A Method for Service Damage Evaluation and Creep Life Prediction of Superalloy Turbine Blades
A technology of turbine blades and high-temperature alloys, applied in measuring devices, using stable tension/pressure to test material strength, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to provide accurate prediction results, differences in creep deformation mechanisms, etc., and achieve true results Reliable, broad prospects, and strong engineering application effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
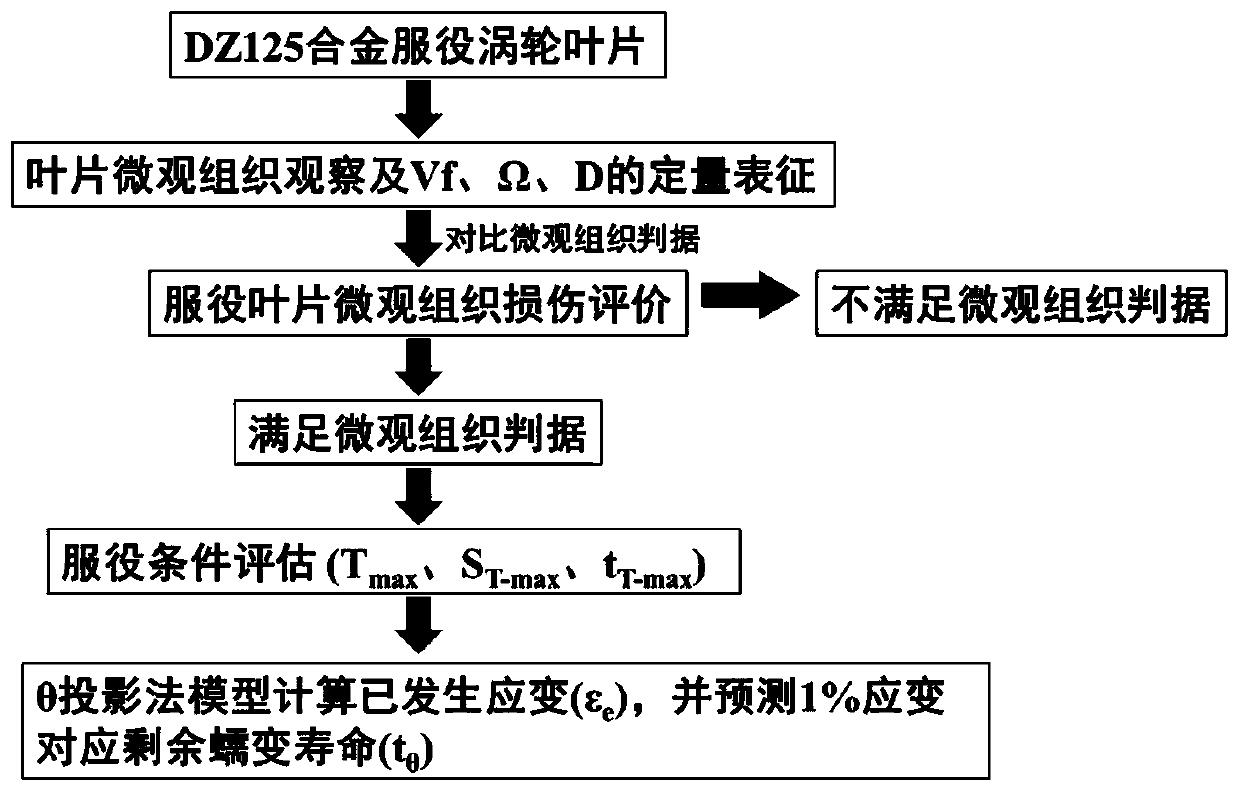
[0028] The following examples will further illustrate the present invention in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, so that those skilled in the art can better understand the advantages and features of the present invention.
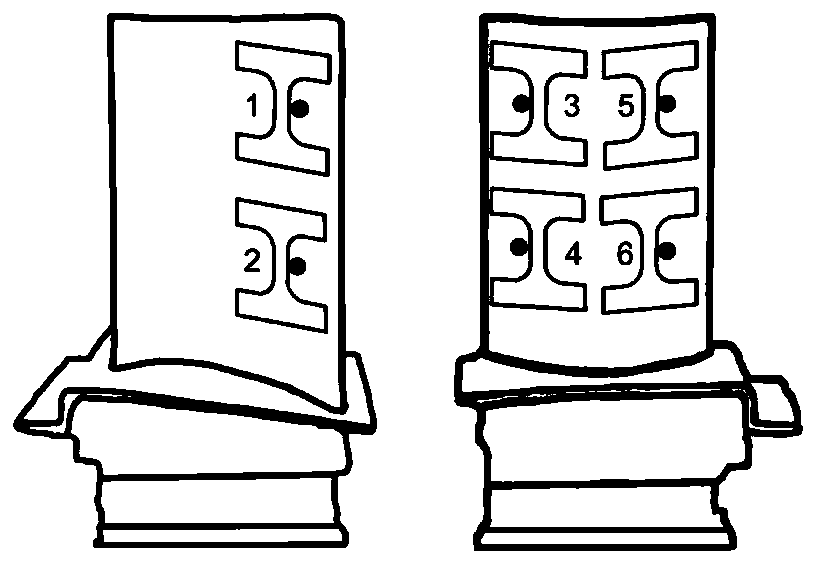
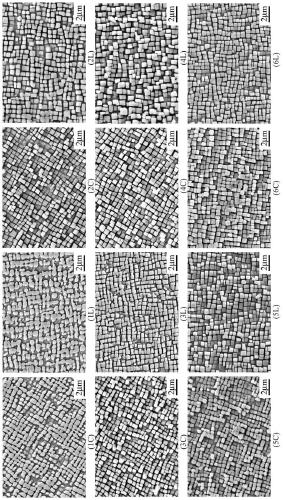
[0029] First of all, taking a DZ125 alloy turbine blade after 300 hours of service as an example, it is carried out as follows figure 2 For the cuts shown, the microstructure of each part was obtained, as image 3 shown. Refer to the grid point method in GB / T 15749 to quantitatively count the volume fraction (Vf) of the γ' phase. Set 216 grid intersection points, when the intersection point is located in the γ′ phase, it is counted as 1, when the intersection point is located at the interface between the γ′ phase and the matrix, it is counted as 0.5, when the intersection point is located in the matrix, it is counted as 0, the ratio of the above statistical results to the total number of intersection points is is Vf. Use the announcement:
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com