Non-volatile memory reading circuit and reading method
A technology of non-volatile memory and readout circuit, which is applied in the field of integrated circuits and can solve the problems of long readout time and large dynamic power consumption of non-volatile memory
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
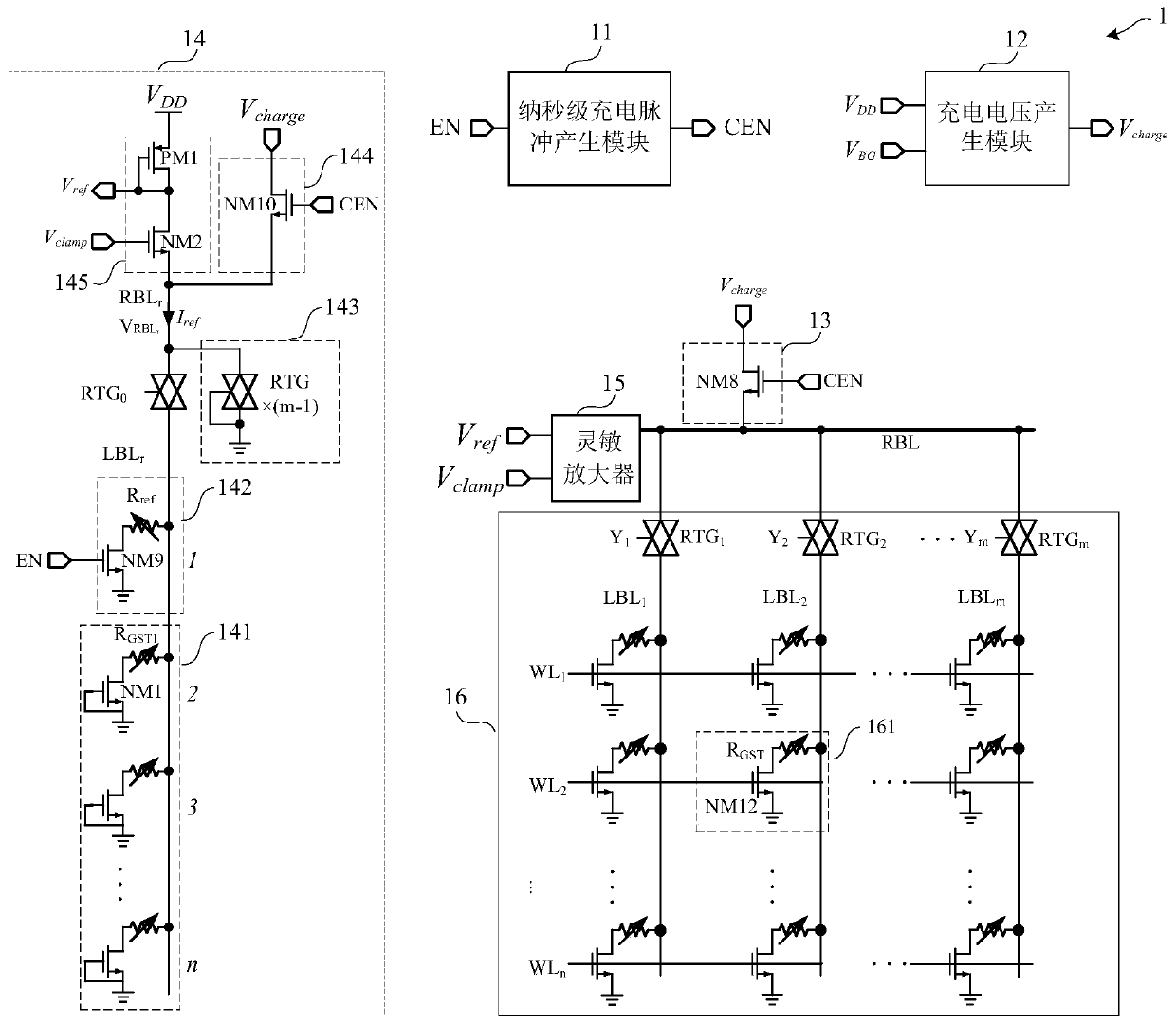
[0090] Such as figure 2 As shown, the present embodiment provides a non-volatile memory readout circuit 1, and the non-volatile memory readout circuit 1 includes: a nanosecond charge pulse generating module 11, a charging voltage generating module 12, and a bit line charging module 13. A first reference read voltage generating circuit 14 and a sense amplifier 15.
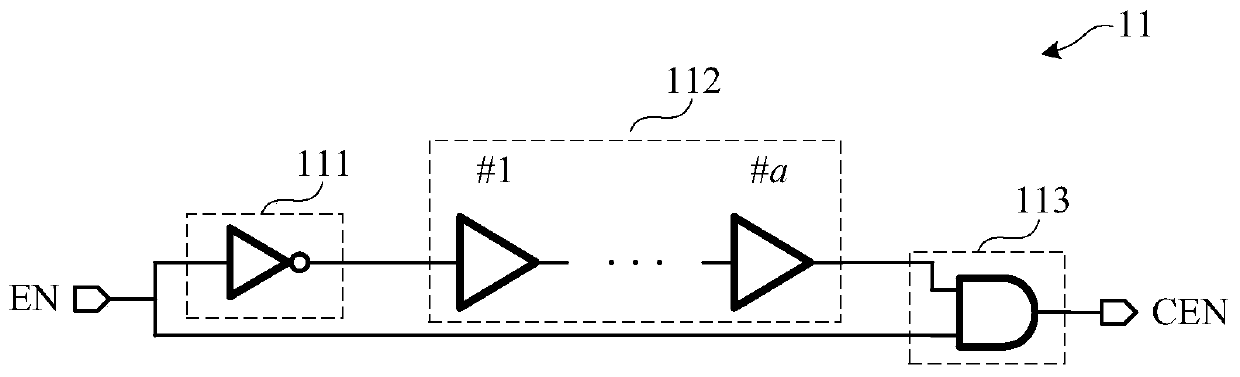
[0091] Such as figure 2 As shown, the nanosecond charging pulse generation module 11 receives the read enable signal EN, and generates a post-charge pulse signal CEN after the read enable signal EN arrives.
