Flight path planning method for coordinated detection and obstacle avoidance of unmanned aerial vehicle group
A track planning and unmanned aerial vehicle technology, applied in the field of unmanned aerial vehicles, can solve the problems of energy difference in optimization, failure to consider the turning radius of the drone, and failure to consider the impact, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
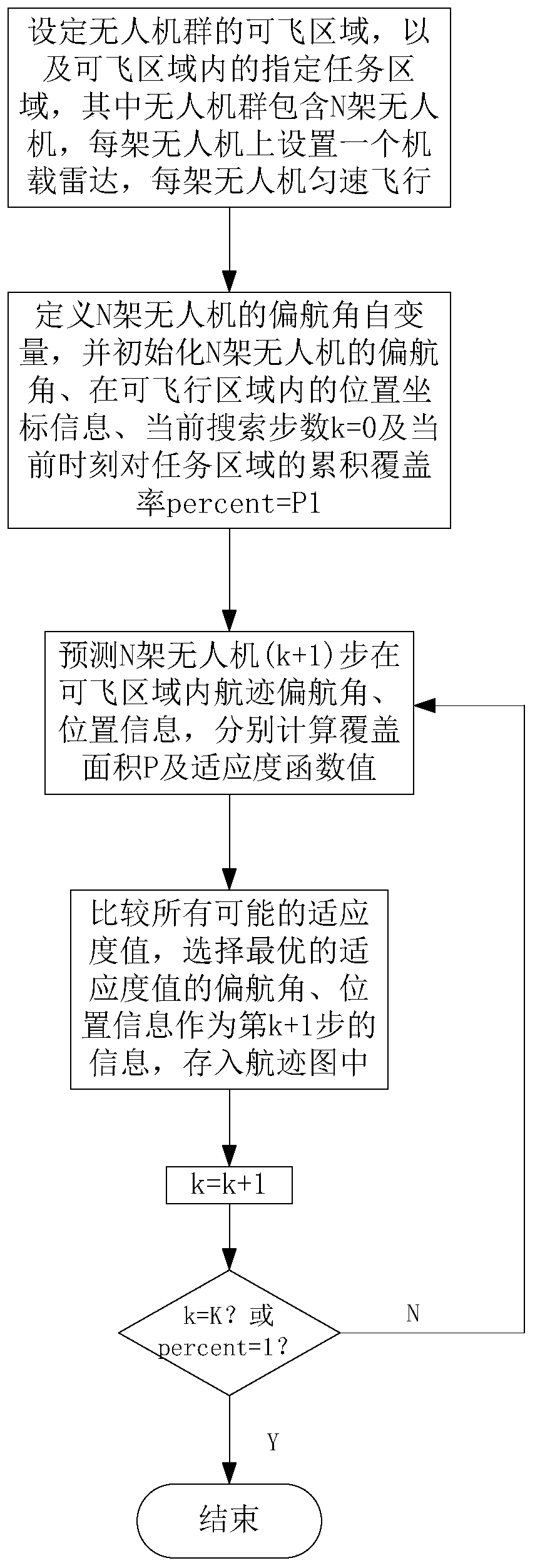
[0026] See figure 1 , figure 1 It is a flow chart of a UAV swarm cooperative detection and obstacle avoidance track planning method provided by an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in the figure, the track planning method of this embodiment includes:
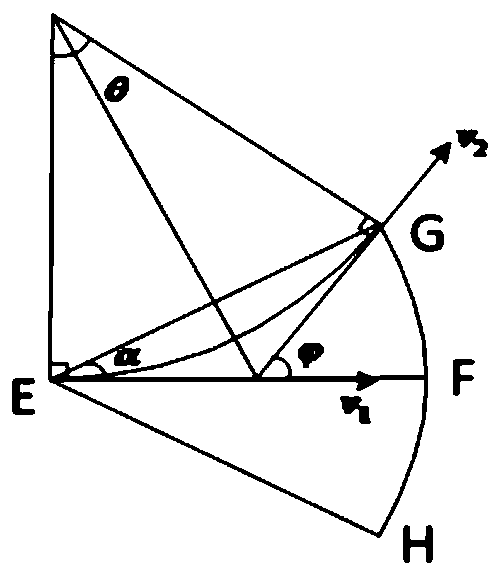
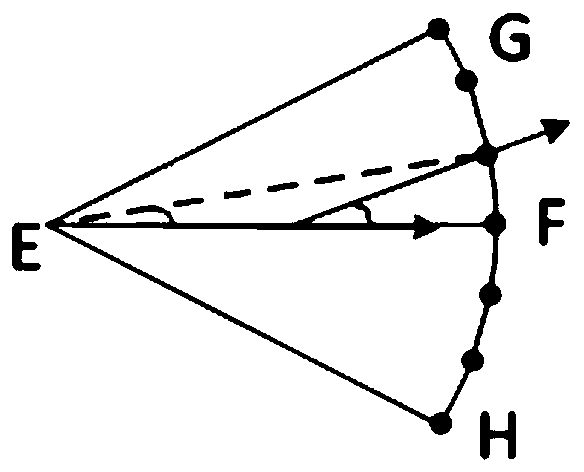
[0027] S1: Set the flying area A of the UAV group, the designated task monitoring area S in the flying area A, and analyze the stress situation of the UAV at the same time, and divide the UAV within the maximum turning angle constraint The prediction target node of the next moment of the UAV, and calculate its node gain weight, the UAV group contains N UAVs, and an airborne radar is set on each UAV, and each UAV The machine flies at a constant speed;
[0028] Specifically, including:
[0029] S11: Setting the flyable area A of the drone swarm and the task monitoring area S, wherein, when the drone swarm performs a flight mission, the safe area where the drone swarm is allowed to fly is the flyable area A, the tas...
Embodiment 2
[0101] This embodiment provides a simulation experiment about the track planning method in Embodiment 1. In this embodiment, please refer to Table 1 for the simulation experiment conditions.
[0102] Table 1 Simulation experiment conditions
[0103]
[0104] See Figure 4 , Figure 4 It is a schematic diagram of the position of the unmanned aerial vehicle group at the initial moment in a simulation experiment provided by the embodiment of the present invention. As shown in the figure, the four symbols in the figure represent the unmanned aerial vehicles respectively. Please refer to Figure 5 with Image 6 , Figure 5 It is a simulation experiment provided by an embodiment of the present invention to obtain a flight path planning result map; Image 6 yes Figure 5 The enlarged view of the obstacle area in the middle, the different curves in the flyable area A in the figure represent the track planning trajectories of the four unmanned aerial vehicles respectively, it ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com