Functional molecular marker of rice nilaparvata lugens resistance gene Bph9, identification method and application
A brown planthopper resistance and functional molecule technology is applied in the fields of rice resistance breeding and molecular genetics, which can solve the problems of limiting the application of Bph9 gene, affecting the efficiency and accuracy of molecular marker-assisted breeding selection, and difficulty in accurately distinguishing rice brown planthopper resistance genes. Achieve the effect of low cost and simple identification operation method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1: Identification method of molecular marker Bph9-M of rice brown planthopper resistance gene Bph9
[0039] A method for identifying the molecular marker Bph9-M of the rice brown planthopper-resistant gene Bph9, the identification method comprising the following steps:
[0040] RIGW searches for the gene sequence of this site in indica rice, which is Zhenshan 97 (OsZS_12T0336600) and / or Minghui 63 (OsMH_12T0305200); MSU searches for the gene sequence of this site in japonica rice, and the japonica rice is Nipponbare (LOC_Os12g37280) ; The gene sequence Bph9 (ID No. KU216221) and its allelic sequences Bph1 (ID No. KX681949), Bph7 (ID No. KU221258), Bph10 (ID No. KX681950), and Bph21 (ID No. KX681951) were obtained from NCBI Genbank.
[0041] After comparing multiple sequences together, select the Indel sequence that exists in the third exon. The online primer design software Primer1 was used to design molecular markers, named Bph9-M, forward primer: TCATTAGGAACA...
Embodiment 2
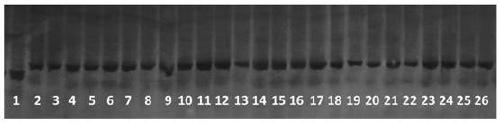
[0053] Embodiment two: mark Bph9-M to the detection of multiple different rice varieties
[0054] 1. Test materials
[0055]
[0056]
[0057] 2. DNA extraction
[0058] In this experiment, the CTAB simple method was used to extract genomic DNA from rice samples, and the specific steps were as follows:
[0059] (1) Cut about 0.5g leaves into pieces and put them into a 2ml centrifuge tube, then put a steel ball into the tube, cover the tube cap, add 600μl CTAB extract into the centrifuge tube, fix it on the proofer at 23~ Vibrate at a speed of 26 rev / S for about 60s.
[0060] (2) Water bath at 65°C for 30 minutes, during which time shake and mix twice.
[0061] (3) Open the centrifuge tube, add 600 μl chloroform, shake well, let stand for 5 minutes, and centrifuge at 12000 rpm for 8 minutes.
[0062] (4) Pipet 400 μl of supernatant into a 1.5ml centrifuge tube prepared in advance, add 1 mL of absolute ethanol pre-cooled in a -20°C refrigerator, shake well, let stand i...
Embodiment 3
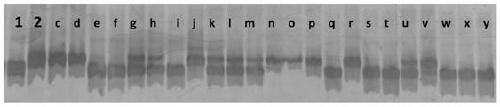
[0067] Embodiment three: Luojia No. 9 / Ganxiang B and F thereof 2 Detection of Bph9-M in populations
[0068] 1. Test materials
[0069]Luojia 9, Ganxiang B, and F prepared with Luojia 9 / Ganxiang B 2 Segregated populations (c-y) were used for validation of marker Bph9-M.
[0070] 2. DNA extraction
[0071] In this experiment, the CTAB simple method was used to extract genomic DNA from rice samples, and the specific steps were as follows:
[0072] (1) Cut about 0.5g leaves into pieces and put them into a 2ml centrifuge tube, then put a steel ball into the tube, cover the tube cap, add 600μl CTAB extract into the centrifuge tube, fix it on the proofer at 23~ Vibrate at a speed of 26 rev / S for about 60s.
[0073] (2) Water bath at 65°C for 30 minutes, during which time shake and mix twice.
[0074] (3) Open the centrifuge tube, add 600 μl chloroform, shake well, let stand for 5 minutes, and centrifuge at 12000 rpm for 8 minutes.
[0075] (4) Pipet 400 μl of supernatant into...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com