[0092] Specifically, in this embodiment, the sustaining time of the post-charging pulse signal CEN is set to 100 ps-10 ns. In actual use, the sustaining time of the post-charging pulse signal CEN can be set according to circuit performance and needs. It is not limited to this embodiment.
[0093] Specifically, such as image 3 As shown, in this embodiment, the nanosecond charging pulse generation module 1...
Embodiment 2
[0124] Such as Figure 2 ~ Figure 6 As shown, this embodiment provides a method for reading out a non-volatile memory, and the method for reading out a non-volatile memory includes:
[0125] After the read enable signal EN is valid, the read operation starts, a word line and a bit line are selected, and a post-charging pulse signal CEN is generated at the same time.
[0126] At the same time when the read enable signal EN is valid, the read current Vread of a selected memory cell in the memory array 16 is read.
[0127] At the same moment when the read enable signal EN is valid, the read bit line is charged based on the post charge pulse signal CEN.
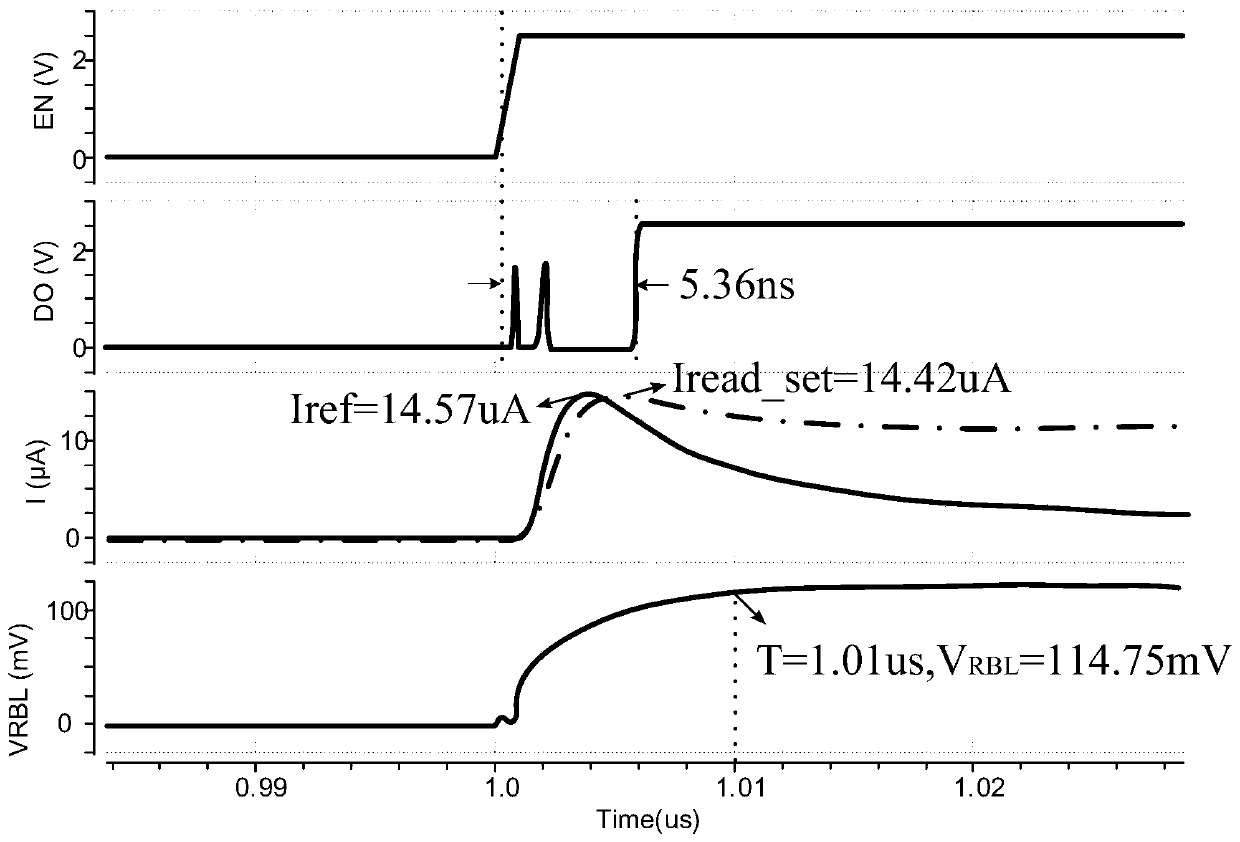
[0128] At the same moment when the read enable signal EN is effective, the reference read bit line is charged based on the post-charge pulse signal CEN to generate a dynamic reference read current Iref, and the reference read current Iref is the same as the read current Iread The transient curves of the reference read current I...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com