Selective absorption emitter
An emitter, selective technology, used in refrigerators, lighting and heating equipment, refrigeration and liquefaction, etc., can solve problems such as limitations, increase the complexity of experimental equipment and manufacturing costs, and achieve the effect of low precision requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
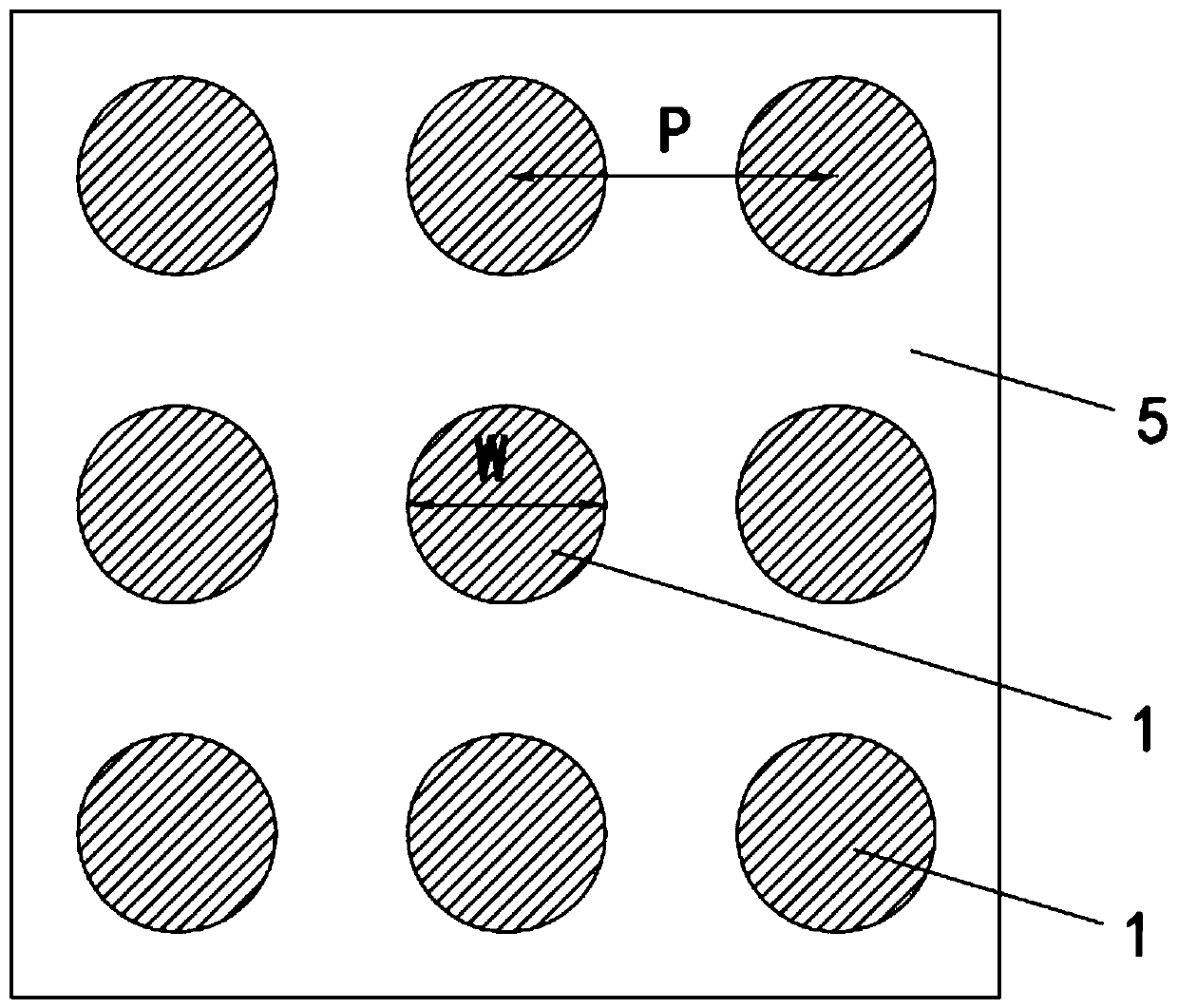
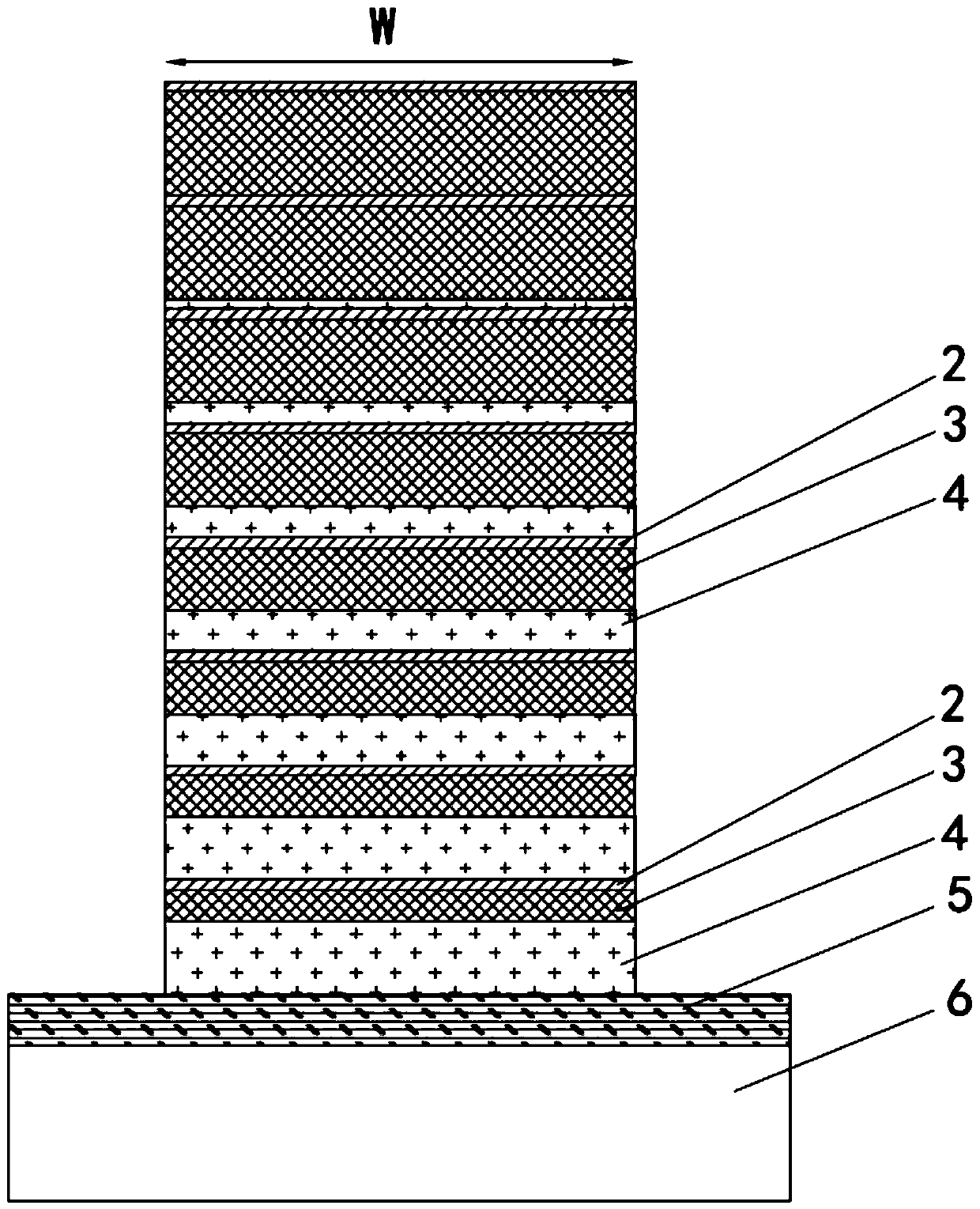
[0032] The selectively absorbing emitter of embodiment 1, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes a substrate 6, a metal film 5 covered on the substrate 6, and a vertical cylindrical two-dimensional periodic cell array arranged on the metal film 5. Each basic unit 1 is composed of 8 stacks stacked sequentially from top to bottom, and each stack includes a metal layer 2 and two dielectric layers with different refractive indices located on the lower side of the metal layer 2, that is, the upper and lower The first dielectric layer 3 and the second dielectric layer 4 are set, and the angle between the side of each basic unit 1 and the normal line of the substrate 6 is 0°, that is, the basic units 1 forming the cell array in this embodiment are all cylindrical .
[0033] In Embodiment 1, the schematic diagram of the structural connection between a single basic unit 1 and the substrate 6 is as follows figure 2 As shown, its period P=5μm, cylinder diameter W=3μm. The metal thin ...
