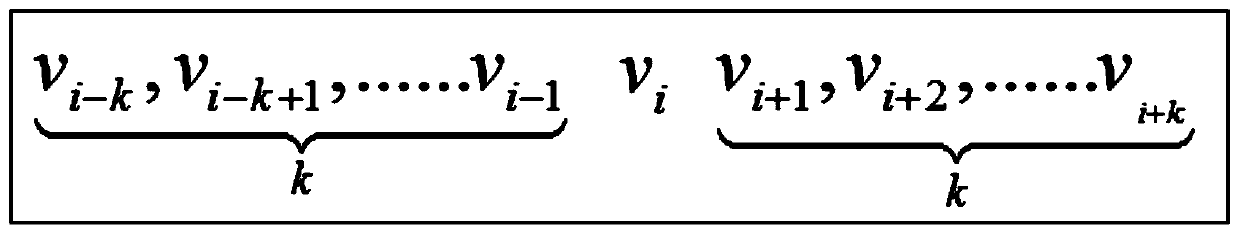Social network representation method based on bidirectional distance network embedding
A social network and directed distance technology, applied in the field of social network representation, can solve the problems of inaccurate representation of the structure and topology information of social relationship networks, no consideration of the direction and distance between nodes and nodes, and low ability to restore real social relationships. To achieve the effect of improving the effect and performance, improving the restoration ability, and improving the effectiveness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
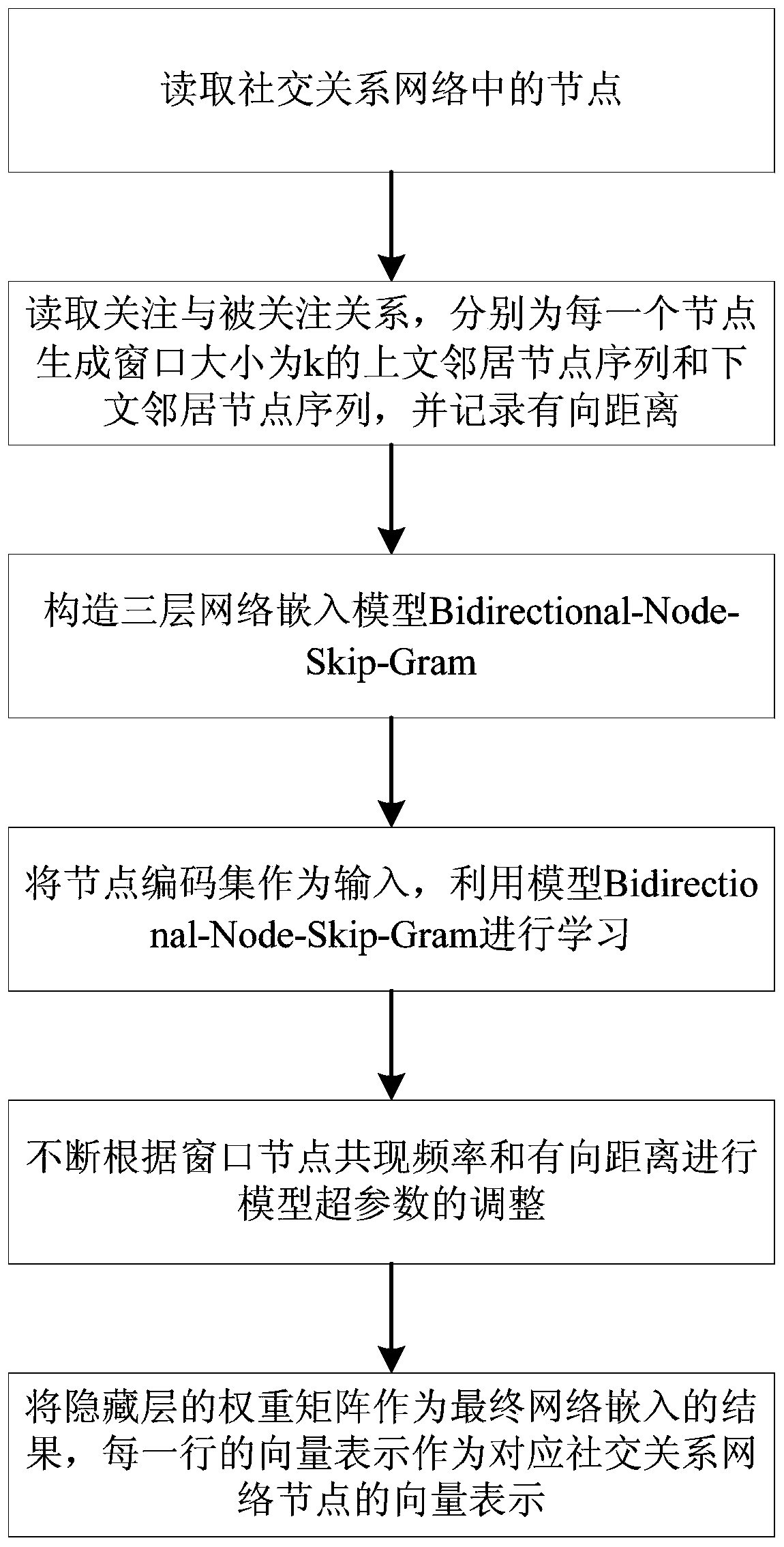
[0021] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 To illustrate this embodiment, a social network representation method based on two-way distance network embedding given in this embodiment specifically includes the following steps:
[0022] Step 1. Read the nodes in the social relationship network, and uniquely encode the nodes to obtain the node code set; the original social relationship network includes the node set V and the directed edge set where v m ,v n ∈V, Represents the existence of a slave node v m point to v n side of v m follow v n ;
[0023] Step 2. Read the attention and followed relationship in the social relationship network, that is, the direction of the edge (directed edge) between nodes, and generate a sequence of upper neighbor nodes and lower neighbors with a window size of k for each node. node sequence, and record the directed distance from each neighbor node to the node; the above neighbor node is a node that directly or indirectly pay...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0031] Specific implementation mode 2: The difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode 1 is that
