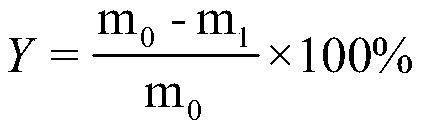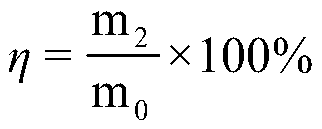Method for catalyzing biomass to prepare levulinate by red mud-based catalyst
A technology of levulinic acid ester and catalyst is applied in the field of red mud-based catalyst catalyzing biomass to prepare levulinic acid ester, and achieves the effects of stable performance, simple operation and cost saving of catalyst
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1 Catalyzing wheat straw to prepare ethyl levulinate
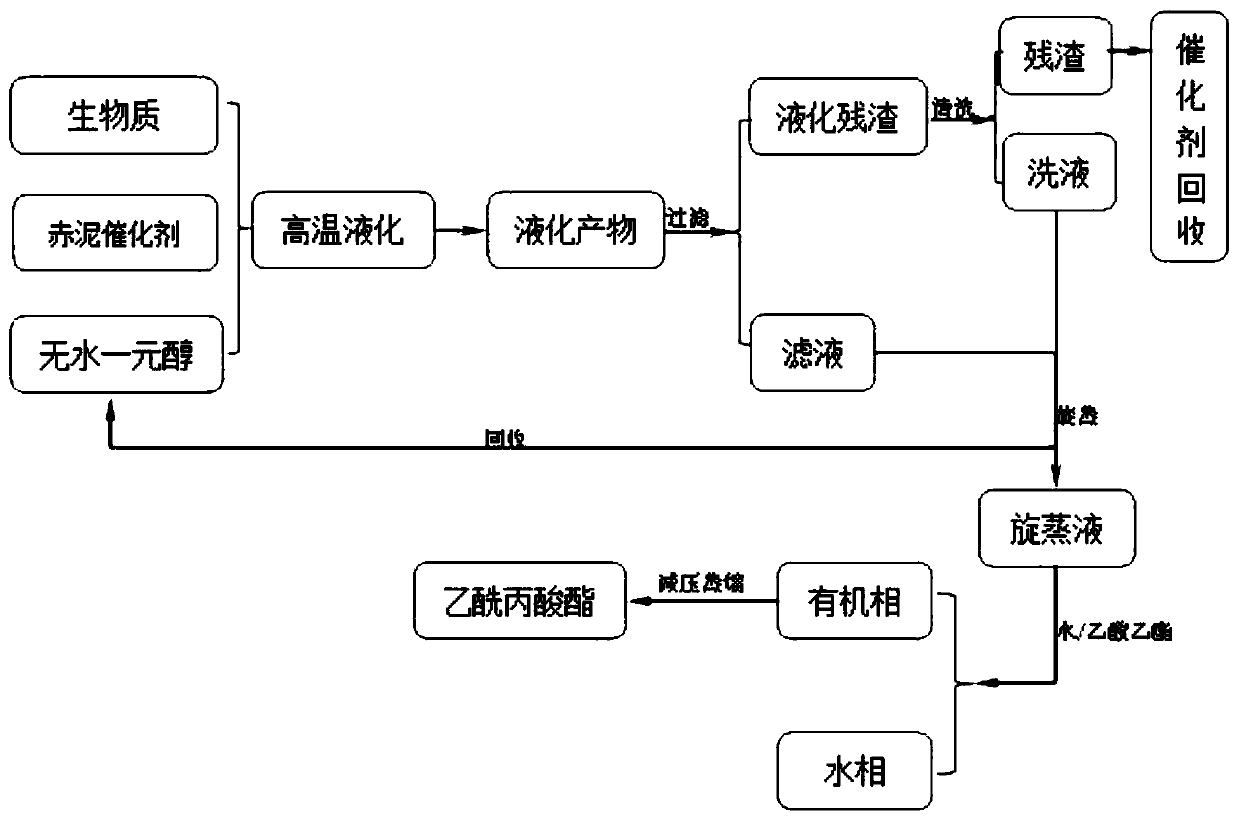
[0026] 5g of wheat straw (40-60 mesh), 1.8g of red mud-based catalyst (the active component is 1-methyl-3-(4-sulfonic acid butyl) imidazole tetraferric chloride with a loading of 5%) After mixing with 75g of absolute ethanol, place it in a high-pressure reaction kettle, raise the temperature to 190°C, and react for 80 minutes. When the cooling water is passed through to cool down to 90°C, the reaction kettle is taken out from the heating kettle, and the temperature continues to drop at room temperature. After cooling down to room temperature, the liquefied product was taken out. The liquefied product is filtered to obtain a liquefied residue and a filtrate.
[0027] Clean the liquefied residue, dry it in an oven at 105°C until it reaches a constant weight, recover the red mud containing the magnetic ionic liquid by using the principle of a magnetic field, weigh the residue again and record it as m 1 , calc...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2 Catalyzing poplar wood chips to prepare methyl levulinate
[0033] 3g poplar sawdust (80-100 mesh), 0.6g red mud-based catalyst (the active component is 1-propylsulfonic acid-3-methylimidazolium tetrachloride ferric salt with a loading of 5%) and 60g anhydrous After mixing methanol, put it in a high-pressure reactor, raise the temperature to 200°C, and react for 60 minutes. When the cooling water is passed through to cool down to 90°C, take out the reactor from the heating kettle, and continue to cool down at room temperature. After the temperature of the reactor drops to room temperature , take out the liquefied product. Filter the liquefied product to obtain the liquefied residue and filtrate, wash the liquefied residue, dry the residue at 105°C, recover the catalyst, weigh the residue, and calculate the liquefaction rate, which is 76.33%. At the same time, the washing liquid and the filtrate are rotary evaporated to reclaim the methanol solvent, and water ...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3 Catalyzing rice straw to prepare methyl levulinate
[0035] 5g of rice straw (80-100 mesh), 1.25g of red mud-based catalyst (the active component is 1-propylsulfonic acid-3-methylimidazolium tetrabromide with a loading capacity of 15%) and 75g of anhydrous methanol After mixing, put it in a high-pressure reactor, raise the temperature to 180°C, and react for 90 minutes. When the cooling water is passed through to cool down to 90°C, take out the reactor from the heating kettle, and continue to cool down at room temperature. After the temperature of the reactor drops to room temperature, Remove the liquefied product. Filter the liquefied product to obtain the liquefied residue and filtrate, wash the liquefied residue, dry the residue at 105°C, recover the catalyst, weigh the residue, and calculate the liquefaction rate, which is 73.46%. Simultaneously, washing liquid and filtrate are rotary-evaporated to reclaim methanol solvent, water is added in gained rotary...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com