
ActiveCN110791462BImprove stabilityHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
A strain of Bacillus subtilis and its application in fermentative production of adenosine, wherein the Bacillus subtilis is Bacillus subtilis ( Bacillus subtilis ) ACA301, the Bacillus subtilis ACA301 is preserved in China General Microorganism Culture Collection Management Center, and the culture preservation number is CGMCC No.16753. The stability of the Bacillus subtilis ACA301 in the present invention is greatly improved, and a breakthrough has been made in technology. The production of adenosine by fermentation of this strain has a relatively high level of yield and conversion rate, and is significantly advanced. , and the fermentation raw materials are easy to obtain, the cultivation conditions are extensive, and the control process is simple, so it is suitable for industrial production and has good industrial application prospects.
Owner:江苏澳创生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com