Marker (TP63) for predicting occurrence of cervical lesions of HPV (human papilloma virus)-positive patients
A technology of cervical lesions and markers, applied in the field of tumor molecular biology, can solve the problems of subjectivity, lack of quality control, lack of unified authoritative consensus, fluctuations in sensitivity and specificity, etc., achieve low false positive rate and reduce work Quantitative, sensitive diagnosis or the effect of
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Embodiment 1: Using immunohistochemical staining to detect the expression of TP63 protein in different tissue samples
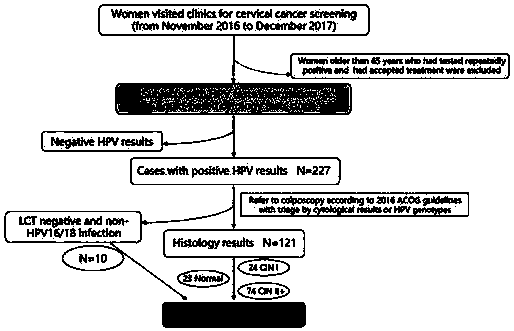
[0026] Cases: From November 2016 to December 2017, patients undergoing cervical cancer screening at the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University. Of the 227 HPV(+) patients, 121 underwent colposcopy, 23 were normal, 24 were CIN I, and 74 were CIN II. Select 10 cases of HPV(+), LCT(-)
[0027] 131 patients were used as controls for immunocytochemical examination, and the case screening process is shown in Figure 1.
[0028] experimental method:
[0029] 1. Immunohistochemical staining was used to detect the expression of TP63 protein in different tissue samples. See Table 1 for the histological information in the histological chips CIN481, CIN1201, CR501 and BC10025.
[0030] (1) Dewaxing and hydration: After baking paraffin sections in a constant temperature oven at 60°C for 2 hours, immerse them in xylene 3 times, 5 minutes each time; 2 ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2. Immunocytochemical method to detect the expression of TP63 protein in different cell samples.
[0047] (1) Dewaxing and hydration: put the prepared cell smear in a 60°C incubator and bake for 2 hours, then immerse in xylene 3 times, 5 minutes each time; 2 times in absolute ethanol, 5 minutes each time; In 95%, 85%, and 75% ethanol for 5 minutes each; wash with PBS 3 times, 5 minutes each time.
[0048] (2) Eliminate endogenous peroxidase: Remove the liquid around the tissue on the smear, place it flat in a wet box, add 3% hydrogen peroxide solution dropwise, incubate at room temperature for 10-15min, wash with PBS 3 times, 5min each time .
[0049] (3) Antigen retrieval: Put the smear into citrate buffer, put it into a pressure cooker and heat it to boiling, 800w, cover the pressure valve and wait for 1-4 minutes after spraying. The temperature of the buffer was naturally cooled to room temperature, and washed 3 times with PBS (containing Triton X-100), 5 m...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Example 3: Sensitivity and Specificity of TP63 Gene as a Molecular Marker in Human Papillomavirus Positive Patients
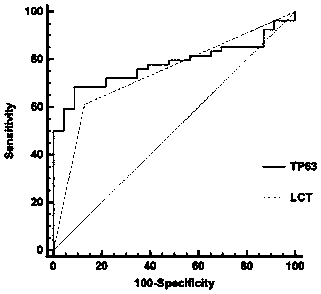
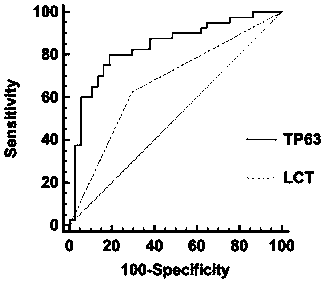
[0060] The specificity and sensitivity of TP63 as a molecular marker were identified by comparing the CIN I+ and CIN II+ stages of HPV-positive patients with TP63 single index detection with LCT detection. The results are shown in Table 2 and figure 2 , 3 shown.
[0061] Table 2: Comparison results of the efficacy of TP63 and LCT in detecting CIN I+ and CIN II+
[0062]
[0063] From Table 2 and Image 6 , 7 It can be seen that the sensitivity and specificity of detecting CIN I+ and CIN II+ in HPV positive patients using TP63 single index are higher than those of LCT detection. The area under the ROC curve of TP63 protein detection was higher than the area under the ROC curve of cytology detection (P<0.001), suggesting that the detection efficiency of TP63 protein in predicting follow-up histological positivity was higher than that of LCT detect...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com