High-throughput identification method for pathogenic differentiation of bipolaria maydis
A technology of corn spot disease and identification method, applied in the field of high-throughput identification of corn spot spot pathogenicity differentiation, can solve the problem of affecting pathogenicity, single infection observation time point, and inability to comprehensively analyze corn spot spot fungus Pathogenicity differentiation and other issues, to achieve the effect of high reliability and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
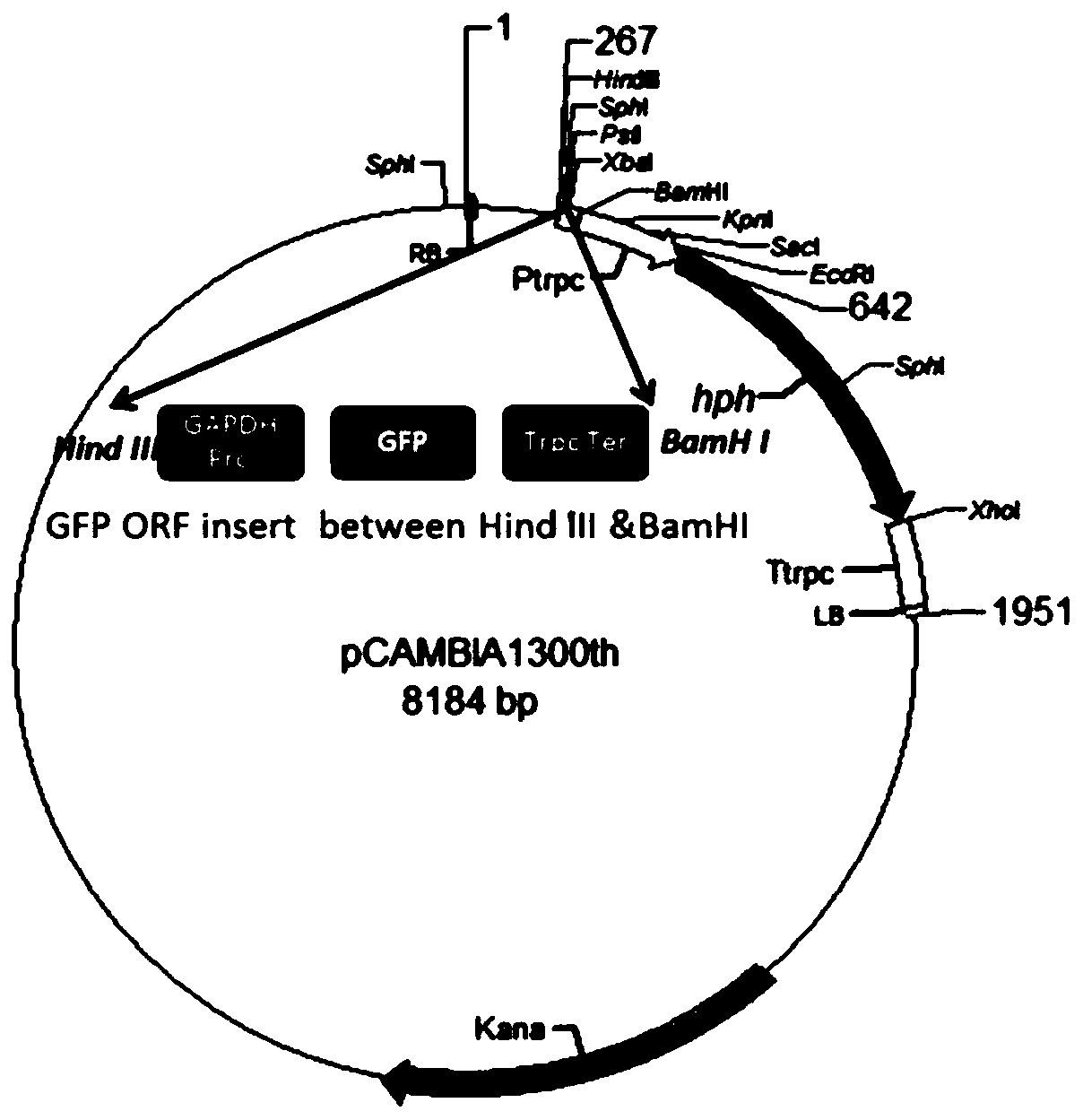
[0048] This embodiment relates to the construction of a high-throughput identification method for pathogenicity differentiation of P. maize spot, specifically as follows:
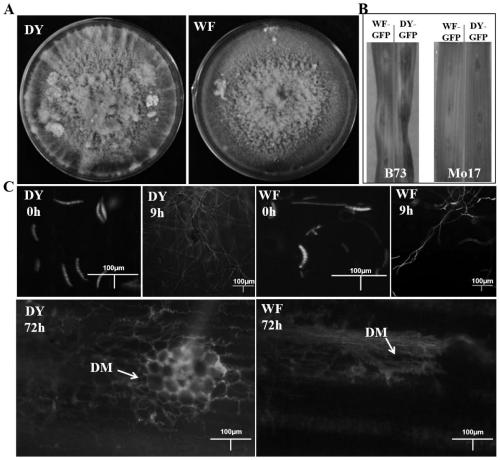
[0049] The inventor has selected the different virulence types of the lesser pathogenicity of maize spot bacterium that the virulence difference is more significant from the bacterial strain isolated in the field: DY, strong pathogenic strain; WF, weak pathogenic strain (wherein, DY is from Zhejiang Province The fungus was isolated and purified from the diseased corn leaves in the field of Dongyang City, and the strain was identified as a strong pathogenic strain by counting the size of the lesion after being reattached to the corn leaves; WF was obtained from the field of Weifang City, Shandong Province. The method of observing the size of the lesion spot after collecting and single spore isolation and purification on the sick leaves of corn and then returning to the corn leaves, identified that the bacteri...
Embodiment 2
[0064] This example relates to the verification of the effect of the high-throughput identification method for pathogenicity differentiation of P. maize spot of the present invention.
[0065] According to the identification standard of strong and weak pathogenic strains, the corn leaf spot fungus collected and purified in 2018 (specifically, collected diseased leaves from all over the country, disinfected the surface of the diseased leaves with sodium hypochlorite and then cultured them in PDA medium for 2 days, Then pick the tip of mycelia and cultivate it in a new PDA medium for 5-7 days. After the spores of the spot bacterium to be purified, carry out the isolation and purification of single spores to obtain the purified spot bacterium). Randomly select 10 strains for verification. The pathogenicity of the isolated and purified bacterial strains was identified by the traditional leaf reconnection method and the high-throughput detection method of the present invention, resp...
Embodiment 3
[0079] This embodiment relates to the application case of the high-throughput identification method of the pathogenicity differentiation of corn leaf spot bacterium of the present invention:
[0080] Henan Province
[0081] A total of 36 strains of Phytophthora spp. were identified in Henan Province, among which 12 strains were strongly pathogenic and 24 strains were weakly pathogenic, accounting for 33.3% and 66.7% respectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com