Application of amino acid with rescue effect on central synapse plasticity change caused by drinking
A technology of tyrosine and glycine, applied in the application of tyrosine in the treatment of alcohol addiction or alcohol dependence, in the field of amino acids, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory clinical treatment effect of drugs and unclear pathogenesis of alcohol addiction, etc. Beneficial for clinical promotion and treatment of alcohol addiction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1: Screening of amino acids with therapeutic effect on alcohol addiction
[0024] FH / Wjd rats have the characteristics of hereditary serotonin hypofunction and a large amount of autonomous drinking. They are ideal animal models of alcoholism. The active ingredients with therapeutic effects on alcohol addiction can be screened through double-bottle experiments and operant self-drinking experiments. .
[0025] The FH / Wjd rats come from the Department of Experimental Animal Science, Peking University Health Science Center, and are SPF grade male FH / Wjd rats aged 12-16 weeks and weighing about 280-360 g.
[0026] The two-bottle experiment is as follows:
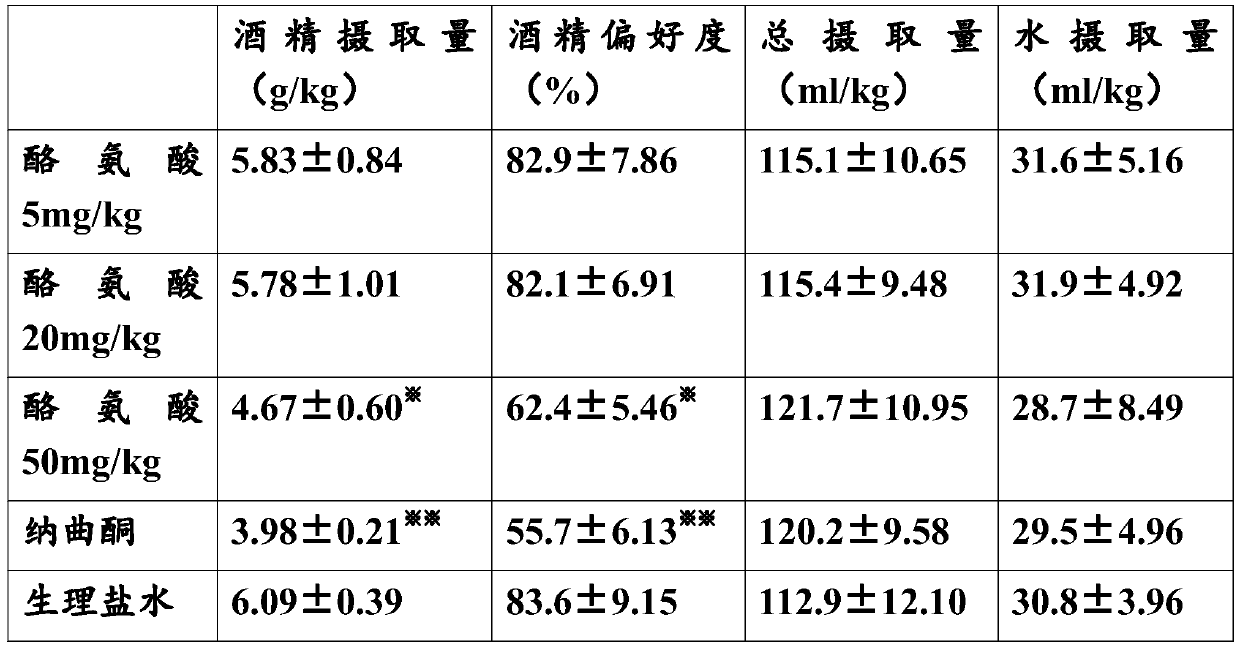
[0027] First, let the FH / Wjd rats freely ingest water with a graduated Richter tube for 2 days, then let them ingest only 10% (v / v) alcohol solution for 3 consecutive days; then let them freely ingest water and 10% alcohol solution for 1 week Alcohol solution, calculate the amount of alcohol, water and alcohol pr...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Example 2: Combination administration of tyrosine with other drugs for the treatment of alcohol addiction
[0054] It is known that tyrosine is the raw material for the synthesis of norepinephrine, epinephrine and thyroxine. Tyrosine can generate dopa through the action of tyrosine hydrogenase, and then generate dopamine through the action of dopamine decarboxylase. Without being bound by theory, administration of high doses of tyrosine can lead to increased dopamine secretion to treat alcohol addiction. Glycine can inhibit the oxidation of dopamine in vitro, thereby enhancing the activity of dopamine. Based on the experimental results of Example 1 and the technical knowledge that known glycine receptor inhibitors can be used to treat alcohol addiction, without being limited by theory, high-dose intraperitoneal Intra-injection of glycine can achieve the effect of inhibiting the oxidation of dopamine and / or inhibiting and / or slowing down the reuptake of glycine in vivo t...
