Method for measuring malonaldehyde content of catalpa bungei leaves
A technology of sheet malondialdehyde and determination method, which is applied in the measurement of color/spectral properties, material analysis by observing the effect on chemical indicators, and analysis by chemical reaction of materials, etc., can solve the problem of malondialdehyde content. detection, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
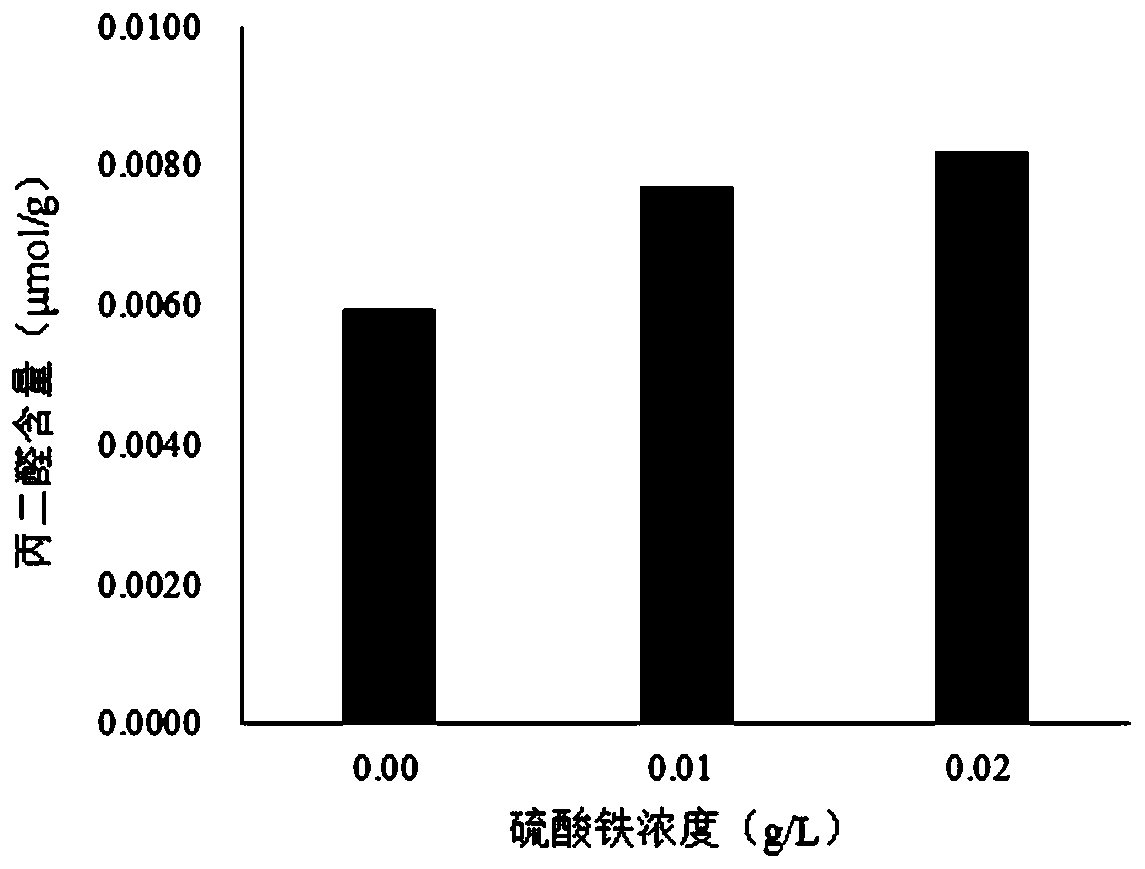
[0035] The detection effect of malondialdehyde content of catalpa leaf under the different concentration of iron sulfate of embodiment 1
[0036] (1) Material
[0037] The young leaves of 1-year-old catalpa seedlings were used as materials.
[0038] (2) Reagent preparation
[0039] Trichloroacetic acid (TCA) solution: configure the concentration of trichloroacetic acid solution to be 0.75%.
[0040] Thiobarbituric acid (TBA) solution: 0.02mol / L.
[0041] Iron Sulfate (Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 ) solution: 0.01g / L and 0.02g / L.