Embodiment 3
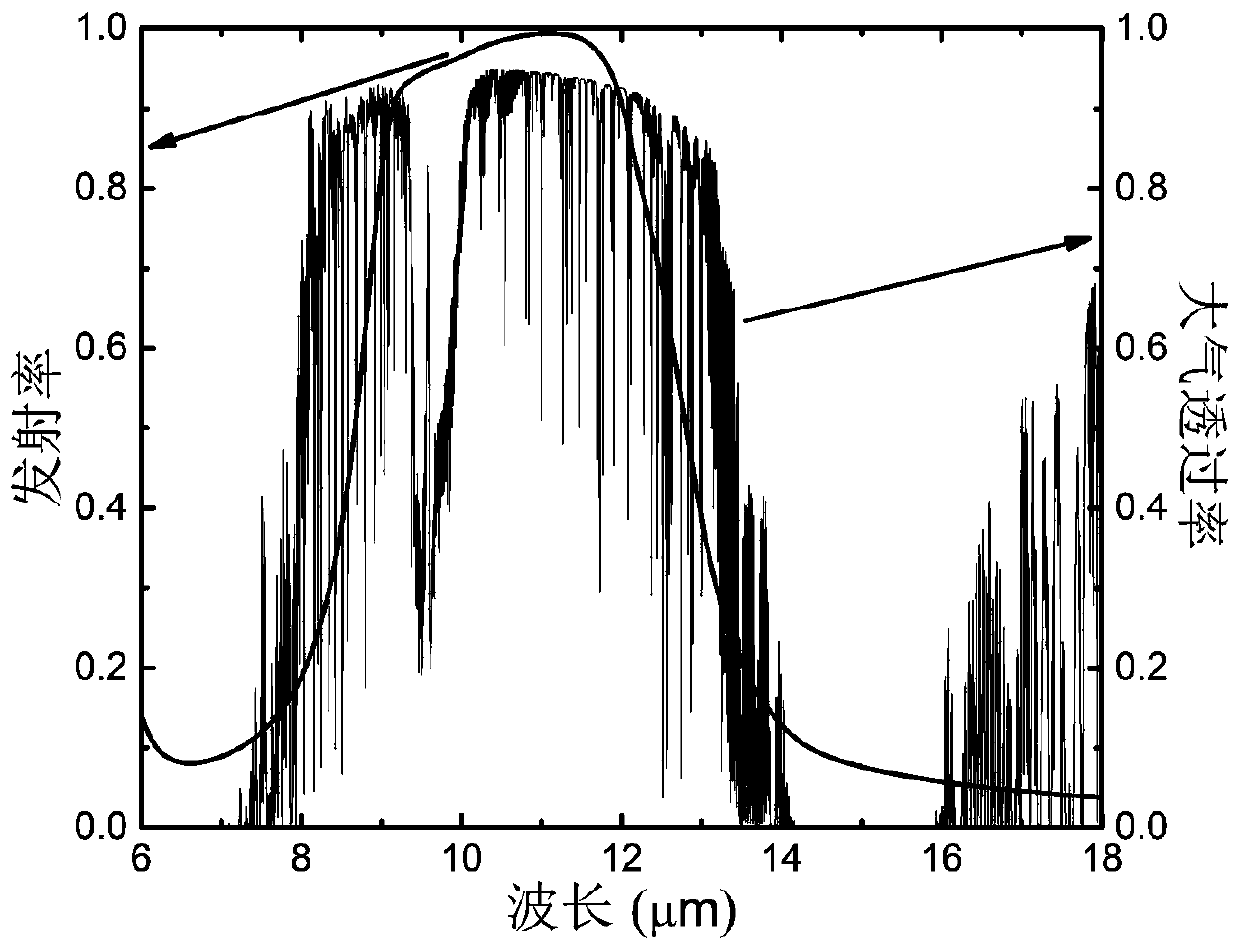
[0039] Example 3 is another case of experimental error. The difference between the selective absorption emitter of embodiment 3 and embodiment 1 is that in embodiment 3, the angle θ between the side surface of each basic unit 1 and the normal line of the substrate 6 is a negative value. Figure 7 It is the emissivity spectrum of the selective absorption emitter of embodiment 3 when there is this angle. The schematic diagram of the longitudinal section of a single basic unit 1 is shown as Figure 7 As shown in the inset below the middle curve, the top dimension of base unit 1 is larger than the bottom dimension. From Figure 7 It can be seen from the middle curve that with the increase of the absolute value of the included angle θ, the emissivity of the selective absorbing emitter at the wavelength of the 8-13 μm atmospheric transparent window decreases, and the bandwidth also decreases, but it still has a good selective absorbing emission characteristic.
[0040] In additi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com