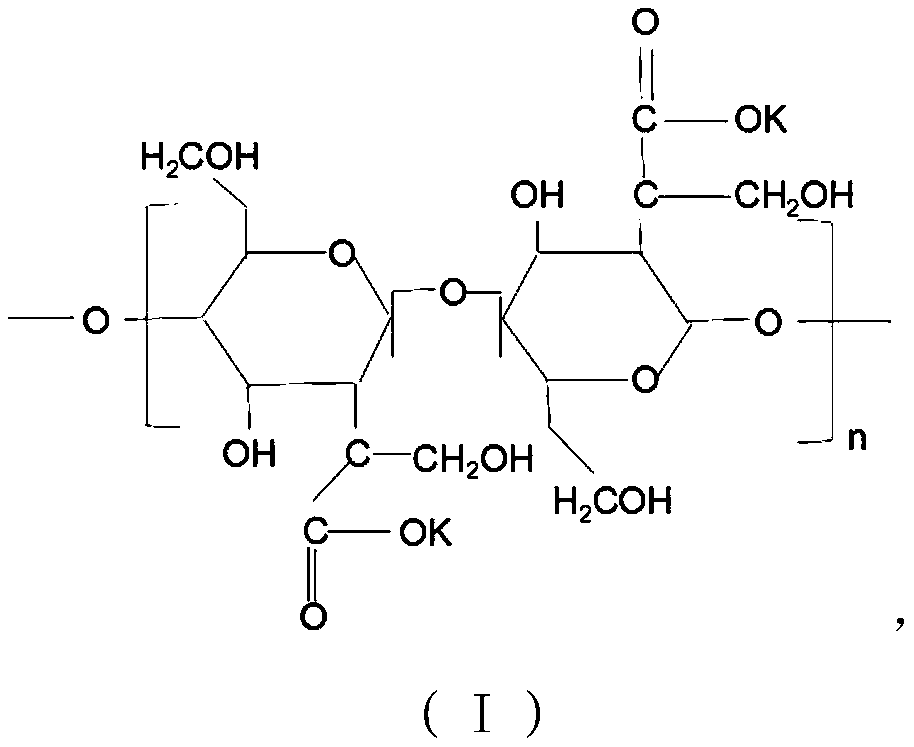
Microbial rooting agent and preparation method thereof
A rooting agent and microbial technology, applied in botany equipment and methods, plant growth regulators, plant growth regulators, etc., can solve problems such as complex work, plant root damage, death, etc., and achieve the effect of simple operation and growth promotion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] A microbial rooting agent is specifically composed of the following raw material components in parts by weight:
[0045] 5 parts of macromolecule bamboo fiber, 5 parts of Bacillus subtilis, 5 parts of brown nitrogen-fixing bacteria, 5 parts of colloid bacillus, 50 parts of bamboo fiber.
[0046] The preparation method of above-mentioned microbial rooting agent specifically comprises the following steps:
[0047] Step 1. Weigh 5 parts of macromolecular bamboo fiber, 5 parts of Bacillus subtilis, 5 parts of brown nitrogen-fixing bacteria, 5 parts of colloidal bacillus, and 50 parts of bamboo fiber according to parts by weight, and set aside;
[0048] Step 2, pulverize the bamboo fiber weighed in step 1 and pass through a 100-mesh sieve, then sterilize at 121° C. for 20 minutes, and dry to obtain bamboo fiber fine particles;
[0049] Step 3, the Bacillus subtilis, brown nitrogen-fixing bacteria and colloid bacillus (the effective number of viable bacteria in the three kin...
Embodiment 2
[0054] A microbial rooting agent is specifically composed of the following raw material components in parts by weight:
[0055] 5 parts of macromolecule bamboo fiber, 2 parts of Bacillus subtilis, 2 parts of brown nitrogen-fixing bacteria, 2 parts of colloid bacillus, 89 parts of bamboo fiber.
[0056] The preparation method of above-mentioned microbial rooting agent specifically comprises the following steps:
[0057] Step 1. Take 5 parts of macromolecular bamboo fiber, 2 parts of Bacillus subtilis, 2 parts of brown nitrogen-fixing bacteria, 2 parts of colloid bacillus, and 89 parts of bamboo fiber by weight respectively, and set aside;
[0058] Step 2, pulverize the bamboo fiber weighed in step 1 and pass through a 60-mesh sieve, then sterilize at 110°C for 30 minutes, and dry at 80°C for 24 hours to obtain bamboo fiber fine particles;
[0059] Step 3, the Bacillus subtilis, brown nitrogen-fixing bacteria and colloid bacillus (the effective number of viable bacteria in the ...
Embodiment 3
[0064] A microbial rooting agent is specifically composed of the following raw material components in parts by weight:
[0065] 10 parts of macromolecule bamboo fiber, 5 parts of Bacillus subtilis, 5 parts of Azotobacter brown, 5 parts of Bacillus colloidus, 75 parts of bamboo fiber.
[0066] The preparation method of above-mentioned microbial rooting agent specifically comprises the following steps:
[0067] Step 1. Weigh 10 parts of macromolecular bamboo fiber, 5 parts of Bacillus subtilis, 5 parts of brown nitrogen-fixing bacteria, 5 parts of colloid bacillus, and 75 parts of bamboo fiber by weight, and set aside;
[0068] Step 2, pulverize the bamboo fiber weighed in step 1 and pass through an 80-mesh sieve, then sterilize at 130°C for 10 minutes, and dry at 80°C for 24 hours to obtain bamboo fiber fine particles;
[0069] Step 3, the Bacillus subtilis, brown nitrogen-fixing bacteria and colloid bacillus (the effective number of viable bacteria in the three kinds of bacte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com