[0042] (3) Measurement process
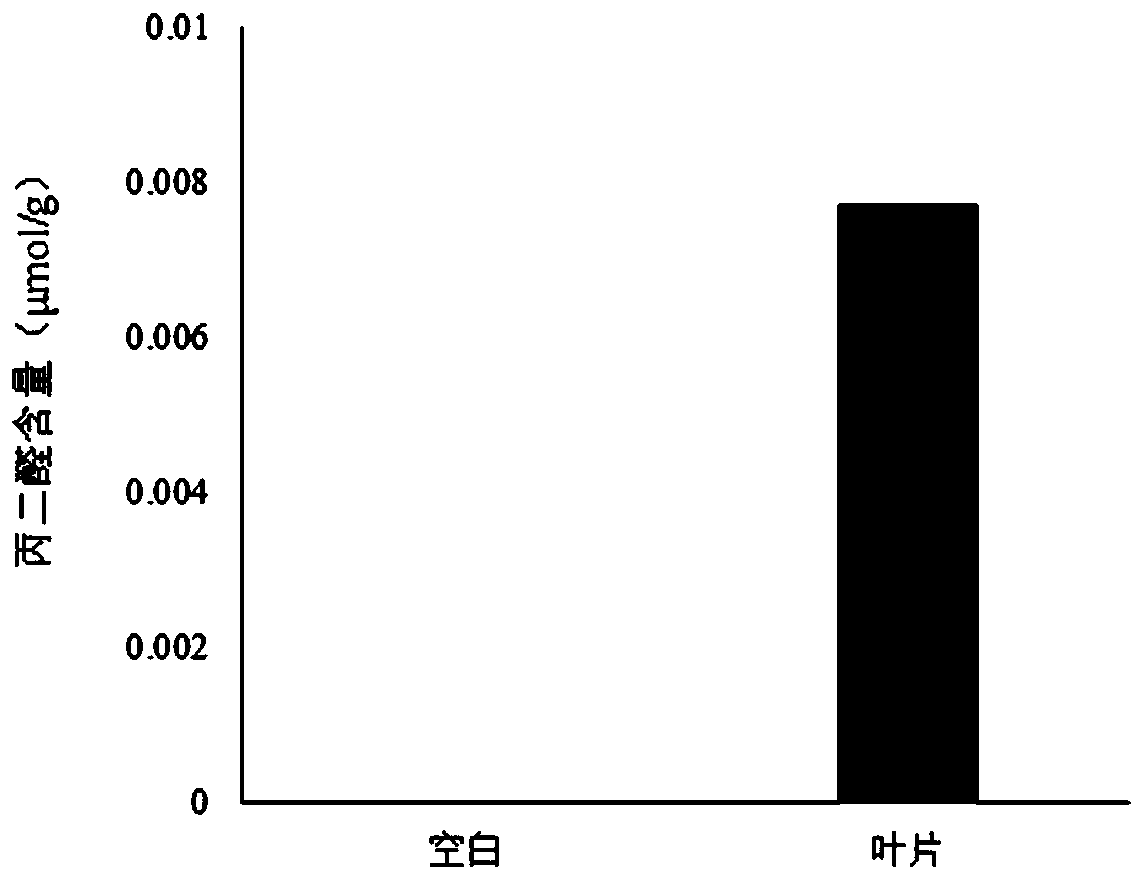
[0043] Grind the leaf sample into powder with liquid nitrogen, weigh 4.50g (accurate to 0.01g) of the sample powder, place it in a stoppered Erlenmeyer flask, add 45mL TCA solution accurately, shake well and stopper, place it on a constant temperature shaker at 50°C 30min, the rotation frequency is 110rpm, take it out, filter with filter paper, and take the filtrate for later use.
[0044] Take 9 extracts respectively and ...
