Rapid screening method of bacillus subtilis fresh-keeping strain
A Bacillus subtilis and screening method technology, applied in the field of rapid screening of Bacillus subtilis fresh-keeping strains, can solve problems affecting the flavor of aquatic products, hidden dangers to human health and safety, and chemical substances affecting flavor, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
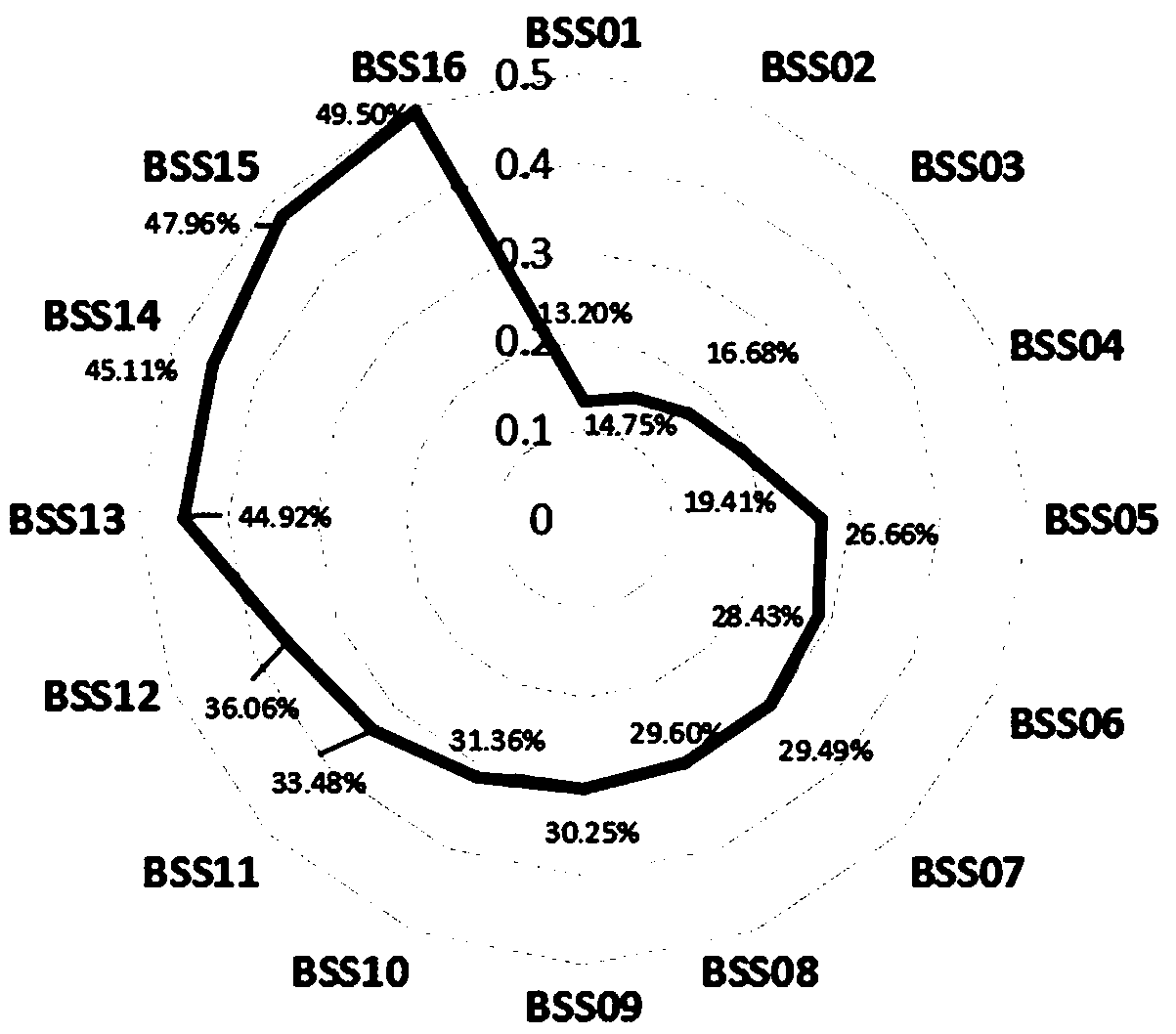
[0034] 16 strains of Bacillus subtilis (numbered BSS01-BSS16) isolated from tilapia intestines and ponds were randomly selected, and 4 cell adhesion indexes and 2 antibacterial indexes of each strain were detected.
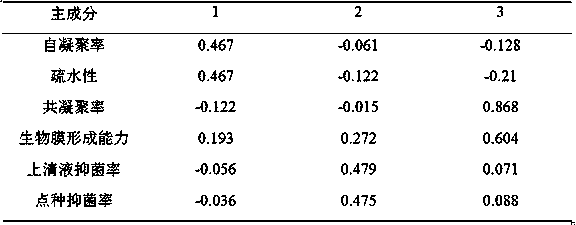
[0035] 1. The hydrophobicity, self-aggregation rate, co-aggregation rate, biofilm formation ability, antibacterial activity and supernatant antibacterial activity of 16 strains of Bacillus subtilis are as follows:
[0036] (1) Hydrophobicity: The surface hydrophobicity of Bacillus subtilis was determined by referring to the microbial adhesion hydrocarbon method, and the fermentation broth was taken after overnight culture and centrifuged to resuspend the bacterial sediment to prepare the bacterial suspension, so that the bacterial suspension was OD 600nm =1.0 ± 0.05. Pipette 2 mL of each bacterial suspension and 2 mL of xylene to mix, vortex for 120 s, and stand at room temperature for 30 min to separate layers. Take 1mL of the aqueous phase and measure its OD 6...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Using the screening equation established in Example 1, Bacillus subtilis with high fresh-keeping activity was rapidly screened.
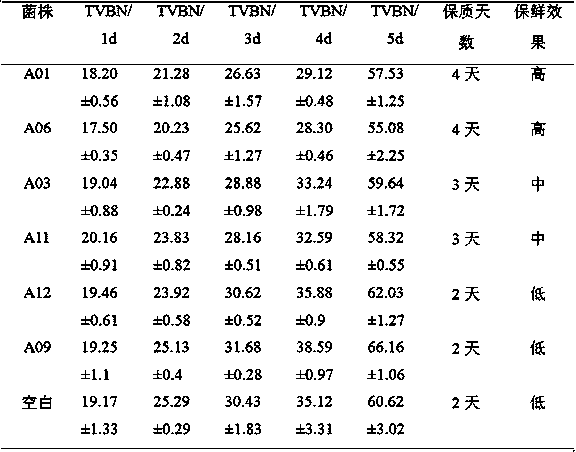
[0058] The other 6 strains of Bacillus subtilis A01, A06, A03, A11, A12 and A09 screened from tilapia intestines and ponds were used to carry out the back substitution verification test of the equation. The hydrophobicity, self-aggregation rate, co-aggregation rate, biofilm formation ability, fermentation supernatant bacteriostasis rate and spot bacteriostasis rate of these 6 strains were measured. The results are shown in Table 4.
[0059] These 6 indicators of hydrophobicity, self-aggregation rate, co-aggregation rate, biofilm formation ability, fermentation supernatant bacteriostasis rate and spot seed bacteriostasis rate of these 6 strains of bacteria are substituted into the screening equation of embodiment 1, and the comprehensive score 46.40%, 43.69%, 33.58%, 26.15%, 15.60%, and 19.63%, respectively, and A01 and A06 strains were high f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com