Embodiment 3
[0063] The influence of embodiment 3 tyrosine on neurotransmitter
[0064] Research in the prior art shows that alcohol addiction is closely related to neurotransmitters, and alcohol can inhibit the release of presynaptic GABA (inhibitory) neurotransmitters for a long time. The role of the preliminary study was carried out.
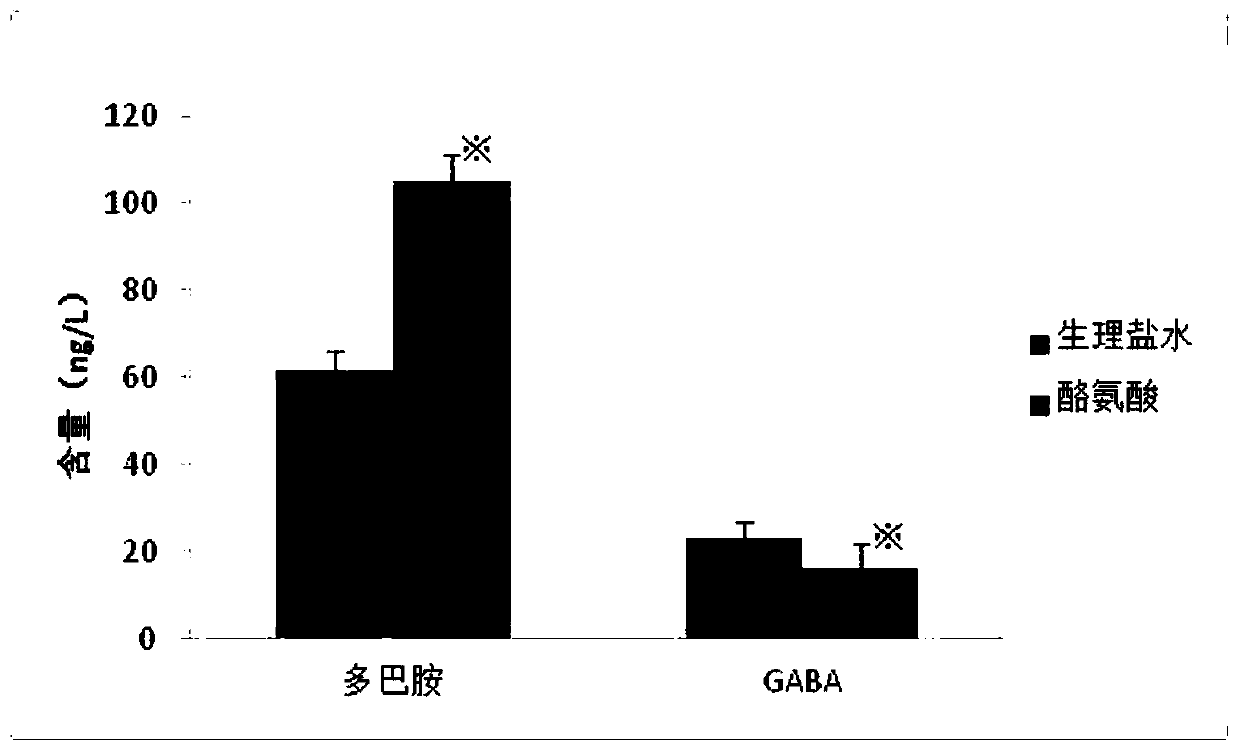
[0065] FH / Wjd rats were divided into 2 groups, 15 rats in each group. They were intravenously injected with normal saline or 50mg / kg of tyrosine respectively. After 10 days of continuous administration, the rats were decapitated immediately, and the brain tissue was taken for testing. The content of dopamine and GABA in the ventral limbic tegmental area VTA and its projection area nucleus accumbens NAC.
[0066] The result is as figure 1 As shown (※ indicates p<0.05), tyrosine treatment leads to a significant decrease in GABA content in rat brain tissue, while a significant increase in dopamine content, suggesting that tyrosine may play a role in alcoh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com