Embodiment 2 3
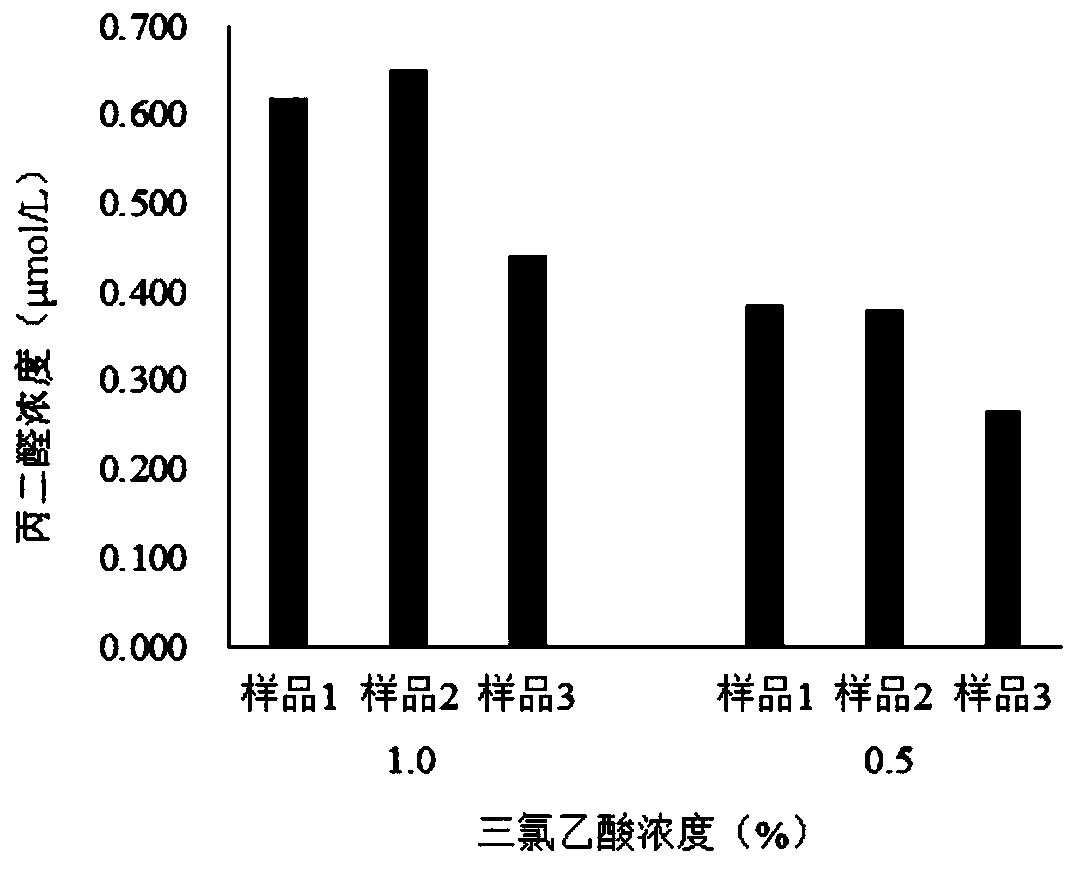
[0047] The detection effect of catalpa leaf malondialdehyde content under the different concentrations of embodiment 2 trichloroacetic acid
[0048] (1) Material
[0049] The young leaves of three 1-year-old catalpa grafted seedlings were used as materials, and they were numbered as sample 1, sample 2 and sample 3 respectively.
[0050] (2) Reagent preparation
[0051]Trichloroacetic acid (TCA) solution: prepare the concentration of trichloroacetic acid solution as 0.5% and 1.0%.
[0052] Thiobarbituric acid (TBA) solution: 0.02mol / L.
[0053] Iron Sulfate (Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 ) solution: 0.02g / L.
[0054] (3) Measurement process
[0055] First, according to the design of 3 repetitions of 2 concentrations of TCA solutions, accurately weigh 6 parts of sample 1, sample 2 and sample 3, each 1.00g, put them into a mortar, add 2ml of 0.5% and 1.0 % TCA, grind until homogenized, transfer the homogenate to a 25ml centrifuge tube, and wash it with 8ml of TCA with a concentration of...
Embodiment 3
[0060] The influence of embodiment 3 different temperatures on MDA extraction effect
[0061] (1) Material
[0062] The leaves of 1-year-old catalpa seedlings were used as materials.
[0063] (2) Reagent preparation
[0064] Trichloroacetic acid (TCA) solution: the concentration is 0.75%.
[0065] Thiobarbituric acid (TBA) solution: the concentration is 0.02mol / L.
[0066] Iron Sulfate (Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 ) solution: the concentration is 0.02g / L.
[0067] (3) Measurement process
[0068] First, according to the design of 3 repetitions at 3 temperatures, 9 samples were accurately weighed, each 1.00g, put into a mortar, 2ml of TCA with a concentration of 0.75% was added, ground to a homogenate, and the homogenate was transferred to 25ml centrifuge tube, and rinsed with 8ml of TCA with a concentration of 0.75%; then, shake the centrifuge tube in a constant temperature shaker at 50°C, 60°C, and 70°C for 30min at a rotation frequency of 110rpm; finally, take out the shaken cent...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com