A method for preparing activated carbon fibers based on centrifugal spinning method
A technology of activated carbon fiber and centrifugal spinning, applied in fiber processing, fiber chemical characteristics, filament/thread forming, etc., can solve the problems of poor activated carbon fiber performance, fiber discontinuity, low efficiency, etc., and achieve good fiber shape retention. , Not easy to melt and deform, and maintain good heat resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~6
[0054] Examples 1-6 provide a method for preparing activated carbon fibers based on the centrifugal spinning method. The composition of the spinning solution is shown in Table 1, and the following steps are used to prepare:
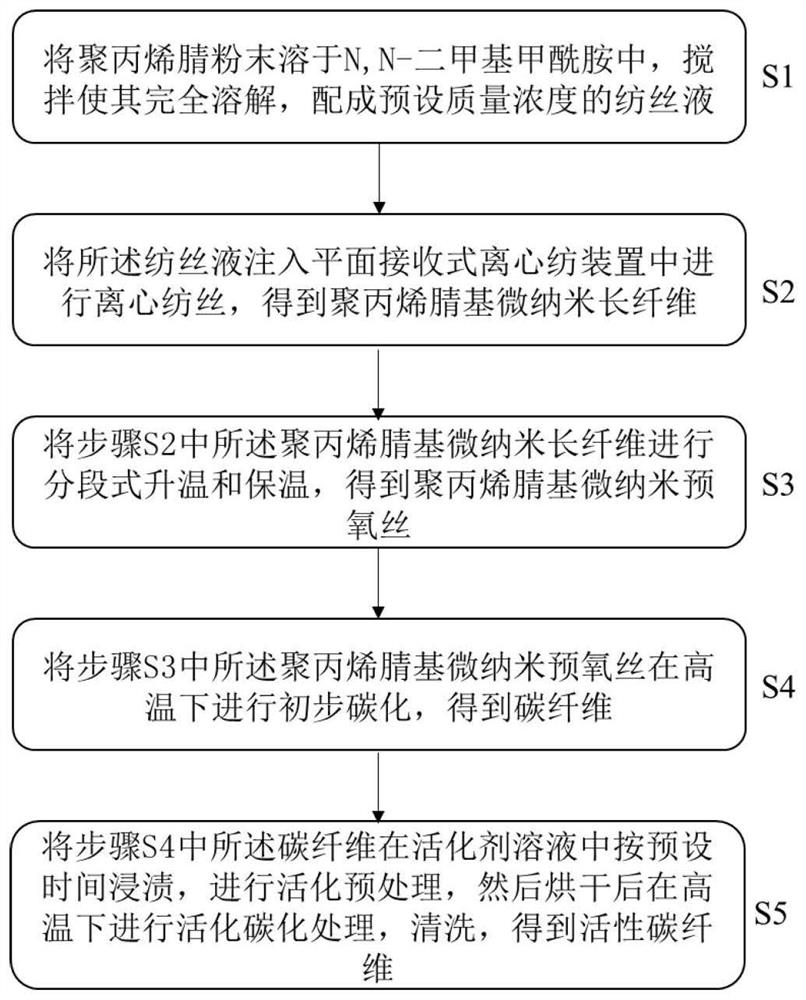
[0055] S1. Preparation of spinning solution: dissolve the dried polyacrylonitrile powder in N,N-dimethylformamide, stir for 2-6 hours to dissolve completely, and then let it stand in a vacuum drying oven for 0.5-2 hours. Formulated into a spinning solution with a certain mass concentration;
[0056] S2. Centrifugal spinning: The spinning solution prepared in step S1 is subjected to centrifugal spinning at 60° C., wherein the spinneret aperture is 0.16 mm, the collection distance is 10 cm, and the spinning speed is 7000 r / min to obtain polyacrylonitrile Based on micro-nano long fibers;
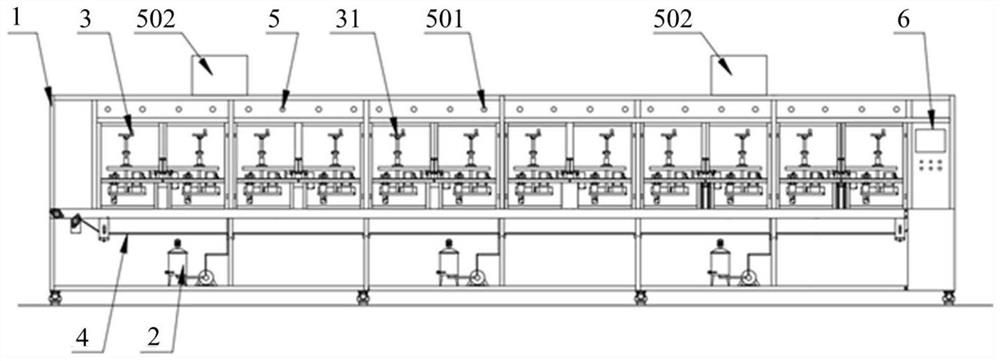
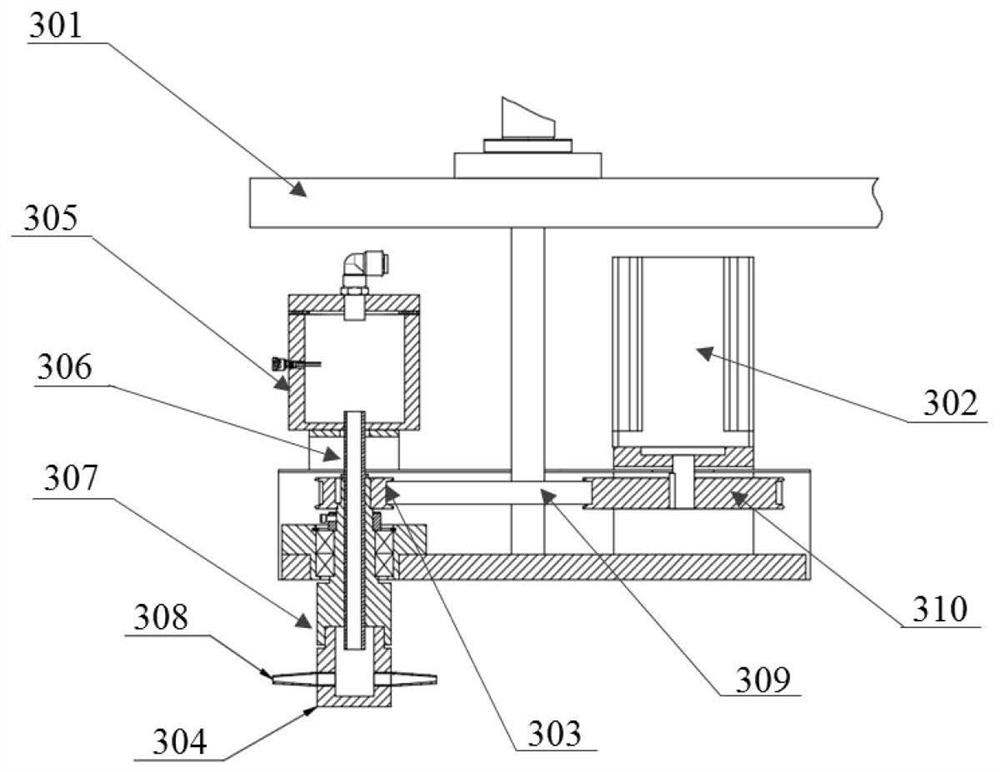
[0057] The centrifugal spinning adopts a flat guide belt collector, and the guide belt is transported and collected by guide rollers; during the spinning process, the jet...
Embodiment 7~17
[0073] Compared with Example 2, Examples 7-17 differ in that the preparation conditions in the step S2 are shown in Table 3, and others are basically the same as Example 2, and will not be repeated here.