[0032] The encoding method described in step 1 is one-hot encoding or binary encoding. The following uses one-hot encoding as an example to describe in detail:
[0033] Establish a mapping relationship from node set V to node one-hot encoding set D, such as (v i )→(0,0,0,1,...,000), where the number of one-hot encoding bits is equal to the number of nodes, and each node is only valid on its feature bit, that is, it is 1 in this position, and in other The values on the feature bits are all 0, and the feature bits of each node are different.
[0034] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
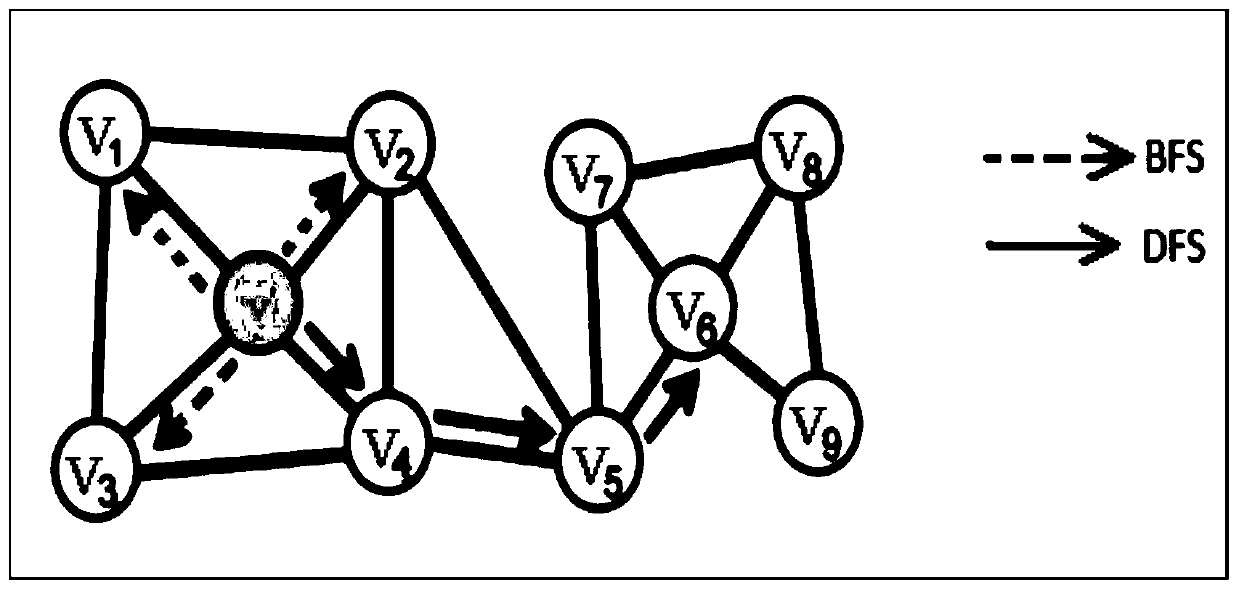
[0035] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 2 is that in the sequence of neighbor nodes mentioned above in Step 2, each step of the walk in the generation process only focuses on the reverse edge, that is, the next node directly focuses on the current node the node;
[0036] Such as image 3 Shown is a schematic diagram of depth-first traversal (DFS) and breadth-first traversal (BFS) strategies in graph traversal. BFS pays more attention to micro-local information, and DFS pays more attention to macro-global information. The Bidirectional-Node-Walk strategy in the present invention separates the above and below sequences of nodes, and the generation strategy formula is as follows:
[0037]
[0038] Among them, t is the previous access node of the current access node, and x is the next node that may be accessed (x1, x2, and x3 in the figure refer to different next node x); d + (t,x) indicates the number of edges that are visited from the dire...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com