[0074] The preparation conditions in the step S2 of table 3 embodiment 7~17
[0075] Example Spinning aperture (mm) Collection distance (cm) Spinning temperature (℃) Spinning speed (r / min) 7 0.25 10 60 7000 8 0.64 10 60 7000 9 1 10 60 7000 10 0.16 1 60 7000 11 0.16 5 60 7000 12 0.16 8 60 7000 13 0.16 12 60 7000 14 0.16 10 40 7000 15 0.16 10 70 7000 16 0.16 10 60 3000 17 0.16 10 60 10000
[0076] The activated carbon fiber specific surface area, total pore volume and micropore pore volume test result prepared by table 4 embodiment 7~17
[0077]
[0078]
[0079] It can be seen from the test results in Table 4 that with the increase of the spinneret aperture, the...
Embodiment 18~25
[0081] Compared with Example 2, Examples 18-25 are different in that the preparation conditions in Step S3 are shown in Table 5, and the others are basically the same as Example 2, and will not be repeated here.
[0082] The preparation conditions in the step S3 of table 5 embodiment 18~25
[0083]
[0084]
[0085]The activated carbon fiber specific surface area, total pore volume and micropore pore volume test results prepared by table 6 embodiment 18~25
[0086] Example Specific surface area S BET (m 2 / g)
[0087] From the test results in Example 2 and Table 6, it can be seen that with the prolongation of the pre-oxidation holding time, the specific surface area, total pore volume, and micropore pore volume of activated carbon fibers first increase and then decrease. When step a, b, c and d in the heating and heat preservation stage, heat preservation time is respectively 20min, 20min, 20min and 120min, when, the specific surface area of activated c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com